Orphan diseases and its management
- 1. ORPHAN DISEASES AND ITS MANAGEMENT K.VISHNUPRIYA, M.Pharm(pharmacology), Ratnam institute of pharmacy, Nellore.
- 2. INTRODUCTION ’é¦ WHO Defines Orphan/ rare disease are ŌĆ£ All pathogenic conditions are affected by 0.65 ŌĆō 1% out of every 1000 inhabitantsŌĆØ. ’é¦ The European organization ŌĆō defines Orphan is one with prevalence of 5:10,000 Europeans. ’é¦ USA defines it is an aliment affecting fewer than 2,00,000 Americans. ’é¦ Australia defines it is an aliment affecting fewer than 2,000. ’é¦ India defines it is an aliment affecting fewer than 50,000 Indian patients. Orphan drugs : The drugs which used to treat Orphan diseases are called as Orphan drugs. Eg: Haem arginate ŌĆō acute Intermittent porphyria Ibuprofen ŌĆō dutus arteriosus
- 3. INTRODUCTION Orphan drug law : In 1984 United states promulgated the 1st law which is specially designed to encourage R&D investments in areas usually neglected by pharmaceutical companies. ’é¦ Subsequently other countries like Japan(1993), Australia(1998) and European union(2000) have adopted similar laws. ’é¦ India follows the European laws ’āś The Orphan drug law depends on 2 criteria 1. Epidemiological criterion: The product is aimed to cure or treat the disease with low prevalence 2. Economic criterion: Irrespective of disease prevalence, there is no reasonable expectation R&D production cost will be recovered by sale revenues in countries where the Orphan status is granted.
- 4. INTRODUCTION Incentives of pharmaceutical companies: 1. Push mechanisms: these are incentives that operates upstream during R&D process and involve costs to the public sector, such as tax credits and research grants. 2. Pull mechanisms: these are incentives that operates downstream reward the research output and offers public incentives for development of product.
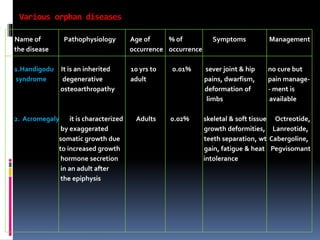
- 5. Various orphan diseases Name of Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management the disease occurrence occurrence 1.Handigodu It is an inherited 10 yrs to 0.01% sever joint & hip no cure but syndrome degenerative adult pains, dwarfism, pain manage- osteoarthropathy deformation of - ment is limbs available 2. Acromegaly it is characterized Adults 0.02% skeletal & soft tissue Octreotide, by exaggerated growth deformities, Lanreotide, somatic growth due teeth separation, wt Cabergoline, to increased growth gain, fatigue & heat Pegvisomant hormone secretion intolerance in an adult after the epiphysis
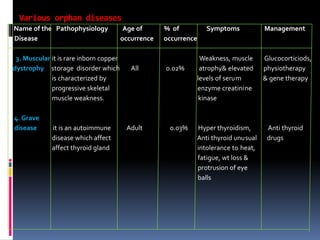
- 6. Various orphan diseases Name of the Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management Disease occurrence occurrence 3. Muscular it is rare inborn copper Weakness, muscle Glucocorticiods, dystrophy storage disorder which All 0.02% atrophy& elevated physiotherapy is characterized by levels of serum & gene therapy progressive skeletal enzyme creatinine muscle weakness. kinase 4. Grave disease it is an autoimmune Adult 0.03% Hyper thyroidism, Anti thyroid disease which affect Anti thyroid unusual drugs affect thyroid gland intolerance to heat, fatigue, wt loss & protrusion of eye balls
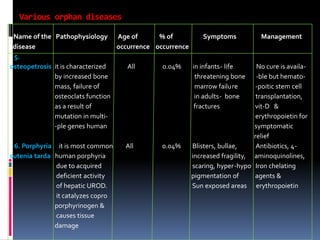
- 7. Various orphan diseases Name of the Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management disease occurrence occurrence 5. osteopetrosis it is characterized All 0.04% in infants- life No cure is availa- by increased bone threatening bone -ble but hemato- mass, failure of marrow failure -poitic stem cell osteoclats function in adults- bone transplantation, as a result of fractures vit-D & mutation in multi- erythropoietin for -ple genes human symptomatic relief 6. Porphyria it is most common All 0.04% Blisters, bullae, Antibiotics, 4- cutenia tarda human porphyria increased fragility, aminoquinolines, due to acquired scaring, hyper-hypo Iron chelating deficient activity pigmentation of agents & of hepatic UROD. Sun exposed areas erythropoietin it catalyzes copro porphyrinogen & causes tissue damage
- 8. Various orphan diseases Name of Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management the disease occurrence occurrence 7. Myasthenia it is an autoimmune All 0.06% Diplopia, eye Cholinesterase gravis neuromuscular lid moment, inhibitors, junction disorder swallowing, corticosteroids which is caused due fatigue & facial with immuno to problems in trans expression modulators -mission of nerve signals to muscles 8. ParkinsonŌĆÖs it is an progressive Elderly 0.5% tremors, brady Levodopa, disease neuro-degenerative kinesia, gait & Carbidopa, moment disorder muscular rigidity Dopamine that impairs speech, Pramipexole moment & others
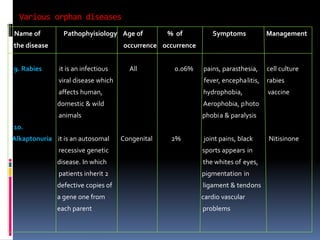
- 9. Various orphan diseases Name of Pathophyisiology Age of % of Symptoms Management the disease occurrence occurrence 9. Rabies it is an infectious All 0.06% pains, parasthesia, cell culture viral disease which fever, encephalitis, rabies affects human, hydrophobia, vaccine domestic & wild Aerophobia, photo animals phobia & paralysis 10. Alkaptonuria it is an autosomal Congenital 2% joint pains, black Nitisinone recessive genetic sports appears in disease. In which the whites of eyes, patients inherit 2 pigmentation in defective copies of ligament & tendons a gene one from cardio vascular each parent problems
- 10. Various orphan diseases Name of the Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management disease occurrence occurrence 11. GaucherŌĆÖs it causes due to Congenital 2% Hepatospleeno- enzyme disease deficiency of - megaly replacement glucocerebrosidase therapy & enzyme which is surgical removal responsible for of spleen&/liver break down of part to improve fatty substances affected person called Gluco - comfort - cerebrosides 12. Kyasanur it is an infectious Adult 5% chills, frontal no treatment forest disease bleeding disease head ache, high is available in monkeyŌĆÖs & fever, vomiting, human caused by diarrhea, cough, pathogenic virus sever pain in called KFD virus neck & low back
- 11. Various orphan diseases Name of the Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management disease occurrence occurrence 13. Alpha-1- affected people Congenital 5% chronic obstructive Lung antitrypsin have lack of alpha- pulmonary disease transplant deficiency 1 antitrypsin protein less commonly in their blood due cause liver damage mutation of SERPINA-1 rarely skin disease gene. It causes uncontrolled neu- -trophil elastage activity. 14. Madras it is an molecular Adult NA patient look slender no treatment motor neuron disease, in which facial & bulbar, is available, disease the pathogenesis hearing loss due to IV Ig is is unknown nerve defect & available muscle bilateral optic atrophy
- 12. Various orphan diseases Name of the Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management disease occurrence occurrence 15. EbsteinŌĆÖs there is an Congenital 5% Dyspnea, atypical ACE inhibitors anomaly embryological chest pain, fatigue, Ca2+ channel malformation of anorexia, decreased blockers, of tricuspid valve energy from cardiac beta-blockers leaflets. So, that failure causes venous Diuretics, there is incomplete congestion in stomach Digoxin alignment of leaf lets at AV junction 16. EhlerŌĆÖs it is an inherited Congenital 8% hyper extensibility no drug is danlos connective tissue of joints & skin, available but syndrome disorder which vascular changes, life style results impaired dental abnormalities modifications formation & & pulmonary & surgery integrity of alterations collagen
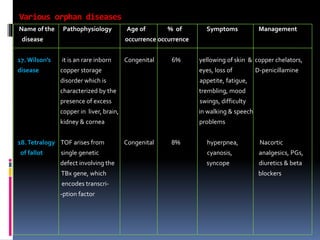
- 13. Various orphan diseases Name of the Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management disease occurrence occurrence 17.WilsonŌĆÖs it is an rare inborn Congenital 6% yellowing of skin & copper chelators, disease copper storage eyes, loss of D-penicillamine disorder which is appetite, fatigue, characterized by the trembling, mood presence of excess swings, difficulty copper in liver, brain, in walking & speech kidney & cornea problems 18.Tetralogy TOF arises from Congenital 8% hyperpnea, Nacortic of fallot single genetic cyanosis, analgesics, PGs, defect involving the syncope diuretics & beta TBx gene, which blockers encodes transcri- -ption factor
- 14. Various orphan diseases Name of Pathophysiology Age of % of Symptoms Management the disease occurrence occurrence 19. Lupus it is an inflammatory All NA it can affect Anti-malarial autoimmune disease any organ like drugs, NSAIDs in which bodyŌĆÖs heart, kidneyŌĆÖs, like Ibuprofen, immune system attack blood vessels, steroids, its own healthy tissues joints/skin, immuno - & causes inflammation skin rashes, supressives joint pains 20. Pulmonic it narrow the pulmonic Congenital NA difficult to valvular valve & the group of 3 breath, chest valvuloplasty stenosis leaflets separates right pain, fatigue, ventricle from the right ventricular pulmonary trunk hypertrophy & hypoxemia