onondaga-county-know-your-rights-power-point-additional.ppt
- 1. Advocating for Youth in the Juvenile Justice System Know Your Rights Presented by the Center for Community Alternatives (CCA)
- 2. Why ItŌĆÖs Important to Know Your Rights Do you sometimes think you donŌĆÖt need to know ŌĆ£legal stuffŌĆØ becauseŌĆ” ŌĆó I am not going to get into trouble ŌĆó the police will inform me of my rights ŌĆó my parents/friends will know what to do ŌĆó juvenile charges are not that serious and no big deal
- 3. Am I In Trouble? Everyday youth are brought into the juvenile justice system for all kinds of different offenses. ŌĆó Loitering ŌĆó Disturbing the peace ŌĆó Vandalism ŌĆó Fighting
- 4. Police Contact What happens when the police want to talk to your child? ŌĆó Identifying information ŌĆó Questions about criminal activity ŌĆó Physical restraint i.e. placing hand on shoulder ŌĆó Consent to search ŌĆó Right to remain silent
- 5. Police Contact: Minor Offenses Police contact for a young person under the age of 16 usually results inŌĆ” ŌĆó the young person receiving an appearance ticket stating that probation will contact them ŌĆó a requirement that the young person and his/her parents/guardians meet with the assigned probation officer
- 6. Police Contact: Serious Offense Police contact for a young person under the age of 16 usually results inŌĆ” ŌĆó the young person being escorted to Family Court where ŌĆō a parent/guardian will be contacted ŌĆō judge decides whether to send to detention facility OR ŌĆó after business hours, Hillbrook staff complete a risk assessment instrument by phone to decide whether to detain youth
- 7. Warn and Release Appearance Ticket for Probation Intake Probation intake and development of diversion plan Probation intake and petition to Family Court Detain Pending Court Appearance Bring directly to court Call Hillbrook to administer the RAI Law Enforcement Options for Juveniles at Initial Contact
- 8. Diversion ŌĆó The majority of young people who have police contact will avoid Family Court ŌĆó An appearance ticket will be issued stating that Probation will contact the young person ŌĆó The young person will be assigned a Probation Officer who will develop a diversion plan that will require the young person to adhere to certain conditions
- 9. Working with the Probation Officer ŌĆó A parent/guardian must accompany the young person to the first meeting with the PO. ŌĆó Remember the PO is trying to help your child avoid Family Court involvement. ŌĆó Share any relevant information about your childŌĆÖs needs with the PO. He/she can help link your child to services. ŌĆó Make a good impression. Be cooperative, respectful, and open to suggestions. ŌĆó Talk to your child about how to appropriately interact with his/her PO
- 10. Taken into Custody If your child is taken into custody, you shouldŌĆ” ŌĆó Get information about where your child is being held and what the charges are ŌĆó Try to see your child immediately ŌĆó Not allow police to talk to your child without you ŌĆó Remind your child NOT to talk without an attorney
- 11. Family Court Process Initial Appearance Release Home Detention Probable Cause Hearing Convert to PINS petition Adjournment in Contemplation of Dismissal Fact Finding Disposition Conditional Discharge Probation Supervision Placement with local service provider Placement with State Office of Children and Family Services
- 12. Juvenile Delinquents Minor Offenses Juvenile Offenders Serious Offenses Definition At least 7 yrs old & less than 16 yrs old A youth 13 to 15 yrs old Where case decided Family Court County or Supreme Court Police Contact Taken into custody Arrested First court appearance Initial appearance Arraignment in Criminal Court Prosecution Deputy County Attorney Assistant District Attorney Custody Options Remand to secure or non secure detention or released Bail, ROR, remand to secure detention Legal Representation Appointed Attorney for the Child Defense Counsel How case decided Fact Finding Hearing Plea/Trial Judicial Options Dispositional Hearing -probation -placement with OCFS -Adjournment in Contemplation of Dismissal (ACD) -conditional discharge -restitution Sentencing, if convicted -probation -confinement in an OCFS secure facility
- 13. Obtaining an Attorney for the Child ŌĆó An Attorney for the Child will be appointed at the young personŌĆÖs first appearance in Family Court to serve as an advocate and represent his/her interests. ŌĆó Parents/Guardians can hire an attorney for their child. Both court-appointed and hired attorneys will work to represent the interest of their client.
- 14. Working with the Attorney: DOŌĆ” ŌĆó Make sure to inform your childŌĆÖs attorney of all pertinent information regarding your child. ŌĆó Offer to assist with ŌĆ£leg workŌĆØ for the Fact-Finding Hearing. ŌĆó Provide the attorney with letters of support to document your childŌĆÖs character. ŌĆó Stay open minded to advice from the Attorney for the Child.
- 15. Working with the Attorney: DONŌĆÖTŌĆ” ŌĆó Forget that the attorney is representing your CHILD, not you. ŌĆó Cross the line from advocate to annoyance. Be mindful that your child is NOT the only client of the attorney. ŌĆó Underestimate the importance of making a good impression. Remember the attorney did not know you before this incident.
- 16. Family Court ŌĆó Your attendance in Family Court is very important. A judge is more likely to allow your child to return home if a parent is present in court. ŌĆó If you cannot attend a specific court date, you should inform your childŌĆÖs lawyer. ŌĆó Be prepared to wait in the waiting area for long periods of time. ŌĆó Always speak to the lawyer prior to a court date so you can all be ŌĆ£on the same page.ŌĆØ
- 17. Social Investigation ŌĆó The court may ask Probation to complete a Social Investigation. ŌĆó A Probation Officer will interview the child, the parents, and other relevant people. They will also obtain documentation like school records. ŌĆó This information will be provided to the Court to: ŌĆō Give a picture of the childŌĆÖs background and history ŌĆō Recommend appropriate dispositions
- 18. How Can I Help With the Social Investigation? ŌĆó Be respectful when speaking to the Probation Officer. Watch your body language and your attitude as his/her impression of you will be documented and may affect your childŌĆÖs outcome in court. ŌĆó It is important you offer positive information about your child such as involvement in after-school activities, good attendance in school, etc. ŌĆó Be honest and try not to become emotional.
- 19. Fact Finding Hearing ŌĆó In a juvenile delinquency case, the trial is called a ŌĆ£fact finding hearing.ŌĆØ A fact-finding hearing is the same as a criminal trial but without a jury. ŌĆó The judge decides whether the child committed the acts described in the petition to Family Court and should be adjudicated a juvenile delinquent.
- 20. Dispositional Hearing ŌĆó In a juvenile delinquency case, a sentencing is called a ŌĆ£dispositional hearing.ŌĆØ ŌĆó The County AttorneyŌĆÖs office will present recommendations (that Probation may have helped develop in the social investigation). ŌĆó The Attorney for the Child should be prepared to suggest alternative dispositions.
- 21. How Can I Help With the Hearings? ŌĆó Be present at all court dates and act appropriately. ŌĆó Offer to work with the attorney to track down witnesses, collect letters of support, etc. ŌĆó Discuss possible dispositions with the attorney: ŌĆō Ask about the various options ŌĆō Make suggestions if you have an idea for an effective disposition
- 22. How Should I Act in Family Court? ŌĆó Come early. Contact your childŌĆÖs lawyer if you are going to be late. ŌĆó Be respectful and cooperative. ŌĆó Dress appropriately. No shorts or party clothes. ŌĆó Be mindful of your body language. ŌĆó Discuss everything you might want to say to the judge with your childŌĆÖs lawyer first.
- 23. You Have the RightŌĆ” ŌĆó to know the charges against your child if he/she is taken into custody. ŌĆó to be involved in creating the diversion plan for your child. ŌĆó to a lawyer. An Attorney for the Child will be assigned to represent your child if the case does go to Family Court. ŌĆó to be notified, in advance, when any court dates are scheduled.
- 24. You Have the RightŌĆ” ŌĆó to be present at all court proceedings and inform the court of how you will supervise your child and meet release requirements. ŌĆó to be informed of alternative programs available for your childŌĆÖs rehabilitation. ŌĆó to work closely with all aftercare authorities and community-based agencies involving your child.
- 25. Why is it Important to Advocate for My Child? ŌĆó If the Probation Officer or Attorney for the Child like you, they may work harder for your child. ŌĆó If you are involved in the process, you may be able to get your child connected to services instead of just punishment. ŌĆó If you know your rights and are paying attention, it is less likely that your child will fall through the cracks.
- 26. Disproportionate Minority Contact (DMC) DMC occurs when the proportion of youth of color who pass through the juvenile justice system exceed the proportion of youth of color in the general population. DMC becomes worse as youth of color pass through the system starting with arrest and ending with placement or incarceration.
- 27. How Does DMC Happen? ŌĆó DMC can occur at any point in the processing of a case in the juvenile justice system from police contact to placement. ŌĆó Decision-making based on race can compound throughout the system resulting in cumulative disadvantage for youth of color.
- 28. Cumulative Disadvantage Law Enforcement Deployment Appearance Ticket/ Warn & Release Court Appearance/ Police Dropoff Release/ Detention Diversion Petition to Family Court Attorney for the Child Probable Cause Hearing Fact Finding Hearing Disposition Probation Violations Reintegration Services Cumulative Disadvantage
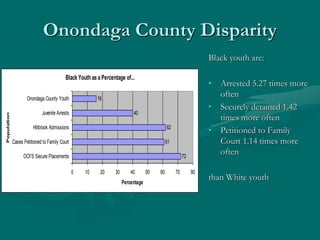
- 29. Onondaga County Disparity Black Youth as a Percentage of... 72 61 62 40 16 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 OCFS Secure Placements Cases Petitioned to Family Court Hillbrook Admissions Juvenile Arrests Onondaga County Youth Population Percentage Black youth are: ŌĆó Arrested 5.27 times more often ŌĆó Securely detained 1.42 times more often ŌĆó Petitioned to Family Court 1.14 times more often than White youth
- 30. Juvenile Record ŌĆó The moment your child enters the juvenile justice system, a record is created. When your child is arrested, there is a record of your childŌĆÖs arrest, even if no charges are filed ŌĆó If charges are filed, the record will also include the charges against your child, whether your child was adjudicated delinquent, and any records from probation
- 31. Parental Involvement ŌĆó RememberŌĆ”your involvement during this difficult process is very important. Your child is scared and, in most instances, will not know how to react to all that is happening to them. ŌĆó Your child will need you to remain calm and show by example how he/she should behave. Talk your child and keep in mind both of you are very emotional.