Opc presentation
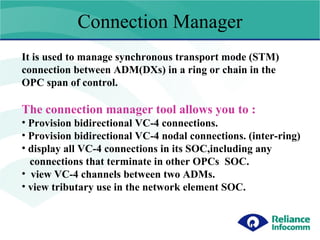
- 1. Connection Manager It is used to manage synchronous transport mode (STM) connection between ADM(DXs) in a ring or chain in the OPC span of control. The connection manager tool allows you to : Provision bidirectional VC-4 connections. Provision bidirectional VC-4 nodal connections. (inter-ring) display all VC-4 connections in its SOC,including any connections that terminate in other OPCs SOC. view VC-4 channels between two ADMs. view tributary use in the network element SOC.
- 2. Connection Manager The connection manager tool allows you to : merge existing VC-4 connection to higher rate connections. In Service Channel rollover (ISCR) In Service Route rollover (ISRR)
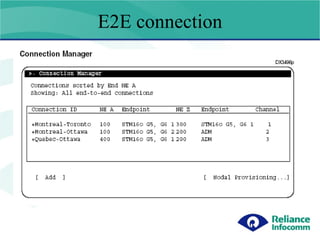
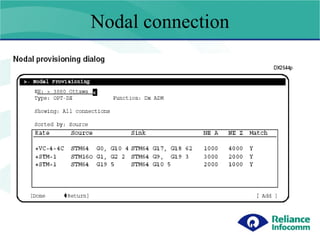
- 3. Creating Connections Using connection manager connections can be provisioned Between 2 ADMs. There are 2 option available in the connection manager. Option 1 : End 2 End (E2E) Option 2: Nodal Connection.
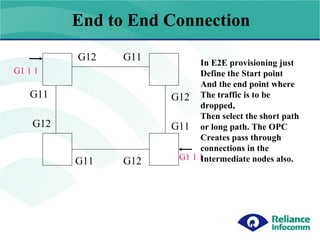
- 4. E2E connection A B C D In E2E provisioning just Define the Start point And the end point where The traffic is to be dropped, Then select the short path or long path. The OPC Creates pass through connections in the Intermediate nodes also. End to End Connection G11 G12 G12 G11 G11 G12 G12 G11 G1 1 1 G1 1 1
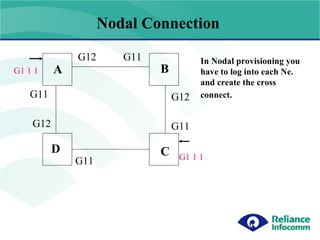
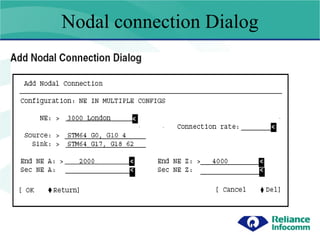
- 7. Nodal connection G11 G12 G11 G11 G12 G12 G11 A B C D G1 1 1 G1 1 1 In Nodal provisioning you have to log into each Ne. and create the cross connect. Nodal Connection
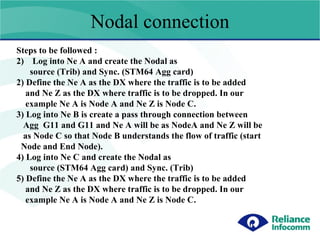
- 8. Nodal connection Steps to be followed : Log into Ne A and create the Nodal as source (Trib) and Sync. (STM64 Agg card) 2) Define the Ne A as the DX where the traffic is to be added and Ne Z as the DX where traffic is to be dropped. In our example Ne A is Node A and Ne Z is Node C. 3) Log into Ne B is create a pass through connection between Agg G11 and G11 and Ne A will be as NodeA and Ne Z will be as Node C so that Node B understands the flow of traffic (start Node and End Node). 4) Log into Ne C and create the Nodal as source (STM64 Agg card) and Sync. (Trib) 5) Define the Ne A as the DX where the traffic is to be added and Ne Z as the DX where traffic is to be dropped. In our example Ne A is Node A and Ne Z is Node C.
- 11. Nodal as E2E In case of Nodal if the Nodal connection is provisioned properly In terms of Ne A and Ne Z then the OPC redas the Nodal connection As and E2E connection because the OPC can read the Add Ne and Also the Drop Ne so the OPC reads it as an E2E connection. In case if Ne A and Ne Z are not defined properly the OPC will not be in a Position to read the Connections as theAdd Ne A and the Drop Ne Z are not defined properly so we cannot se it in E2E Dialog box . But there will not be any traffic hit .
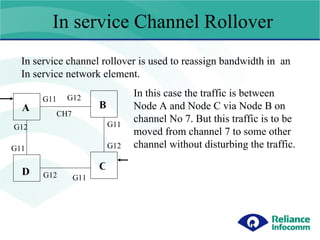
- 12. In service Channel Rollover In service channel rollover is used to reassign bandwidth in an In service network element. G11 G12 G11 G11 G12 G12 G11 G12 D A B C CH7 In this case the traffic is between Node A and Node C via Node B on channel No 7. But this traffic is to be moved from channel 7 to some other channel without disturbing the traffic.
- 13. In service Channel Rollover
- 14. In service Channel Rollover
- 15. In service Channel Rollover
- 16. In service Route Rollover G11 G12 G11 G12 G12 G11 G12 A B C D In service route rollover is used to reassign bandwidth in an In service network element via a second route. In this case the traffic is between Node A and Node C via Node B on channel No 7. But now this traffic is to be Routed via Node D without affecting the Traffic. The steps remains the same as In service channel roll over. In this case the channel remains the same As Channel 7 so before this steps make sure that the same channel is available in The second route. CH7
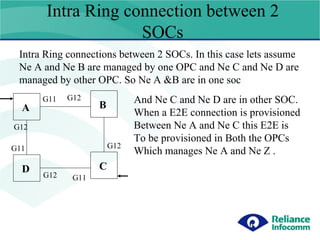
- 17. Intra Ring connection between 2 SOCs G11 G12 G11 G12 G12 G11 G12 A B C D Intra Ring connections between 2 SOCs. In this case lets assume Ne A and Ne B are managed by one OPC and Ne C and Ne D are managed by other OPC. So Ne A &B are in one soc And Ne C and Ne D are in other SOC. When a E2E connection is provisioned Between Ne A and Ne C this E2E is To be provisioned in Both the OPCs Which manages Ne A and Ne Z .