Organophosphate poisoning
- 1. Organophosphate poisoning (Ops) Fatma F. Abu-Qados To: Dr. Jehad H. Hammad
- 2. Introduction Organophosphate ( OP ) compounds are a diverse group of chemicals used in both domestic and industrial settings . Many organophosphates are potent nerve agents, functioning by inhibiting the action of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in nerve cells. They are one of the most common causes of poisoning worldwide, and are frequently intentionally used in suicides in agricultural areas.
- 3. Examples Examples of organophosphates include: insecticides ( malathion, parathion, diazinon, fenthion, dichlorvos, chlorpyrifos, ethion ) nerve gases ( soman, sarin, tabun, VX ) ophthalmic agents ( echothiophate, isoflurophate ) antihelmintics ( trichlorfon ). Herbicides ( tribufos [ DEF ] , merphos ) are tricresyl phosphateŌĆōcontaining industrial chemicals .
- 4. Organophosphate compounds were first synthesized in the early 1800 when Lassaigne reacted alcohol with phosphoric acid . Shortly thereafter in 1854, Philip de Clermount described the synthesis of tetraethyl pyrophosphate at a meeting of the French Academy of Sciences . Eighty years later, Lange, in Berlin, and, Schrader, a chemist at Bayer AG, Germany, investigated the use of organophosphates as insecticides . History
- 6. Cont.. However, the German military prevented the use of organophosphates as insecticides and instead developed an arsenal of chemical warfare agents ( ie, tabun, sarin, soman ). A fourth agent, VX, was synthesized in England a decade later . During World War II, in 1941, organophosphates were reintroduced worldwide for pesticide use, as originally intended .
- 7. Massive organophosphate intoxication from suicidal and accidental events, such as the Jamaican ginger palsy incident in 1930, led to the discovery of the mechanism of action of organophosphates. In 1995, a religious sect, Aum Shinrikyo, used sarin to poison people on a Tokyo subway. Mass poisonings still occur today; in 2005, 15 victims were poisoned after accidentally ingesting ethion-contaminated food in a social ceremony in Magrawa, India. Cont..
- 8. Cont.. Nerve agents have also been used in battle, notably in Iraq in the 1980s. Additionally, chemical weapons still pose a very real concern in this age of terrorist activity. Exposure to organophosphates (OPs) is also possible via intentional or unintentional contamination of food sources. Although no clinical effects of chronic, low-level organophosphates (OPs) exposure from a food source have been shown, advancements in risk assessment and preparedness are ongoing
- 9. Use OP in pesticide ..
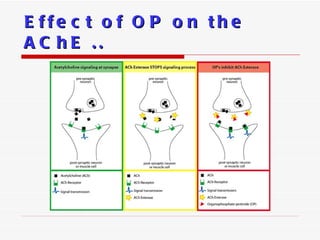
- 10. Pathophysiology The primary mechanism of action of organophosphate pesticides is inhibition of carboxyl ester hydrolases, particularly acetylcholinesterase ( AChE ). AChE is an enzyme that degrades the neurotransmitter acetylcholine ( ACh ) into choline and acetic acid . ACh is found in the central and peripheral nervous system, neuromuscular junctions, and red blood cells ( RBCs). Organophosphates inactivate AChE by phosphorylating the serine hydroxyl group located at the active site of AChE . The phosphorylation occurs by loss of an organophosphate leaving group and establishment of a covalent bond with AChE .
- 11. Once AChE has been inactivated, ACh accumulates throughout the nervous system, resulting in overstimulation of muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. Clinical effects are manifested via activation of the autonomic and central nervous systems and at nicotinic receptors on skeletal muscle. Cont..
- 12. Effect of OP on the AChE ..
- 13. Cont.. Once an organophosphate binds to AChE, the enzyme can undergo one of the following: -Endogenous hydrolysis of the phosphorylated enzyme by esterases or paraoxonases -Reactivation by a strong nucleophile such as pralidoxime (2-PAM) -Irreversible binding and permanent enzyme inactivation (aging)
- 14. Cont.. Organophosphates can be absorbed cutaneously, ingested, inhaled, or injected. Although most patients rapidly become symptomatic, the onset and severity of symptoms depend on the specific compound, amount, route of exposure, and rate of metabolic degradation
- 15. Frequency United States In 2007, The American Association of Poison Control Centers' received 96,307 calls (3.4% of all human exposures) related to pesticide exposures, many of which involved organophosphate (OP) agents and 80 uses of 2-PAM. However, poison center ŌĆō recorded exposures to organophosphates (OPs) from 1995 to 2004 have declined because of the United States Environmental Protection Agency phasing out commonly used household and agricultural organophosphate (OP) agents.
- 16. Cont.. International Pesticide poisonings are among the most common modes of poisoning fatalities. In countries such as India and Nicaragua, organophosphates (OPs) are easily accessible and, therefore, a source of both intentional and unintentional poisonings. The incidence of international organophosphate-related human exposures appears to be underestimated.
- 17. In GAZA Strip ’üŖ ŌĆ”... study by Dr.MaJed Yassen 1. The major causes of OPP in children in the Gaza Strip were domestic use of pesticides particularly to fight rodents and unsafe storage of pesticides, and spraying pesticides in their presence. 2. The most common diagnosed symptoms of OPP in children were pin point pupils followed by vomiting, drawsy, conscious and then by convulsions. 3. There was a depression in serum cholinesterase in the cases compared to the controls. Changes in enzyme activity was significantly associated with drawsy, conciuos and pin point.
- 18. 4. Glucose level was significantly increase in the patients compared to the controls. 5. Liver enzymes ALT, AST and ALP were significantly higher in the cases 6. Urea and creatinine levels were increased in the cases compared to the controls. 7. Of the electrolytes studied, potassium and phosphorus were decreased significantly in the cases.
- 19. 8. There were significant decreases in total protein, albumin and globulin in the cases compared to the controls. 9. White blood cell count and blood platelets were higher in the cases. 10. Hemoglobin and hematocrit, MCV and MCH were significantly decreased in the cases compared to the controls. 11. Pearson's correlation test showed negative significant correlation between cholinesterase and glucose, ALT, AST or creatinine. On the other hand,positive significant correlation between cholinesterase and phosphorus was achieved.
- 20. Mortality / Morbidity -Worldwide mortality studies report mortality rates from 3-25%. The compounds most frequently involved include malathion, dichlorvos, trichlorfon, and fenitrothion/malathion. -Mortality rates depend on the type of compound used, amount ingested, general health of the patient, delay in discovery and transport, insufficient respiratory management, delay in intubation, and failure in weaning off ventilatory support. -Complications include severe bronchorrhea, seizures, weakness, and neuropathy. Respiratory failure is the most common cause of death.
- 21. Age Organophosphates ( OPs ) may affect children or other at - risk populations differently . The increased susceptibility has not been elucidated but may involve delayed or persistent effects . More work in this area is underway and should help identify the true risk potential.
- 22. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of organophosphate poisoning can be divided into 3 broad categories, including ( 1 ) muscarinic effects, ( 2 ) nicotinic effects, and ( 3 ) CNS effects . 1- Mnemonic devices used to remember the muscarinic effects of organophosphates are SLUDGE ( salivation, lacrimation, urination, diarrhea, GI upset, emesis ) and DUMBELS ( diaphoresis and diarrhea; urination; miosis; bradycardia, bronchospasm, bronchorrhea; emesis; excess lacrimation; and salivation ).
- 23. Cont.. Muscarinic effects by organ systems include the following Cardiovascular : Bradycardia, hypotension Respiratory : Rhinorrhea, bronchorrhea, bronchospasm, cough, severe respiratory distress Gastrointestinal : Hypersalivation, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, fecal incontinence Genitourinary : Incontinence Ocular : Blurred vision, miosis Glands : Increased lacrimation, diaphoresis signs and symptoms include muscle fasciculations, cramping, weakness, and diaphragmatic failure .
- 24. ╠²
- 25. Cont.. 2- Autonomic nicotinic effects include hypertension, tachycardia, mydriasis, and pallor . 3- CNS effects include anxiety, emotional lability, restlessness, confusion, ataxia, tremors, seizures, and coma .
- 26. Treatment Atropine can be used as an antidote in conjunction with pralidoxime, though the use of "-oximes" has been found to be of no benefit, or possibly harmful, in at least two meta-analyses. Atropine blocks the parasympathetic nervous system, both vagal effects on the heart.
- 27. How do I avoid it? avoidance of contact with chemicals like pesticides. You should take the usual precautions like making sure thereŌĆÖs adequate ventilation when using pesticides indoors, Washing all fresh fruit and vegetables before eating, Using gloves when working with pesticides, etc.
- 28. ..ThanQ ..



![Examples Examples of organophosphates include: insecticides ( malathion, parathion, diazinon, fenthion, dichlorvos, chlorpyrifos, ethion ) nerve gases ( soman, sarin, tabun, VX ) ophthalmic agents ( echothiophate, isoflurophate ) antihelmintics ( trichlorfon ). Herbicides ( tribufos [ DEF ] , merphos ) are tricresyl phosphateŌĆōcontaining industrial chemicals .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ops-110322124851-phpapp01/85/Organophosphate-poisoning-3-320.jpg)