Orange developers day-Application Caching
- 1. Web Application Caching DB ORM Caching Gamal Shaaban International Centers Orange Labs P&S Cairo Mobile Applications & Software Development
- 2. Agenda ? Why Caching ¨C The Theory of Caching ? ORM Caching ¨C 1st Level of Caching ¨C 2nd Level of Caching ¨C Query Caching
- 3. Why Caching?
- 4. Why Caching How much faster will caching make an application?
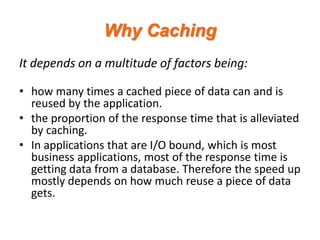
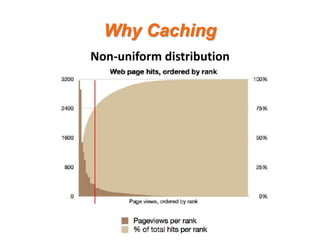
- 5. Why Caching It depends on a multitude of factors being: ? how many times a cached piece of data can and is reused by the application. ? the proportion of the response time that is alleviated by caching. ? In applications that are I/O bound, which is most business applications, most of the response time is getting data from a database. Therefore the speed up mostly depends on how much reuse a piece of data gets.
- 6. Why Caching Amdahl's Law & How to calculate entire system speed up. ? Amdahl's law, after Gene Amdahl, is used to find the system speed up from a speed up in part of the system. 1/ ((1 - Proportion Sped Up) + Proportion Sped Up / Speed up)
- 7. Why Caching Speed up from a Web Page Cache Un-cached page time: 2 seconds Cache retrieval time: 2ms Proportion: 100% The expected server side system speedup is: 1 / ((1 - 1) + 1 / 1000) = 1 / (0 + .001) = 1000 times system speedup The to the browser ˇ°systemˇ± speed up is much less
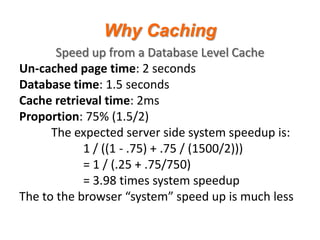
- 8. Why Caching Speed up from a Database Level Cache Un-cached page time: 2 seconds Database time: 1.5 seconds Cache retrieval time: 2ms Proportion: 75% (1.5/2) The expected server side system speedup is: 1 / ((1 - .75) + .75 / (1500/2))) = 1 / (.25 + .75/750) = 3.98 times system speedup The to the browser ˇ°systemˇ± speed up is much less
- 10. ORM Caching
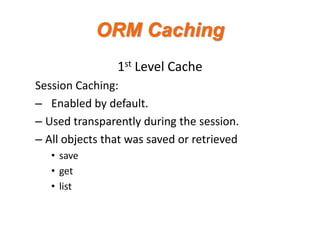
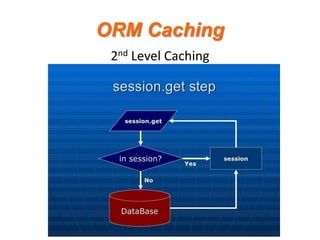
- 11. ORM Caching 1st Level Cache Session Caching: ¨C Enabled by default. ¨C Used transparently during the session. ¨C All objects that was saved or retrieved ? save ? get ? list
- 12. ORM Caching 1st Level Cache Session Caching: ¨C flush() - will sync cache to DB. ¨C clear() - will evict all objects.
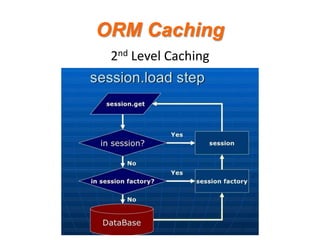
- 13. ORM Caching 2nd Level Caching
- 14. ORM Caching 2nd Level Caching
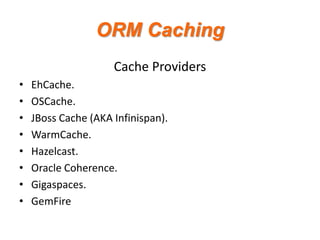
- 15. ORM Caching Cache Providers ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? EhCache. OSCache. JBoss Cache (AKA Infinispan). WarmCache. Hazelcast. Oracle Coherence. Gigaspaces. GemFire
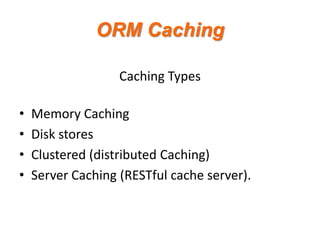
- 17. ORM Caching Caching Types ? ? ? ? Memory Caching Disk stores Clustered (distributed Caching) Server Caching (RESTful cache server).
- 18. Questions ?
- 19. Thank You
Editor's Notes
- #17: Read-only:?A concurrency strategy suitable for data which never changes. Use it for reference data only.Read-write:?Use this strategy for read-mostly data where it is critical to prevent stale data in concurrent transactions, in the rare case of an update.Transactional:?Again use this strategy for read-mostly data where it is critical to prevent stale data in concurrent transactions, in the rare case of an update.Nonstrict-read-write:?This strategy makes no guarantee of consistency between the cache and the database. Use this strategy if data hardly ever changes and a small likelihood of stale data is not of critical concern.
- #18: GimFire server cache & Spring data integration.