Pai Forest
- 1. PAI FOREST ECOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE AND THREATS TAYYAB SHAFIQUE MS ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES Sindh Madressatul Islam University
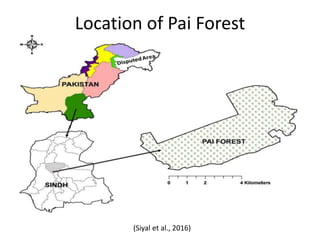
- 2. LOCATION OF PAI FOREST âĒ Pai is known as riverine forest and is located on easternside of the river Indus near Sakrand town of district Nawab Shah, about a distance of 5 km nearby National Highway. âĒ This forest has a total area of 1933 ha (4777 acres). Out of which only 1502 ha (78%) are under tree cover while remaining 319 and 112 ha are either blank or on high lying areas, respectively.
- 3. Location of Pai Forest (Siyal et al., 2016)
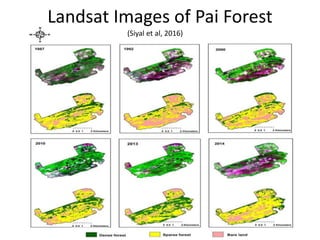
- 4. Landsat Images of Pai Forest (Siyal et al, 2016)
- 5. ECOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE âĒ Trees and shrubs play a vital role in the daily life of rural communities. âĒ They provide sources of timber, fuel wood, food, fodder, essential oils, gums, resins and latex, medicines and shade. âĒ Forest animals have a vital role in forest ecology such as pollination, seed dispersal and germination.
- 8. Hog Deer
- 9. ECOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE âĒ Trees absorb carbon dioxide and are vital carbon sinks.
- 10. âĒ It is estimated that the worldâs forests store 283 Gigatonnes of carbon in their biomass alone, and that carbon stored in forest biomass, deadwood, litter and soil together is roughly 50 per cent more than the carbon in the atmosphere. (UNEP) ECOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE
- 11. THREATS Encroachment The game reserve is under the influence of political pressure especially from the influential local farm owners. These formers not only control the canal water but also keep on encroachment the Pai forest land.
- 12. THREATS Hunting Hunting also increase disturbance which has ultimately led to the dispersal of wildlife from the area.
- 13. THREATS Deforestation Cutting of forest for fuel wood by the local communities has significantly contributed to the destruction of the forest ecosystem. After the approval of lease policy of forest land by Sindh Cabinet in 2005 the Riverine forest has been deteriorated and encroached by local influential.
- 14. RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES âĒ Provide alternative to fuel wood âĒ Monitoring of Deforestation âĒ Halt Hunting âĒ Evaluation of Carbon Stock âĒ Biodiversity Maintenance
- 15. RECOMMENDATIONS âĒ Farmers should be made aware about the importance of small mammal as natural pest controllers and be given instructions on wise-use of pesticides and other agro-chemicals on farmed land âĒ The local communities should be educated about the importance of wild fauna like amphibian, reptilian and small mammals especially in the forest Ecosystem in close coordination with local community, through frequent visits, exposure visits/ tours for representatives
- 16. THANK YOU