OS unit 1 ppt.ppt
- 1. Operating System Unit ŌĆōI Prepared By Prof. Amit Purohit 9/16/2022 1
- 2. Topics to be covered ŌĆó Introduction of Operating Systems ŌĆó History of Operating Systems ŌĆó Functions of Operating Systems ŌĆó Types of Operating Systems ŌĆó Operating System Services ŌĆó Operating System Structure ŌĆó System Calls and System Boots 9/16/2022 2
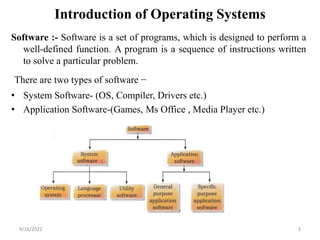
- 3. Introduction of Operating Systems Software :- Software is a set of programs, which is designed to perform a well-defined function. A program is a sequence of instructions written to solve a particular problem. There are two types of software ŌłÆ ŌĆó System Software- (OS, Compiler, Drivers etc.) ŌĆó Application Software-(Games, Ms Office , Media Player etc.) 9/16/2022 3
- 4. Introduction of Operating Systems ŌĆó An Operating system (OS) is a System software which acts as an interface between the user and computer hardware. ŌĆó Every computer must have at least one OS to run other programs. An application like Chrome, MS Word, Games, etc needs some environment in which it will run and perform its task. ŌĆó Example: Windows OS, UNIX/LINUX OS, MAC OS, Android OS etc. 9/16/2022 4
- 5. Computer system can be divided into four components. ’é¦ User ’é¦System and application programs ’é¦Operating system ’é¦Hardware Introduction to Operating Systems 9/16/2022 5
- 6. History of Operating Systems The First Generation (1940's to early 1950's) All programming was done in absolute machine language. During this generation computers were generally used to solve simple math calculations, operating systems were not necessarily needed. 9/16/2022 6
- 7. History of Operating Systems The Second Generation (1955-1965) Operating systems in the 1950's were called single-stream batch processing systems because the data was submitted in groups 9/16/2022 7
- 8. History of Operating Systems The Third Generation (1965-1980) The third generation operating systems also introduced multiprogramming. 9/16/2022 8
- 9. History of Operating Systems The Fourth Generation (1980-Present Day) Windows went on to become the largest operating system used in technology today with releases of Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP ,Windows 7 & Apple is the other major operating system created in the 1980's. 9/16/2022 9
- 10. Operating System with Market Share 9/16/2022 10
- 11. Functions of OS 9/16/2022 11
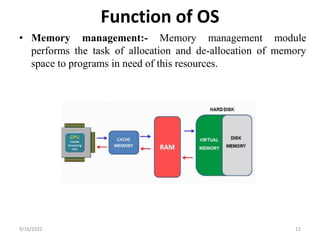
- 12. Function of OS ŌĆó Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources. 9/16/2022 12
- 13. Function of OS ŌĆó Process Management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes. 9/16/2022 13
- 14. Function of OS ŌĆó File Management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files. 9/16/2022 14
- 15. Function of OS ŌĆó Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de- allocation of the devices. ŌĆó Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access. 9/16/2022 15
- 16. Function of OS ŌĆó Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network. ŌĆó Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users. 9/16/2022 16
- 17. Types of operating Systems Batch Operating System ŌĆō ŌĆó In this type of system, there is no direct interaction between user and the computer. ŌĆó The user has to submit a job (written on cards or tape) to a computer operator. ŌĆó Then computer operator places a batch of several jobs on an input device. ŌĆó Jobs are batched together by type of languages and requirement. 9/16/2022 17
- 18. Time-Sharing Operating Systems These systems are also known as Multitasking Systems. The task can be from single user or from different users also. The time that each task gets to execute is called quantum. After this time interval is over OS switches over to next task. 9/16/2022 18
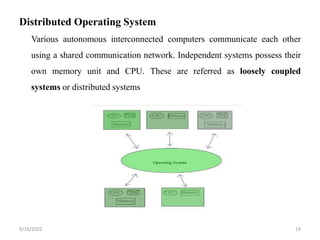
- 19. Distributed Operating System Various autonomous interconnected computers communicate each other using a shared communication network. Independent systems possess their own memory unit and CPU. These are referred as loosely coupled systems or distributed systems 9/16/2022 19
- 20. Network Operating System ŌĆō These systems run on a server and provide the capability to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. These type of operating systems allow shared access of files, printers, security, applications, and other networking functions over a small private network. 9/16/2022 20
- 21. Real-Time Operating System ŌĆō These types of OSs serves the real-time systems. The time interval required to process and respond to inputs is very small. This time interval is called response time. Two types of Real-Time Operating System which are as follows: ŌĆó Hard Real-Time Systems ŌĆó Soft Real-Time Systems 9/16/2022 21
- 22. Operating system services ŌĆó Program execution ŌĆó I/O operations ŌĆó File System manipulation ŌĆó Communication ŌĆó Error Detection ŌĆó Resource Allocation ŌĆó Protection 9/16/2022 22
- 23. Operating System structure Simple Structure:-Such operating systems do not have well defined structure and are small, simple and limited systems. The interfaces and levels of functionality are not well separated. MS-DOS is an example of such operating system. 9/16/2022 23
- 24. Layered structure: An OS can be broken into pieces and retain much more control on system. In this structure the OS is broken into number of layers (levels). The bottom layer (layer 0) is the hardware and the topmost layer (layer N) is the user interface. 9/16/2022 24
- 25. System Calls and System Boots ŌĆó System Calls:- The interface between a process and an operating system is provided by system calls ŌĆó There are many different system calls ŌĆō open() ŌĆō read() ŌĆō write() ŌĆō close() 9/16/2022 25
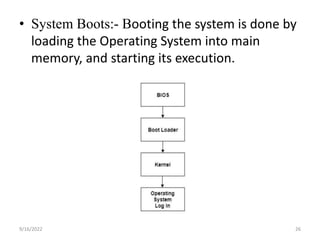
- 26. ŌĆó System Boots:- Booting the system is done by loading the Operating System into main memory, and starting its execution. 9/16/2022 26