paediatric monteggia fracture dr mohamed ashraf alleppey kerala india.pptx
- 1. paediatric monteggia fractures Dr Mohamed Ashraf Prof and Head Govt Medical College Alleppey Kerala,india drashraf369@gmail.com
- 2. GIOVANNI BATTISTA MONTEGGIA 1814 EPONYMOUSLY NAMED BY PERRIN,1909
- 3. Why important? • Rapid recovery of elbow mobility • Prevention of late complications • Symptomatic radial head pain flexion block cubitus valgus neurological supination limitation
- 4. How often missed • 1.5-3 % of all pediatric elbow injuries • Peak age- 4 to 10 years • Missed- upto 20 % • Radial head unreduced for 4 weeks or more- NEGLECTED
- 5. Why missed • Clinical suspicion • Proper interpretation of well exposed properly centered x-rays. • Redisplacement of fracture or radial head • Plastic deformation-often missed • Bae-2016 • Most missed by non-pediatric ortho,ER person,residents
- 7. Patho anatomy • Shortened or angulated ulna leads to radial head dislocation. • Interosseous membrane contracted and shortened.[hence corrective osteotomy proximal] • Untreated- progressive elbow instability,progressive deformity and stiffness of elbow and forearm. • Missed case -multiple procedures with inferior outcome
- 8. types • 4 types • 3 variants-isolated rad head,#ulna and rad neck,bb#with radius proximal • Letts-green stick ulna
- 9. Classification JOSE LUIS BADO 1958
- 10. BADO TYPE • Type depends on injury mechanism • Neurodeficite in 10-20 % cases • Bado 2 -ulnar nerve • Bado 3 -PIN • waters 2012
- 11. Bado 1 70-75 % apex anterior, anterior dislocation pronated FA fall
- 12. Bado 2 rare in children 3-6 % axial load on partly flexed elbow direct trauma to mid-supinated FA penrose 1951
- 13. Bado 3 15-20 % apex lateral lateral dislocation fall on pronated FA with varus stress
- 14. Bado 4 high energy trauma FA pronated fall
- 16. Clinical
- 17. radiology
- 19. Never miss this line!!!
- 20. X-ray • Doubtful-take contralateral elbow • Dynamic imaging with fluroscopy
- 21. X-ray mimicker • Congenital head dislocation • Hypoplastic capitellum • Convex radial head • Radial shaft bowing and too long • No trauma • Difficult reduction • Usually post dislocation • Opposite elbow affected Waters 2012
- 22. management • Closed reduction and casting[ under C-arm] • Open reduction and nailing [ESIN] • Open reduction and plating
- 23. Current principles RING and WATERS • Restoration of length and alignment of ulna • Closedreduction-lengthstable fractures [transverse and short oblique] • Unstable radial head in stable#- nail • plating-length unstable fractures [long oblique and comminuted] • Osteotomy Plating ,radial head stabilisation- neglected#
- 24. Treatment RING AND RAMSKI • Depends on fracture pattern • Plastic deformation-closed manipulation • Greenstick injury-closed manipulation • Unstable radial head even @100-ulna fixation • Stable radial head-close observation • Transverse/short oblique-CMR +/_ fixation • Long oblique/comminuted- ORIF/plate fixation • ORIF- upto 4-6 weeks
- 25. Plastic deformity • Cosmetic and Functional aspects • 10 yr - 15 deg • 6-10 yrs- 20 deg correction • 5 yrs-remodelling • Under GA ,3-5 mts transverse force over the apex • Avoid epiphysis INJURY
- 26. missed • If elbow not included in xray • If radial head position overlooked
- 27. Late cases • DCP or LCP preferred for neglected cases. • More chance of radial head dislocation • More chance of forearm restriction. • Plastic deformation difficult to identify later. • Dysplastic radial head may be the only sign
- 28. Radial head • Closed reduction • Open-clear soft tissue,repair annular,elbow 120 deg,transarticular pin.
- 29. missed Radial head • Can be open reduced -6 months • After 6 months-1 year-leave till skeletal maturity-excision later • Late annular reconstruction- Extensor aponeurosis[boyd], Triceps middle fascia[bell tawse] Triceps lateral fascia[lloyd roberts]
- 30. Late cases problem solving • Annular ligament reconstruction- • 1]palmaris longus • 2]pedicled forearm fascia • 3]pedicled triceps fascia. • 4]remnant repair • 5]synthetic annular ligament levin et al cureus
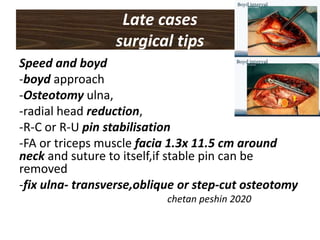
- 31. Late cases surgical tips Speed and boyd -boyd approach -Osteotomy ulna, -radial head reduction, -R-C or R-U pin stabilisation -FA or triceps muscle facia 1.3x 11.5 cm around neck and suture to itself,if stable pin can be removed -fix ulna- transverse,oblique or step-cut osteotomy chetan peshin 2020
- 32. Thank you delegates and team palakkad






![Patho anatomy
• Shortened or angulated ulna leads to radial head
dislocation.
• Interosseous membrane contracted and
shortened.[hence corrective osteotomy proximal]
• Untreated- progressive elbow
instability,progressive deformity and stiffness of
elbow and forearm.
• Missed case -multiple procedures with inferior
outcome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paediatricmonteggiafracturedrmohamedashrafalleppeykeralaindia-230319115122-f308ee03/85/paediatric-monteggia-fracture-dr-mohamed-ashraf-alleppey-kerala-india-pptx-7-320.jpg)












![management
• Closed reduction and casting[ under C-arm]
• Open reduction and nailing [ESIN]
• Open reduction and plating](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paediatricmonteggiafracturedrmohamedashrafalleppeykeralaindia-230319115122-f308ee03/85/paediatric-monteggia-fracture-dr-mohamed-ashraf-alleppey-kerala-india-pptx-22-320.jpg)
![Current principles
RING and WATERS
• Restoration of length and alignment of ulna
• Closedreduction-lengthstable fractures
[transverse and short oblique]
• Unstable radial head in stable#- nail
• plating-length unstable fractures
[long oblique and comminuted]
• Osteotomy Plating ,radial head stabilisation-
neglected#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paediatricmonteggiafracturedrmohamedashrafalleppeykeralaindia-230319115122-f308ee03/85/paediatric-monteggia-fracture-dr-mohamed-ashraf-alleppey-kerala-india-pptx-23-320.jpg)





![missed Radial head
• Can be open reduced -6 months
• After 6 months-1 year-leave till skeletal
maturity-excision later
• Late annular reconstruction-
Extensor aponeurosis[boyd],
Triceps middle fascia[bell tawse]
Triceps lateral fascia[lloyd roberts]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paediatricmonteggiafracturedrmohamedashrafalleppeykeralaindia-230319115122-f308ee03/85/paediatric-monteggia-fracture-dr-mohamed-ashraf-alleppey-kerala-india-pptx-29-320.jpg)
![Late cases
problem solving
• Annular ligament reconstruction-
• 1]palmaris longus
• 2]pedicled forearm fascia
• 3]pedicled triceps fascia.
• 4]remnant repair
• 5]synthetic annular ligament
levin et al cureus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paediatricmonteggiafracturedrmohamedashrafalleppeykeralaindia-230319115122-f308ee03/85/paediatric-monteggia-fracture-dr-mohamed-ashraf-alleppey-kerala-india-pptx-30-320.jpg)