Optimization Optimization Optimi(v6).pdf
- 2. Last time ˇ small Small? median large Shallow Deep A target function ?? to fit Eventually cover??? ?? What is the difference? 1 2 3 Optimization: Is it possible to find ?? in the function space.
- 3. Optimization Network: ?? ? Training data: ?1, ? ?1 ?2, ? ?2 ??, ? ?? ..... ? ? = ? ?=1 ? ? ?? ?? ? ? ?? ?? = ??? min ? ? ? Optimization ˇŮ Learning In Deep Learning, ? ? is not convex. Non-convex optimization is NP-hard. Why can we solve the problem by gradient descent?
- 4. Loss of Deep Learning is not convex There are at least exponentially many global minima for a neural net. ? Permutating the neurons in one layer does not change the loss.
- 5. Non-convex ˇŮ Difficult ? ? Not guarantee to find optimal solution by gradient descent ? ? ? ?
- 6. Outline Review: Hessian Deep Linear Model Deep Non-linear Model Conjecture about Deep Learning Empirical Observation about Error Surface
- 7. Hessian Matrix: When Gradient is Zero Some examples in this part are from: https://www.math.upenn.edu/~kazdan/312F12/Notes/ max-min-notesJan09/max-min.pdf
- 8. Training stops ˇ. ? People believe training stuck because the parameters are near a critical point local minima How about saddle point? http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/optimization.html critical point: gradient is zero
- 9. When Gradient is Zero ? ? = ? ?0 + ? ? ?0 ?? + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 + ? Gradient g is a vector Hessian H is a matrix ?? = ?? ?0 ??? ??? = ?2 ?????? ? ?0 = ?2 ?????? ? ?0 = ??? symmetric ?? ?0
- 10. Hessian ? ? = ? ?0 + ? ? ?0 ?? + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 + ? H determines the curvature Source of image: http://www.deeplearningbook.org /contents/numerical.html
- 11. Hessian ? ? = ? ?0 + ? ? ?0 ?? + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 + ? NewtonˇŻs method ?? ? ˇÖ ? ? ? ?0 ?? + ? 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 ? ? ? ?0 ?? ??? = ?? = ? ? 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 ??? ? ? ? ?0 ?? ? = 0 Find the space such that
- 12. Hessian ? ? = ? ?0 + ? ? ?0 ?? + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 + ? NewtonˇŻs method ?? ? ˇÖ ? ? ? ?0 ?? + ? 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 = ? ? ? ? ?0 ?? ? ˇÖ ? + ? ? ? ?0 = 0 ? ? ? ?0 = ?? ? ? ?0 = ???1? ? = ?0 ? ??1? ? = ?0 ? ?? v.s. Change the direction, determine step size
- 13. Hessian ? ? = ? ?0 + ? ? ?0 ?? + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 + ? NewtonˇŻs method What is the problem? If ? ? is a quadratic function, obtain critical point in one step. Consider that ? = ? Source of image: https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/60 9680/newtons-method-intuition ? Not suitable for Deep Learning
- 14. Hessian Source of image: http://www.offconvex.org/2016/03/22/saddlepoints/ ? ? = ? ?0 + ? ? ?0 ?? + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 + ? At critical point (? = 0) H tells us the properties of critical points.
- 15. Review: Linear Algebra http://speech.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~tlkagk/courses/LA_2016/Lecture/eigen.pdf ? If ?? = ?? (? is a vector, ? is a scalar) ? ? is an eigenvector of A ? ? is an eigenvalue of A that corresponds to ? Eigen value Eigen vector A must be square excluding zero vector
- 16. Review: Positive/Negative Definite ? An nxn matrix A is symmetric. ? For every non-zero vector x (? ˇŮ 0) positive definite: positive semi-definite: negative definite: negative semi-definite: ???? > 0 ???? ˇÝ 0 ?? ?? < 0 ???? ˇÜ 0 All eigen values are positive. All eigen values are negative. All eigen values are non-negative. All eigen values are non-positive. 1 0 0 1
- 17. Hessian ? ? ˇÖ ? ?0 + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 At critical point: H is positive definite ???? > 0 Local minima Around ?0: ? ? > ? ?0 All eigen values are positive. H is negative definite ?? ?? < 0 Local maxima Around ?0: ? ? < ? ?0 All eigen values are negative ???? ˇÝ 0? ?? ?? ˇÜ 0? Sometimes???? > 0, sometimes???? < 0 Saddle point ????
- 18. Hessian ? ? ˇÖ ? ?0 + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 At critical point: ? is an eigen vector ?? ?? = ?? ?? = ? ? 2 Unit vector = ? ? ?0 +? Because H is an nxn symmetric matrix, H can have eigen vectors ?1, ?2, ˇ , ?? form a orthonormal basis. ? = ?1?1 + ?2?2 ?1 ?0 +?1 = ?1 2 ?1 + ?? 2 ?2? ?2 +?2 ? ???? = ?1?1 + ?2?2 ?? ?1?1 + ?2?2 ?1 and ?2 are orthogonal (Ignore 1/2 for simplicity)
- 19. Hessian ? ? ˇÖ ? ?0 + 1 2 ? ? ?0 ?? ? ? ?0 At critical point: ? is an eigen vector ?? ?? = ?? ?? = ? ? 2 Unit vector = ? ? ?0 +? Because H is an nxn symmetric matrix, H can have eigen vectors ?1, ?2, ˇ , ?? form a orthonormal basis. ? = ?1?1 + ?2?2 + ? + ???? ?1 2 ?1 + ?2 2 ?2 + ? + ?? 2 ??
- 20. Examples ? ?, ? = ?2 + 3?2 ?? ?, ? ?? = 2? ?? ?, ? ?? = 6? ? = 0, ? = 0 ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? = 2 = 0 = 0 = 6 ? = 2 0 0 6 Positive-definite Local minima
- 21. Examples ? ?, ? = ??2 + 3?2 ?? ?, ? ?? = ?2? ?? ?, ? ?? = 6? ? = 0, ? = 0 ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? = ?2 = 0 = 0 = 6 ? = ?2 0 0 6 Saddle
- 22. Degenerate ? Degenerate Hessian has at least one zero eigen value ? ?, ? = ?2 + ?4 ?? ?, ? ?? = 2? ?? ?, ? ?? = 4?3 ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? = 2 = 0 = 0 = 12?2 ? = 2 0 0 0 ? = ? = 0
- 23. Degenerate ? Degenerate Hessian has at least one zero eigen value ? ?, ? = ?2 + ?4 ? = 2 0 0 0 ? = 0 0 ? ?, ? = ?2 ? ?4 ? = 2 0 0 0 ? = 0 0 ? = ? = 0 ? = ? = 0 No Difference
- 24. Degenerate ? ?, ? = ??4 ? ?4 ?? ?, ? ?? = ?4?3 ?? ?, ? ?? = ?4?3 ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? = ?12?2 = 0 = 0 = ?12?2 ? = 0 0 0 0 ? ?, ? = 0 ? = 0 0 0 0 ? = 0 0 ? = ? = 0
- 25. Degenerate http://homepages.math.uic.edu/~juliu s/monkeysaddle.html ? ?, ? = ?3 ? 3??2 ?? ?, ? ?? = 3?2 ? 3?2 ?? ?, ? ?? = ?6?? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? ?2 ???? ? ?, ? = 6? = ?6? = ?6? = ?6? Monkey Saddle c.f.
- 26. Training stuck ˇŮ Zero Gradient ? People believe training stuck because the parameters are around a critical point !!! http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/optimization.html
- 27. Training stuck ˇŮ Zero Gradient http://videolectures.net/deeplearning2015_bengio_theoretical_motivations/ Approach a saddle point, and then escape
- 29. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6544 ?1 ?2 ? ? ? ? = 1 = 1
- 30. ? = ? ? ? ?1?2? 2 ?? ??1 = 2 1 ? ?1?2 ??2 ?? ??2 = 2 1 ? ?1?2 ??1 ?2? ??1 2 = 2 ??2 ??2 ?2 ? ??2 2 = 2 ??1 ??1 ?2? ??1??2 = ?2 + 4?1?2 ?2 ? ??2??1 = ?2 + 4?1?2 ?1 ?2 ? ? ? ? = 1 = 1 The probability of stuck as saddle point is almost zero. Easy to escape = 1 ? ?1?2 2
- 31. ? = 1 ? ?1?2?3 2 ?? ??1 = 2 1 ? ?1?2?3 ??2?3 ?2? ??1 2 = 2 ??2?3 2 ?2? ??2??1 = ?2?3 + 4?1?2 ?3 2 2-hidden layers ?1 ?2 ? ? ? ? ?3 ?? ??2 = 2 1 ? ?1?2?3 ??1?3 ?? ??3 = 2 1 ? ?1?2?3 ??1?2 ?1 = ?2 = ?3 = 0 ? = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ?1 = ?2 = 0, ?3 = ? ? = 0 ?2 0 ?2 0 0 0 0 0 Saddle point So flat ?1?2?3 = 1 global minima All minima are global, some critical points are ˇ°badˇ±.
- 32. 10 hidden layers 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 10-hidden layers ?1 ?2 origin
- 33. Demo
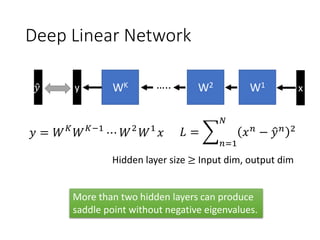
- 34. Deep Linear Network x ? = ?? ???1 ? ?2 ?1 ? y WK W1 W2 ˇ.. ? = ? ?=1 ? ?? ? ? ?? 2 ? ? Hidden layer size ˇÝ Input dim, output dim More than two hidden layers can produce saddle point without negative eigenvalues.
- 35. Reference ? Kenji Kawaguchi, Deep Learning without Poor Local Minima, NIPS, 2016 ? Haihao Lu, Kenji Kawaguchi, Depth Creates No Bad Local Minima, arXiv, 2017 ? Thomas Laurent, James von Brecht, Deep linear neural networks with arbitrary loss: All local minima are global, arXiv, 2017 ? Maher Nouiehed, Meisam Razaviyayn, Learning Deep Models: Critical Points and Local Openness, arXiv, 2018
- 36. Non-linear Deep Network Does it have local minima? ×CĂ÷ĘÂÇ鲻´ćÔÚşÜëyŁ¬×CĂ÷ĘÂÇé´ćÔÚĎŕŚ¦ČÝŇ× ¸ĐÖxÔř×ÓĽŇͬŚW°l¬FͶӰƬÉϵÄĺe×Ö
- 37. Even Simple Task can be Difficult
- 38. ReLU has local + 1 ? + 1 ? + 1 ? + 1 ? 1 0 -3 1 + 1 ? + 1 ? 1 0 -4 -7 (-1.3) (1,-3) (3,0) (4,1) (5,2) This relu network has local minima.
- 39. ˇ°Blind Spotˇ± of ReLU x y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Gradient is zero It is pretty easy to make this happens ˇˇ
- 40. ˇ°Blind Spotˇ± of ReLU ? MNIST, Adam, 1M updates Consider your initialization
- 41. k neurons ?1 + + ˇ + ?2 ˇˇ Label generator ? ? + If ? ˇÝ ? and ?? = ?? n neurons ?1 + + ˇ ? + The number of k and n matters We obtain global minima ? + ?2 ˇˇ ?1 ?2 ?? ?1 ?? ?2 ?? ?? ?? 1 1 1 ? ?1 ?2 ?? ?1 ?? ?2 ? ? ?? ? ? 1 1 1 Considering Data Network to be trained N(0,1)
- 42. No local for ? ˇÝ ? + 2 Considering Data
- 43. Considering Data
- 44. Reference ? Grzegorz Swirszcz, Wojciech Marian Czarnecki, Razvan Pascanu, ˇ°Local minima in training of neural networksˇ±, arXiv, 2016 ? Itay Safran, Ohad Shamir, ˇ°Spurious Local Minima are Common in Two-Layer ReLU Neural Networksˇ±, arXiv, 2017 ? Yi Zhou, Yingbin Liang, ˇ°Critical Points of Neural Networks: Analytical Forms and Landscape Propertiesˇ±, arXiv, 2017 ? Shai Shalev-Shwartz, Ohad Shamir, Shaked Shammah, ˇ°Failures of Gradient- Based Deep Learningˇ±, arXiv, 2017 The theory should looks like ˇ Under some conditions (initialization, data, ˇˇ), We can find global optimal.
- 45. Conjecture about Deep Learning Almost all local minimum have very similar loss to the global optimum, and hence finding a local minimum is good enough.
- 46. Analyzing Hessian ? When we meet a critical point, it can be saddle point or local minima. ? Analyzing H If the network has N parameters ?1 ?2 ?3 ?? ˇˇ We assume ? has 1/2 (?) to be positive, 1/2 (?) to be negative. ?1 ?2 ?3 ?? ˇˇ
- 47. Analyzing Hessian ? If N=1: ? If N=2: ? If N=10: ?1 ?1 1/2 local minima, 1/2 local maxima, Saddle point is almost impossible ?1 ?1 ?2 ?2 1/4 local minima, 1/4 local maxima, 1/2 Saddle points 1/1024 local minima, 1/1024 local maxima, Almost every critical point is saddle point When a network is very large, It is almost impossible to meet a local minima. Saddle point is what you need to worry about. + + - - + -, - +
- 48. Error v.s. Eigenvalues Source of image: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/pennington17a/pennington17a.pdf We assume ? has 1/2 (?) to be negative. p is a probability related to error Larger error, larger p p
- 49. Guess about Error Surface https://stats385.github.io/assets/lectures/Understanding_and_improving_deep_lea ring_with_random_matrix_theory.pdf global minima local minima saddle (good enough)
- 50. Training Error v.s. Eigenvalues
- 51. Training Error v.s. Eigenvalues Portion of positive eigenvalues ˇ°Degree of Local Minimaˇ± 1 - ˇ°degree of local minimaˇ± (portion of negative eigen values)
- 52. ? ˇŘ ? ? ? 1 3/2 1 - ˇ°degree of local minimaˇ± empirical theoretical 1 - ˇ°degree of local minimaˇ± (portion of negative eigen values)
- 53. Spin Glass v.s. Deep Learning ? Deep learning is the same as spin glass model with 7 assumptions. spin glass model network
- 54. More Theory ? If the size of network is large enough, we can find global optimal by gradient descent ? Independent to initialization
- 55. Reference ? Razvan Pascanu, Yann N. Dauphin, Surya Ganguli, Yoshua Bengio, On the saddle point problem for non-convex optimization, arXiv, 2014 ? Yann Dauphin, Razvan Pascanu, Caglar Gulcehre, Kyunghyun Cho, Surya Ganguli, Yoshua Bengio, ˇ°Identifying and attacking the saddle point problem in high-dimensional non-convex optimizationˇ±, NIPS, 2014 ? Anna Choromanska, Mikael Henaff, Michael Mathieu, G¨¦rard Ben Arous, Yann LeCun, ˇ°The Loss Surfaces of Multilayer Networksˇ±, PMLR, 2015 ? Jeffrey Pennington, Yasaman Bahri, ˇ°Geometry of Neural Network Loss Surfaces via Random Matrix Theoryˇ±, PMLR, 2017 ? Benjamin D. Haeffele, Rene Vidal, ˇ± Global Optimality in Neural Network Trainingˇ±, CVPR, 2017
- 56. What does the Error Surface look like?
- 58. Profile ?0 ?? ?0 + 2 ?? ? ?0 local minima is rare?
- 59. Profile
- 60. Profile two random starting points two ˇ°solutionsˇ±
- 61. ?0 ??
- 63. Profile - LSTM
- 64. Training Processing 6-layer CNN on CIFAR-10 Different initialization / different strategies usually lead to similar loss (there are some exceptions). Different initialization
- 65. Training Processing ? Different strategies (the same initialization)
- 66. 8% disagreement
- 67. Training Processing şÎ•r·ÖµŔ“PčsŁż Different training strategies Different basins http://mypaper.pchome.com.tw /ccschoolgeo/post/1311484084
- 68. Training Processing ? Training strategies make difference at all stages of training
- 71. Skip Connection
- 72. Reference ? Ian J. Goodfellow, Oriol Vinyals, Andrew M. Saxe, ˇ°Qualitatively characterizing neural network optimization problemsˇ±, ICLR 2015 ? Daniel Jiwoong Im, Michael Tao, Kristin Branson, ˇ°An Empirical Analysis of Deep Network Loss Surfacesˇ±, arXiv 2016 ? Qianli Liao, Tomaso Poggio, ˇ°Theory II: Landscape of the Empirical Risk in Deep Learningˇ±, arXiv 2017 ? Hao Li, Zheng Xu, Gavin Taylor, Christoph Studer, Tom Goldstein, ˇ°Visualizing the Loss Landscape of Neural Netsˇ±, arXiv 2017
- 74. Concluding Remarks ? Deep linear network is not convex, but all the local minima are global minima. ? There are saddle points which are hard to escape ? Deep network has local minima. ? We need more theory in the future ? Conjecture: ? When training a larger network, it is rare to meet local minima. ? All local minima are almost as good as global ? We can try to understand the error surface by visualization. ? The error surface is not as complexed as imagined.