Opiods .................................................
- 1. 1 Analgesics [ Opioids & Non Opioids] By Berhan Begashaw Pharmacy Department DBU Nov, 2023
- 3. Pain (Algesia) ? “Unpleasant sensory & emotional experience ? Associated with actual or potential tissue damage” ? Evoked by an external or internal noxious stimuli ? Latin “poena” for punishment from God, Reflects the deleterious effects that can be inflicted upon the body. ? Mediated by different NTs & peptides such as glutamate & substance P ? It is a warning, primarily protective in nature Berhan B. 3
- 4. Generally, the pain can be ?Acute ? Superficial ? Stimulation of skin & mucous membranes ? Fast response ? Deep ? Arises from muscles, joints, tendons, heart, etc. ? Slow response ? Visceral ? Inflammation ? Chronic pain ? Unknown origin Berhan B. 4
- 5. Classification 1. Physiological: Nociceptive, Neuropathic, Psychological ? ?Nociceptive? ? Normal physiology (mechanisms known) ? Treated with analgesics [ NSAIDs, acetaminophen, opioids] ? ?Neuropathic? ? Aberrant physiology (mechanisms unknown) ? Associated with neural damage ? Difficult to treat with opioid analgesics 2. Clinical: Acute, Chronic, Malignant Berhan B. 5
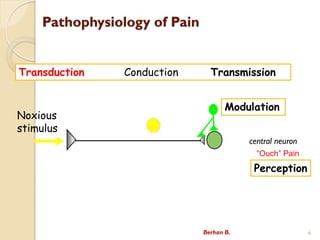
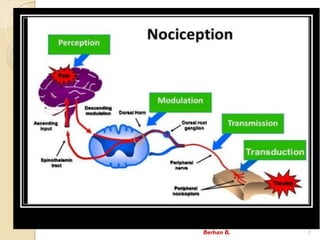
- 6. Pathophysiology of Pain Noxious stimulus Transduction Conduction Transmission Modulation “Ouch” Pain Perception central neuron Berhan B. 6
- 7. Berhan B. 7
- 8. Noxious stimulus [ trauma, infection,..] Release of inflammatory substances (PG, His, 5-HT, Bks, Sub.P, etc.) Transduction (generation & electrical impulses) Transmission (conduction by nerve fibers) Modulation (Modification with spinal cord) Perception NSAIDs Opioids Pathophysiology of pain… Berhan B. 8
- 9. Analgesics ? Drugs that selectively relieve pain with out significant change on patient consciousness ? Act on CNS or periphery pain mechanism Classification ? Narcotics /opioids/ ? Morphine & morphine like drugs ? Non-narcotics - NSAIDs ? Adjuvant analgesics /coanalgesics ? TCAs, Antiepileptics, Steroids Berhan B. 9
- 10. Sites of Action of Analgesics ?Drugs can prevent pain at the site of injury ? By blocking peripheral nerves (local anesthetics) ? By closing the ?gates? in the dorsal horn & thalamus (one action of opioids & TCAs that inhibit axonal re-uptake of 5-HT & NE) ? By altering the central appreciation of pain (another effect of opioids). Berhan B. 10
- 11. Management of Pain 1. Mild pain ? NSAID + Adjuvant 2. Moderate pain ? Weak narcotic + NSAID + Adjuvant 3. Severe pain ? Strong narcotic + NSAID + Adjuvant Berhan B. 11
- 12. Opioids Analgesics ? Opium: A mixture of alkaloids from seed capsule of opium poppy [ Papaver somniferum ] ? Opioids ? Any drug, natural, semisynthetic or synthetic, with actions like morphine ? Morphine has 5 rings, 3- & 6-OH grps (phenolic & alcoholic), piperidine ring with N-methyl grp & a quaternary carbon at position 13 Berhan B. 12
- 13. Opioids … ? Codeine is morphine O-methylated at position 3 ? Heroin is morphine O-acetylated at positions 3 & 6 ? Replacing N-methyl with something larger (allyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl) produces opioid with antagonist properties ? Meperidine (pethidine) is a synthetic opioid with only fragments of the morphine structure Berhan B. 13
- 14. ? Act by binding to specific opioid receptors in the CNS to produce effects that mimic the action of endogenous opioids peptide NTs; ? Endorphins [ μ (Mu) receptor] ? Enkephalins [ δ (Delta) receptor] ? Dynorphins [ Κ (Kappa) receptor] ? Primary use is to relieve intense pain that results from surgery, injury, or chronic disease. ? Widespread availability of opioids has led to abuse of agents with euphoric properties. ? Antagonists that reverse the actions of opioids ? Clinically important in cases of overdose Berhan B. 14
- 15. Opioid Receptors 1) μ (Mu) receptor- Most important & activation leads to analgesia, resp. depression, sedation, physical dependence, euphoria, miosis, NV & constipation. 2) Κ (Kappa) receptor - Activation produces modest analgesia, sedation, miosis & dysphoria. 3) δ (Delta) receptor- Responsible for producing little effect in analgesia, NV 4) σ (Sigma) receptor Berhan B. 15
- 16. ? Drugs that act at opioid receptors 1. Pure opioid agonists ? Activate mu & kappa receptors o Strong opioid agonists ? Morphine, pethidine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, ... & o Moderate-to-strong opioid agonists ? Codeine, tramadol, dhydrocodeine, … 16 Berhan B.
- 17. 2. Opioids agonist-antagonist/Partial agonists ? When administered alone, produce analgesia, but given to a person taking opioids, produce antagonistic effect. ? Pentazocine, nalbuphine, butorphanol, buprenorphine,... 3. Pure opioid antagonists ? Antagonize mu & kappa receptors for reversal of respiratory & CNS depression. ? Naloxone, naltrexone, nalmefen,… 17 Berhan B.
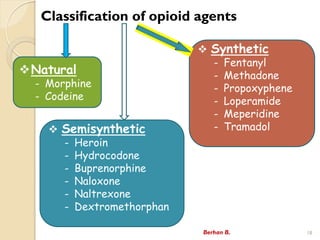
- 18. Classification of opioid agents Berhan B. 18 ?Natural - Morphine - Codeine ? Synthetic - Fentanyl - Methadone - Propoxyphene - Loperamide - Meperidine - Tramadol ? Semisynthetic - Heroin - Hydrocodone - Buprenorphine - Naloxone - Naltrexone - Dextromethorphan
- 19. MoA of Opioids ? Produce analgesia by binding to specific receptors located in brain & spinal cord regions involved in the transmission & modulation of pain ? Inhibit adenylyl cyclase ? ↓ cAMP ? Reduce neuronal excitability ? B/c of the ? K+ conductance ? hyperpolarization of the membrane ? Reduce transmitter release ? Due to inhibition of Ca 2+ entry ? Blockage of nociceptive transmission Berhan B. 19
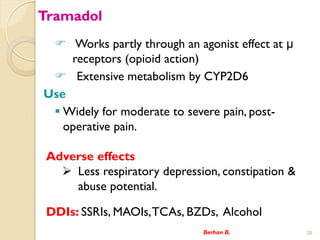
- 20. Tramadol ? Works partly through an agonist effect at μ receptors (opioid action) ? Extensive metabolism by CYP2D6 Use ? Widely for moderate to severe pain, post- operative pain. Berhan B. 20 Adverse effects ? Less respiratory depression, constipation & abuse potential. DDIs: SSRIs, MAOIs,TCAs, BZDs, Alcohol
- 21. Codeine ? Has only about 10% of its analgesic potency. ? Converted to morphine by CYP2D6 enzyme ? Produces little euphoria & low addiction potential. ? Mild to moderate pain, cough suppressant [ preferred: Dextromethorphan] & symptomatic relief of diarrhea. ?With PCM--- pain ? Adverse effects: Resp. depression & death [Children] ? DDIs: BZDs, Alcohol Berhan B. 21
- 22. Morphine ? Isolated from opium & named representing the Greek God of Dreams “Morpheus.” ? Somewhat selective to the μ receptor, has some affinity for the κ & δ receptors. ? Also inhibits the release of many excitatory NTs from nerve terminals carrying nociceptive (painful) stimuli. ? Glutamate Berhan B. 22
- 23. Morphine… Uses ? Most importantly for moderate to severe & chronic pain relief. ? May be given as an IV bolus if rapid relief is required (e.g. during MI). ? Alternatively, can be given continuously by an infusion pump (Eg. post-operatively), ivly or scly. ? Effective in the relief of acute left ventricular failure. ? Inhibits cough, but codeine is preferred. ? Relieves diarrhea, but codeine is preferred. Berhan B. 23
- 24. Morphine… Adverse effects ? Respiratory depression [acute overdose] ? Miosis ? Emesis ? Biliary pain ? Constipation ? Hypotension & bradycardia may occur [higher doses] Berhan B. 24
- 25. Morphine… Adverse effects… ? Increases CSF pressure ? Bronchoconstriction ? Euphoria ? Androgen deficiency [prolonged use]- ?ed testosterone ? Prolong 2nd stage of labor ? Moderate immunosuppression – infec. & tumor metastasis ? Tolerance & dependence Berhan B. 25
- 26. Drug interactions ? CNS depressant medications ? Phenothiazines ? Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), & ? Benzodiazepines ? Alcohol Berhan B. 26
- 27. Pethidine (Meperidine) ? Lower potency synthetic opioid structurally unrelated to morphine ? Acute pain & acts primarily as a κ agonist, with some μ agonist activity. ? Very lipophilic & has anticholinergic effects ? increased incidence of delirium ? Does not constrict the pupil, release histamine or suppress cough. Berhan B. 27
- 28. Pethidine … ? Primarily as an analgesic & in preanesthetic medication ? Control shivering during the postsurgical recovery period ? Management of cancer pain [ Transdermal] ? Sometimes used in obstetrics, but morphine is often preferred. Berhan B. 28
- 29. Pethidine … Adverse effects ? Delayed gastric emptying (common to all opioids): particular concern in obstetrics ? Delirium, hyper-reflexia, myoclonus, & seizures [overdose, long term use, esp. in pts with renal insufficiency] D/Is: MAOIs, SSRIs C/Is: Renal & hepatic insufficiency, pre-existing respiratory compromise Berhan B. 29
- 30. Fentanyl ? Derivatives of pethidine ? Extremely potent analgesic (100X morphine) ? Highly lipophilic, shorter-acting [15-30mins] & rapid onset ? Treat severe acute pain or as an adjunct to anesthesia. ? Usually administered IV, epidurally, or intrathecally ? With LAs: Epidural analgesia for labor & post pain ? IV: In anesthesia for analgesic & sedation effect ? Transmucosal & nasal: Cancer related pain ? Transdermal patch: Chronic severe pain Berhan B. 30
- 31. Mixed Agonist –Antagonists & Partial Agonists ? Drugs that stimulate one receptor but block another. ? Bind to the opioid receptor, but they have less intrinsic activity than full agonists ? Effects depend on previous exposure to opioids a) Produce excitatory & hallucinogenic effects b) Produce a low degree of physical dependence c) Induce withdrawal signs that differ from morphine d) Produce excitatory effects related to the sympathetic discharge of NE Berhan B. 31
- 32. ?Pentazocine- Moderate pain, premedication & supplement to surgical ?Butorphanol- Moderate to severe pain [ more potent than morphine & pentazocine] - Nasal spray: Post operative pain & migraine [abuse] ?Nalbuphine- Moderate to severe pain, postsurgical & obstetrical analgesia ?Buprenorphine-More potent than morphine as moderate to severe pain - Opiate detoxification Berhan B. 32
- 33. Clinical Uses of Opioids 1. Analgesic effect [ severe pain-chronic, acute] ? Selective relief of pain at doses which do not produce hypnosis or impair sensation ? Some types of pain more responsive to opioids than others ? More effect in prolonged, burning pain than sharp, intermittent pain ? Neuropathic pain can be resistant Berhan B. 33
- 34. ? Therefore, opioids are mainly used for severe & constant pain ? Chronic pain such as in cancer patients may need continuous use of potent opioid analgesics ? Potent opioid analgesics associated with tolerance & dependence ?But this should not be barrier to provide the best possible care for the patients ? Slow release dosage forms may give longer & more stable level of analgesia Berhan B. 34
- 35. ? Fentanyl transdermal system (fentanyl patch) can be used over long periods if disturbances of GIT ? Opioid analgesics are used during obstetric labor ? As opioids cross the placental barrier, care must be taken to minimize neonatal depression ? If it occurs, immediate use of naloxone will reverse the depression ? Meperidine produce less depression (particularly respiratory depression) in newborn infants than does morphine Berhan B. 35
- 36. 2. Cough suppression/antitussives [at low dose] ? Depression of cough centers in the medulla (possibly in the periphery too) ? Different molecular mechanism than analgesia or respiratory depression ? Cough suppressed by dextro-isomers of opioids [Dextromethorphan], compounds which have no analgesic activity Berhan B. 36
- 37. 3.Anti-diarrhael agent ? Cause constipation beneficial for Rx of diarrhea ? Diarrhea from almost any cause can be controlled with the opioid analgesics ? But if associated with infection, appropriate chemotherapy should be used ? Synthetic drugs [ Diphenoxylate & loperamide] with selective effect on GIT poorly-absorbed & have little/no central effects Berhan B. 37
- 38. 4. Post anesthetic shivering ?All opioid agonists have some propensity to reduce shivering ?Meperidine is the most pronounced anti-shivering properties ?Single doses is effective in the treatment of post- anesthetic shivering via the action on subtypes of the α 2 adrenoceptor. Berhan B. 38
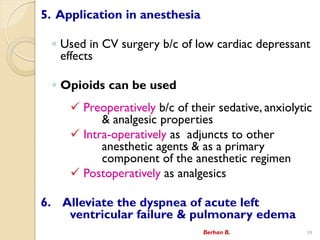
- 39. 5. Application in anesthesia ? Used in CV surgery b/c of low cardiac depressant effects ? Opioids can be used ? Preoperatively b/c of their sedative, anxiolytic & analgesic properties ? Intra-operatively as adjuncts to other anesthetic agents & as a primary component of the anesthetic regimen ? Postoperatively as analgesics 6. Alleviate the dyspnea of acute left ventricular failure & pulmonary edema Berhan B. 39
- 40. Side effects of opioids o Most are associated with mu receptors o Respiratory depression o Euphoria o Sedation o Hypothermia o Constipations o Tolerance & dependence o Bronchoconstriction (Histamine release stimulated) Berhan B. 40
- 41. Opioid Antagonists ? Bind with high affinity to opioid receptors ? Opioid-dependent pts: Rapidly reverse the effect of any full μ agonist ? Naloxone ? A pure competitive antagonist of opioid agonists at μ-receptors [10X higher than K receptors] ? Short duration of action (30-80 mins) ? Rx of morphine poisoning IVly ? Dx opioid dependence ? Oral: No clinical effect Berhan B. 41
- 42. ? Naltrexone ? Orally active reduce the risk of relapse in former opioid addicts in addition to supportive therapy ? Longer duration of action ? With clonidine or buprenorphine ? Rapid opioid detoxification ? Cause hepatotoxicity Berhan B. 42
- 43. Good Time! Berhan Begashaw Thank U So Much !!! Read More & Fill the Gap…!
![1
Analgesics
[ Opioids & Non Opioids]
By
Berhan Begashaw
Pharmacy Department
DBU
Nov, 2023](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-1-320.jpg)

![Classification
1. Physiological: Nociceptive, Neuropathic, Psychological
? ?Nociceptive?
? Normal physiology (mechanisms known)
? Treated with analgesics [ NSAIDs, acetaminophen,
opioids]
? ?Neuropathic?
? Aberrant physiology (mechanisms unknown)
? Associated with neural damage
? Difficult to treat with opioid analgesics
2. Clinical: Acute, Chronic, Malignant
Berhan B. 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-5-320.jpg)
![Noxious stimulus [ trauma, infection,..]
Release of inflammatory substances
(PG, His, 5-HT, Bks, Sub.P, etc.)
Transduction (generation & electrical impulses)
Transmission (conduction by nerve fibers)
Modulation (Modification with spinal cord)
Perception
NSAIDs
Opioids
Pathophysiology of pain…
Berhan B. 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-8-320.jpg)



![Opioids Analgesics
? Opium: A mixture of alkaloids from seed capsule of
opium poppy [ Papaver somniferum ]
? Opioids
? Any drug, natural, semisynthetic or synthetic, with
actions like morphine
? Morphine has 5 rings, 3- & 6-OH grps (phenolic &
alcoholic), piperidine ring with N-methyl grp & a
quaternary carbon at position 13
Berhan B. 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-12-320.jpg)

![? Act by binding to specific opioid receptors in the CNS
to produce effects that mimic the action of endogenous
opioids peptide NTs;
? Endorphins [ μ (Mu) receptor]
? Enkephalins [ δ (Delta) receptor]
? Dynorphins [ Κ (Kappa) receptor]
? Primary use is to relieve intense pain that results
from surgery, injury, or chronic disease.
? Widespread availability of opioids has led to abuse
of agents with euphoric properties.
? Antagonists that reverse the actions of opioids
? Clinically important in cases of overdose
Berhan B. 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-14-320.jpg)




![Codeine
? Has only about 10% of its analgesic potency.
? Converted to morphine by CYP2D6 enzyme
? Produces little euphoria & low addiction potential.
? Mild to moderate pain, cough suppressant
[ preferred: Dextromethorphan] & symptomatic
relief of diarrhea.
?With PCM--- pain
? Adverse effects: Resp. depression & death [Children]
? DDIs: BZDs, Alcohol
Berhan B. 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-21-320.jpg)


![Morphine…
Adverse effects
? Respiratory depression [acute overdose]
? Miosis
? Emesis
? Biliary pain
? Constipation
? Hypotension & bradycardia may occur [higher doses]
Berhan B. 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-24-320.jpg)
![Morphine…
Adverse effects…
? Increases CSF pressure
? Bronchoconstriction
? Euphoria
? Androgen deficiency [prolonged use]- ?ed testosterone
? Prolong 2nd stage of labor
? Moderate immunosuppression – infec. & tumor metastasis
? Tolerance & dependence
Berhan B. 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-25-320.jpg)


![Pethidine …
? Primarily as an analgesic & in preanesthetic
medication
? Control shivering during the postsurgical recovery
period
? Management of cancer pain [ Transdermal]
? Sometimes used in obstetrics, but morphine is
often preferred.
Berhan B. 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-28-320.jpg)
![Pethidine …
Adverse effects
? Delayed gastric emptying (common to all opioids):
particular concern in obstetrics
? Delirium, hyper-reflexia, myoclonus, & seizures
[overdose, long term use, esp. in pts with renal
insufficiency]
D/Is: MAOIs, SSRIs
C/Is: Renal & hepatic insufficiency, pre-existing
respiratory compromise
Berhan B. 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-29-320.jpg)
![Fentanyl
? Derivatives of pethidine
? Extremely potent analgesic (100X morphine)
? Highly lipophilic, shorter-acting [15-30mins] & rapid onset
? Treat severe acute pain or as an adjunct to anesthesia.
? Usually administered IV, epidurally, or intrathecally
? With LAs: Epidural analgesia for labor & post pain
? IV: In anesthesia for analgesic & sedation effect
? Transmucosal & nasal: Cancer related pain
? Transdermal patch: Chronic severe pain
Berhan B. 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-30-320.jpg)

![?Pentazocine- Moderate pain, premedication &
supplement to surgical
?Butorphanol- Moderate to severe pain [ more
potent than morphine & pentazocine]
- Nasal spray: Post operative pain & migraine [abuse]
?Nalbuphine- Moderate to severe pain, postsurgical
& obstetrical analgesia
?Buprenorphine-More potent than morphine as
moderate to severe pain
- Opiate detoxification
Berhan B. 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-32-320.jpg)
![Clinical Uses of Opioids
1. Analgesic effect [ severe pain-chronic, acute]
? Selective relief of pain at doses which do not
produce hypnosis or impair sensation
? Some types of pain more responsive to opioids
than others
? More effect in prolonged, burning pain than
sharp, intermittent pain
? Neuropathic pain can be resistant
Berhan B. 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-33-320.jpg)


![2. Cough suppression/antitussives [at low dose]
? Depression of cough centers in the medulla
(possibly in the periphery too)
? Different molecular mechanism than analgesia or
respiratory depression
? Cough suppressed by dextro-isomers of opioids
[Dextromethorphan], compounds which have no
analgesic activity
Berhan B. 36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-36-320.jpg)
![3.Anti-diarrhael agent
? Cause constipation beneficial for Rx of diarrhea
? Diarrhea from almost any cause can be controlled
with the opioid analgesics
? But if associated with infection, appropriate
chemotherapy should be used
? Synthetic drugs [ Diphenoxylate & loperamide]
with selective effect on GIT poorly-absorbed &
have little/no central effects
Berhan B. 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-37-320.jpg)


![Opioid Antagonists
? Bind with high affinity to opioid receptors
? Opioid-dependent pts: Rapidly reverse the effect of
any full μ agonist
? Naloxone
? A pure competitive antagonist of opioid agonists at
μ-receptors [10X higher than K receptors]
? Short duration of action (30-80 mins)
? Rx of morphine poisoning IVly
? Dx opioid dependence
? Oral: No clinical effect
Berhan B. 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opiodsberhanb-231215175137-5af64513/85/Opiods-41-320.jpg)

