1 of 1
Recommended
Nociceptors the sensors of the pain pathway 



Nociceptors the sensors of the pain pathway Asmae LGUENSAT
Ėý
Nociceptors are sensory neurons that detect potentially damaging stimuli and mediate the pain response. The document discusses the anatomy and physiology of nociception, including:
1) Nociceptors express receptors that detect noxious heat, cold, and mechanical stimuli.
2) Nociceptor activation leads to action potentials that are conducted to the spinal cord and brain.
3) Central modulation and sensitization can lower pain thresholds and lead to hyperalgesia and allodynia.
4) While specific nociceptor populations respond to different stimuli, their roles in transmitting specific pain modalities require further study.Anatomy of pain pathway



Anatomy of pain pathwayDhritiman Chakrabarti
Ėý
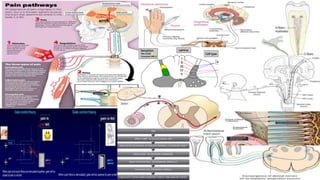
1. The document discusses the anatomy and pathways of the pain sensation system. It describes how nociceptors detect painful stimuli and transmit signals to the spinal cord and brain.
2. The spinal cord plays an important role in pain processing. It contains ascending tracts that carry pain signals to the brain and descending tracts that modulate pain. Key nuclei in the spinal cord dorsal horn relay and modulate pain transmission.
3. Pain signals are transmitted from the spinal cord via the spinothalamic tract to the thalamus and then to regions of the cerebral cortex involved in pain perception and modulation like the somatosensory, cingulate, and insular cortices. The periaqueductalDr liu fibromyalgia disease overview-1



Dr liu fibromyalgia disease overview-1Chau Nguyen
Ėý
Firmly palpates each of the 18 tender points with the thumb or finger, pressing into the muscle/fascia approximately 4 kg of pressure.
Patient: Rates pain on a scale of 0-3:
0 = No pain
1 = Mild pain (patient states "that's tender")
2 = Moderate pain (patient grimaces or withdraws)
3 = Severe pain (patient cries out)
*11/18 tender points must be rated 2/3 for diagnosis of FM per ACR criteria
Adapted from: Wolfe F, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:160-172. 20
Diagnostic Criteria for FMPain and pain pathways



Pain and pain pathwaysDhwani Gohil
Ėý
This document provides an overview of pain and pain pathways. It defines pain, discusses the history of pain theories, and describes the different types of pain receptors and neural pathways involved in pain perception and modulation. Specifically, it outlines fast and slow pain pathways conducted by myelinated and unmyelinated fibers, discusses peripheral and central mechanisms of injury-induced pain, and classification of pain including somatic and visceral pain.12.04.08(a): Pathogenesis and Treatment of Fibromyalgia



12.04.08(a): Pathogenesis and Treatment of FibromyalgiaOpen.Michigan
Ėý
šÝšÝßĢshow is from the University of Michigan Medical School's M2 Musculoskeletal sequence
View additional course materials on Open.Michigan:
openmi.ch/med-M2Muscu Fibromyalgia disease overview



Fibromyalgia disease overviewdrangelosmith
Ėý
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tender points. The pathogenesis involves central sensitization leading to amplification of pain signaling and processing in the central nervous system. It is diagnosed based on chronic widespread pain for at least 3 months and tenderness in at least 11 of 18 tender point sites. Management includes non-pharmacological approaches like exercise, cognitive behavioral therapy, and education, as well as medications to reduce pain and improve sleep, mood, and function.Fibromyalgia



FibromyalgiaDr. Md. Rashedul Islam
Ėý
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain and tenderness. It is more common in women than men. While pain is the primary symptom, it also involves fatigue, sleep issues, cognitive problems, anxiety and depression. There is no known cause but factors like genetics and abnormal pain processing in the central nervous system may play a role. Treatment involves lifestyle changes like exercise and stress management as well as medications like antidepressants. While not curable, some patients are able to adapt well through treatment, but a minority have severe, treatment-resistant symptoms.Fibromyalgia 2



Fibromyalgia 2Mukesh Sriwastva
Ėý
Steven Smith presents a continuing education lecture on fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) for nurses and nurse practitioners. He begins by providing his conflict of interest statement, then asks a series of questions about what FMS is and whether it is a musculoskeletal, mental, or inflammatory condition. He explains that FMS is thought to be an illness of the central nervous system, specifically the neuroendocrine system. Smith discusses central sensitization syndrome and concepts like wind-up phenomenon and neurotransmitters involved in ascending and descending pain pathways. He emphasizes the importance of understanding the pathophysiology of FMS in order to properly treat it. Smith stresses that FMS is diagnosed through a thorough history and physical exam to rule out other conditions. He provides examples ofFibromyalgia powerpoint completed



Fibromyalgia powerpoint completedLaura Dunn
Ėý
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread muscle pain, tenderness, and stiffness. It predominantly affects women between 25-55 years old. Common symptoms include fatigue, headaches, sleep disturbances, and abnormal pain sensation. While the cause is unknown, genes and physical trauma may play a role. Treatments include exercise, acupuncture, massage, medications, and psychotherapy to manage pain and fatigue.Fibromyalgia



Fibromyalgiapunita85
Ėý
Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, stiffness, and tender points. It predominantly affects women and prevalence increases with age. The diagnosis is based on a history of widespread pain for at least 3 months and pain in 11 of 18 tender points. While the cause is unknown, it involves central sensitization and neuroendocrine abnormalities. Treatment includes medications, exercise, stress management, CBT, and alternative therapies. The ACR is proposing new diagnostic criteria incorporating symptoms like fatigue and cognitive problems in place of tender points.Updates in Fibromyalgia: Diagnosis and Management



Updates in Fibromyalgia: Diagnosis and ManagementSidney Erwin Manahan
Ėý
I was asked to present something on Fibromyalgia during a Pain Summit. I ended up describing what we know so far about clinical features, evolution of diagnostic criteria and synthesized some recent guidelines.Classification of Pain



Classification of PainTehran University of Medical Sciences
Ėý
This document discusses classifications of pain. It defines pain according to several organizations and researchers. It notes the historical understanding of pain from Greek, Latin, and early philosophers' perspectives. It then describes types of pain based on speed of onset and duration, including experimental, transient, acute, and chronic pain. It also discusses types based on stimulation level, including somatic and visceral pain. The document outlines specific pains such as headaches, toothaches, and trigeminal neuralgia. It concludes by defining abnormal pains including hyperalgesia, allodynia, hyperpathia, and phantom limb pain.Pain pathways



Pain pathwaysMeghana Devulapalli
Ėý
Pain is the common symptom in many chronic conditions such as cancers, neuropathies, and chronic disease. It is also experienced in trauma varying from mild to severe based on the location and degree of trauma. This presentation is a brief outline on types of pain, classification of pain, pain pathways and management of painThe Physiology Of Pain



The Physiology Of PainHunyady
Ėý
Understanding the pain pathway is the first step to effective pain management in veterinary patients.PHYSIOLOGY OF PAIN SENSATION 



PHYSIOLOGY OF PAIN SENSATION Dr Nilesh Kate
Ėý
Dr. Nilesh Kate gives a lecture on pain physiology covering definitions of pain, types of pain like fast and slow pain transmitted by different nerve fibers, varieties of pain including acute, chronic, cutaneous, deep somatic, and visceral pain. Referred pain and its mechanisms like convergence and dermatomal theories are explained. The pathways of pain from transduction to transmission, perception, and modulation in the central nervous system are outlined.Ppt. pain



Ppt. painNursing Path
Ėý
This document discusses pain in several sections:
1. It defines pain and its subjective nature. Pain is the most common reason people seek medical care and acts as a protective mechanism.
2. It describes pain transmission and the gate control theory of pain. Nociceptors transmit pain impulses and can be modulated by other stimuli.
3. It categorizes acute, chronic, and cancer-related pain and discusses factors influencing individual pain responses. Non-pharmacological and pharmacological pain management strategies are also outlined.Biofilm



BiofilmSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document provides an overview of biofilms and dental plaque. It defines biofilms and dental plaque, describes the structure and composition of dental plaque biofilms. Key points include that dental plaque biofilms are composed of bacteria embedded in an extracellular matrix, form rapidly on teeth, and contribute to dental caries and periodontal disease. The document also summarizes the history of biofilm research and the multistep process of biofilm formation, including initial bacterial adhesion and attachment to the acquired pellicle coating teeth.Alveolar bone



Alveolar boneSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Alveolar bone forms tooth sockets and provides attachment for the periodontal ligament. It is composed of outer cortical and inner cancellous bone. Osteoblasts form bone matrix containing collagen fibers and hydroxyapatite crystals. Osteoclasts resorb bone. Bone is remodeled through the balanced actions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, regulated by hormones and growth factors.Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF/ Sulcular Fluid)



Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF/ Sulcular Fluid)Sk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document provides an overview of gingival crevicular fluid (GCF). It discusses the history and pioneering researchers in the field. J. Waerhaug in 1950 focused on the anatomy of the gingival sulcus and its transformation during periodontitis. GCF forms via two mechanisms - increased permeability of blood vessels or as an inflammatory exudate. The document outlines the composition of GCF, including cells, electrolytes, proteins, and metabolic products. Finally, it discusses the clinical significance of GCF and how certain components can serve as diagnostic markers for periodontal disease.Carbohydrate: Chemistry & Function



Carbohydrate: Chemistry & FunctionSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document discusses the chemistry and functions of carbohydrates. It defines carbohydrates as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones and classifies them into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. The document discusses isomerism, mutarotation, epimers, and the reactions of monosaccharides. It describes the roles of carbohydrates as an energy source, precursor for other biomolecules, and structural component in cells. Key monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose and their importance are highlighted.Faulty radiograph



Faulty radiographSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Good quality radiographs should have optimum density and contrast, minimal distortion, and sharp borders and details. Faulty radiographs can result from errors in processing, exposure factors, or film defects. The most common causes of faulty radiographs are light or dark images, insufficient contrast, film fog, dark or light spots, yellow or brown stains, blurring, partial images, dimensional changes, and scratches.Dry socket



Dry socketSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Dry socket, also known as alveolar osteitis, is a common postoperative complication following tooth extraction where the blood clot in the extraction socket becomes dislodged, causing severe pain that increases 1-3 days after the procedure. Symptoms include pain in and around the extraction site and bad breath. Treatment focuses on cleaning out the socket and using medicated dressings to rapidly relieve pain.Developmental anomalies of jaws



Developmental anomalies of jawsSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
1) Micrognathia is an underdeveloped jaw, giving the appearance of a small bird-like face. It can be true micrognathia or apparent micrognathia.
2) Agnathia is the absence of the maxilla or mandible. In the maxilla, the maxillary process or premaxilla may be absent. In the mandible, the ramus or condyle may be missing.
3) Developmental anomalies of the jaws include micrognathia, agnathia, macrognathia, facial hemihypertrophy, and facial hemiatrophy. Surgical correction may be used as treatment.Trigeminal neuralgia



Trigeminal neuralgiaSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Trigeminal neuralgia is a sudden, severe, stabbing pain that affects one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is usually idiopathic but can be caused by injury to the nerve root. Common causes include dental issues, infections, multiple sclerosis, tumors, and vascular abnormalities. The pain is unilateral, intermittent and triggered by light touch to specific points on the face. It typically affects those in their 50s-60s and is more common in women and on the right side of the face. Diagnosis involves identifying trigger points that induce the sharp, shock-like pain.Principles of tooth extraction



Principles of tooth extractionSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
The document outlines principles of tooth extraction using forceps or elevators. Extraction with forceps aims to expand the bony socket and leverage the tooth out with minimal trauma. Extraction with elevators uses lever, wedge, and wheel and axle principles to force the tooth from its socket along the path of least resistance. The elevator acts as a lever, with the fulcrum located between the effort applied and load resisted to gain mechanical advantage.Mta presentation



Mta presentationSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document discusses mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), including its composition, properties, mechanisms of action, and clinical applications. MTA is comprised primarily of Portland cement and bismuth oxide for radiopacity. It has an alkaline pH, is biocompatible, promotes hard tissue formation, and provides a good seal. The document outlines MTA's uses for pulp capping, apical plugs, root-end fillings, repair of root/furcal perforations and resorptive defects, apexification, and apexogenesis.Management of patient with anticoagulant therapy



Management of patient with anticoagulant therapySk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document discusses the management of patients undergoing dental procedures who are taking anticoagulant medications. It notes that anticoagulants prevent blood clotting by suppressing clotting factors. For patients taking warfarin, the INR should be monitored and lowered to 1.5 times normal range prior to procedures to reduce bleeding risk if deemed safe by a physician. Heparin can be stopped 6 hours before surgery and restarted once clotting occurs. Post-operative care includes use of antifibrinolytics and penicillin to prevent excess bleeding and diet of cool liquids for several days.Corticosteroid



CorticosteroidSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
The document discusses hormones produced by the adrenal cortex called corticosteroids, which include mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. The cortex is divided into three regions: the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The document then lists various medical conditions and diseases that corticosteroids can be used for in areas like allergy/respiratory medicine, dermatology, gastroenterology, hematology, and oral medicine/surgery. Contraindications for corticosteroid use include peptic ulcer, diabetes, hypertension, epilepsy, and various infections.Complete Denture on Implant



Complete Denture on ImplantSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Implants can provide support and retention for fixed or removable prostheses. There are various types of implants classified based on location and surgical exposure. Osseointegration is the key mechanism for implant integration with bone. Implants are indicated for fully and partially edentulous patients to improve function, aesthetics and quality of life over conventional dentures. Treatment options include implant overdentures, fixed bridges and single tooth implants. Masticatory performance is improved with implant supported or retained dentures compared to conventional dentures.Syncope



SyncopeSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Syncope is defined as a sudden, transient loss of consciousness caused by a temporary decrease in blood flow to the brain. The pathophysiology involves increased catecholamines during stress or pain, which causes blood vessels to dilate in the muscles and pool blood in the periphery. This decreases venous return to the heart and cardiac output, lowering blood pressure and cerebral blood flow. Compensatory mechanisms attempt to maintain brain blood flow but can fail, resulting in reflex bradycardia, further drops in cardiac output and cerebral ischemia, causing loss of consciousness. Prevention focuses on reducing stress, maintaining proper temperature and positioning, while treatment involves stopping any stimuli, loosening clothes, placing the patient head-low with legs elevated, and administeringMore Related Content
Viewers also liked (8)
Fibromyalgia powerpoint completed



Fibromyalgia powerpoint completedLaura Dunn
Ėý
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread muscle pain, tenderness, and stiffness. It predominantly affects women between 25-55 years old. Common symptoms include fatigue, headaches, sleep disturbances, and abnormal pain sensation. While the cause is unknown, genes and physical trauma may play a role. Treatments include exercise, acupuncture, massage, medications, and psychotherapy to manage pain and fatigue.Fibromyalgia



Fibromyalgiapunita85
Ėý
Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, stiffness, and tender points. It predominantly affects women and prevalence increases with age. The diagnosis is based on a history of widespread pain for at least 3 months and pain in 11 of 18 tender points. While the cause is unknown, it involves central sensitization and neuroendocrine abnormalities. Treatment includes medications, exercise, stress management, CBT, and alternative therapies. The ACR is proposing new diagnostic criteria incorporating symptoms like fatigue and cognitive problems in place of tender points.Updates in Fibromyalgia: Diagnosis and Management



Updates in Fibromyalgia: Diagnosis and ManagementSidney Erwin Manahan
Ėý
I was asked to present something on Fibromyalgia during a Pain Summit. I ended up describing what we know so far about clinical features, evolution of diagnostic criteria and synthesized some recent guidelines.Classification of Pain



Classification of PainTehran University of Medical Sciences
Ėý
This document discusses classifications of pain. It defines pain according to several organizations and researchers. It notes the historical understanding of pain from Greek, Latin, and early philosophers' perspectives. It then describes types of pain based on speed of onset and duration, including experimental, transient, acute, and chronic pain. It also discusses types based on stimulation level, including somatic and visceral pain. The document outlines specific pains such as headaches, toothaches, and trigeminal neuralgia. It concludes by defining abnormal pains including hyperalgesia, allodynia, hyperpathia, and phantom limb pain.Pain pathways



Pain pathwaysMeghana Devulapalli
Ėý
Pain is the common symptom in many chronic conditions such as cancers, neuropathies, and chronic disease. It is also experienced in trauma varying from mild to severe based on the location and degree of trauma. This presentation is a brief outline on types of pain, classification of pain, pain pathways and management of painThe Physiology Of Pain



The Physiology Of PainHunyady
Ėý
Understanding the pain pathway is the first step to effective pain management in veterinary patients.PHYSIOLOGY OF PAIN SENSATION 



PHYSIOLOGY OF PAIN SENSATION Dr Nilesh Kate
Ėý
Dr. Nilesh Kate gives a lecture on pain physiology covering definitions of pain, types of pain like fast and slow pain transmitted by different nerve fibers, varieties of pain including acute, chronic, cutaneous, deep somatic, and visceral pain. Referred pain and its mechanisms like convergence and dermatomal theories are explained. The pathways of pain from transduction to transmission, perception, and modulation in the central nervous system are outlined.Ppt. pain



Ppt. painNursing Path
Ėý
This document discusses pain in several sections:
1. It defines pain and its subjective nature. Pain is the most common reason people seek medical care and acts as a protective mechanism.
2. It describes pain transmission and the gate control theory of pain. Nociceptors transmit pain impulses and can be modulated by other stimuli.
3. It categorizes acute, chronic, and cancer-related pain and discusses factors influencing individual pain responses. Non-pharmacological and pharmacological pain management strategies are also outlined.More from Sk Aziz Ikbal (20)
Biofilm



BiofilmSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document provides an overview of biofilms and dental plaque. It defines biofilms and dental plaque, describes the structure and composition of dental plaque biofilms. Key points include that dental plaque biofilms are composed of bacteria embedded in an extracellular matrix, form rapidly on teeth, and contribute to dental caries and periodontal disease. The document also summarizes the history of biofilm research and the multistep process of biofilm formation, including initial bacterial adhesion and attachment to the acquired pellicle coating teeth.Alveolar bone



Alveolar boneSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Alveolar bone forms tooth sockets and provides attachment for the periodontal ligament. It is composed of outer cortical and inner cancellous bone. Osteoblasts form bone matrix containing collagen fibers and hydroxyapatite crystals. Osteoclasts resorb bone. Bone is remodeled through the balanced actions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, regulated by hormones and growth factors.Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF/ Sulcular Fluid)



Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF/ Sulcular Fluid)Sk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document provides an overview of gingival crevicular fluid (GCF). It discusses the history and pioneering researchers in the field. J. Waerhaug in 1950 focused on the anatomy of the gingival sulcus and its transformation during periodontitis. GCF forms via two mechanisms - increased permeability of blood vessels or as an inflammatory exudate. The document outlines the composition of GCF, including cells, electrolytes, proteins, and metabolic products. Finally, it discusses the clinical significance of GCF and how certain components can serve as diagnostic markers for periodontal disease.Carbohydrate: Chemistry & Function



Carbohydrate: Chemistry & FunctionSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document discusses the chemistry and functions of carbohydrates. It defines carbohydrates as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones and classifies them into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. The document discusses isomerism, mutarotation, epimers, and the reactions of monosaccharides. It describes the roles of carbohydrates as an energy source, precursor for other biomolecules, and structural component in cells. Key monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose and their importance are highlighted.Faulty radiograph



Faulty radiographSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Good quality radiographs should have optimum density and contrast, minimal distortion, and sharp borders and details. Faulty radiographs can result from errors in processing, exposure factors, or film defects. The most common causes of faulty radiographs are light or dark images, insufficient contrast, film fog, dark or light spots, yellow or brown stains, blurring, partial images, dimensional changes, and scratches.Dry socket



Dry socketSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Dry socket, also known as alveolar osteitis, is a common postoperative complication following tooth extraction where the blood clot in the extraction socket becomes dislodged, causing severe pain that increases 1-3 days after the procedure. Symptoms include pain in and around the extraction site and bad breath. Treatment focuses on cleaning out the socket and using medicated dressings to rapidly relieve pain.Developmental anomalies of jaws



Developmental anomalies of jawsSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
1) Micrognathia is an underdeveloped jaw, giving the appearance of a small bird-like face. It can be true micrognathia or apparent micrognathia.
2) Agnathia is the absence of the maxilla or mandible. In the maxilla, the maxillary process or premaxilla may be absent. In the mandible, the ramus or condyle may be missing.
3) Developmental anomalies of the jaws include micrognathia, agnathia, macrognathia, facial hemihypertrophy, and facial hemiatrophy. Surgical correction may be used as treatment.Trigeminal neuralgia



Trigeminal neuralgiaSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Trigeminal neuralgia is a sudden, severe, stabbing pain that affects one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is usually idiopathic but can be caused by injury to the nerve root. Common causes include dental issues, infections, multiple sclerosis, tumors, and vascular abnormalities. The pain is unilateral, intermittent and triggered by light touch to specific points on the face. It typically affects those in their 50s-60s and is more common in women and on the right side of the face. Diagnosis involves identifying trigger points that induce the sharp, shock-like pain.Principles of tooth extraction



Principles of tooth extractionSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
The document outlines principles of tooth extraction using forceps or elevators. Extraction with forceps aims to expand the bony socket and leverage the tooth out with minimal trauma. Extraction with elevators uses lever, wedge, and wheel and axle principles to force the tooth from its socket along the path of least resistance. The elevator acts as a lever, with the fulcrum located between the effort applied and load resisted to gain mechanical advantage.Mta presentation



Mta presentationSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document discusses mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), including its composition, properties, mechanisms of action, and clinical applications. MTA is comprised primarily of Portland cement and bismuth oxide for radiopacity. It has an alkaline pH, is biocompatible, promotes hard tissue formation, and provides a good seal. The document outlines MTA's uses for pulp capping, apical plugs, root-end fillings, repair of root/furcal perforations and resorptive defects, apexification, and apexogenesis.Management of patient with anticoagulant therapy



Management of patient with anticoagulant therapySk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document discusses the management of patients undergoing dental procedures who are taking anticoagulant medications. It notes that anticoagulants prevent blood clotting by suppressing clotting factors. For patients taking warfarin, the INR should be monitored and lowered to 1.5 times normal range prior to procedures to reduce bleeding risk if deemed safe by a physician. Heparin can be stopped 6 hours before surgery and restarted once clotting occurs. Post-operative care includes use of antifibrinolytics and penicillin to prevent excess bleeding and diet of cool liquids for several days.Corticosteroid



CorticosteroidSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
The document discusses hormones produced by the adrenal cortex called corticosteroids, which include mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. The cortex is divided into three regions: the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The document then lists various medical conditions and diseases that corticosteroids can be used for in areas like allergy/respiratory medicine, dermatology, gastroenterology, hematology, and oral medicine/surgery. Contraindications for corticosteroid use include peptic ulcer, diabetes, hypertension, epilepsy, and various infections.Complete Denture on Implant



Complete Denture on ImplantSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Implants can provide support and retention for fixed or removable prostheses. There are various types of implants classified based on location and surgical exposure. Osseointegration is the key mechanism for implant integration with bone. Implants are indicated for fully and partially edentulous patients to improve function, aesthetics and quality of life over conventional dentures. Treatment options include implant overdentures, fixed bridges and single tooth implants. Masticatory performance is improved with implant supported or retained dentures compared to conventional dentures.Syncope



SyncopeSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Syncope is defined as a sudden, transient loss of consciousness caused by a temporary decrease in blood flow to the brain. The pathophysiology involves increased catecholamines during stress or pain, which causes blood vessels to dilate in the muscles and pool blood in the periphery. This decreases venous return to the heart and cardiac output, lowering blood pressure and cerebral blood flow. Compensatory mechanisms attempt to maintain brain blood flow but can fail, resulting in reflex bradycardia, further drops in cardiac output and cerebral ischemia, causing loss of consciousness. Prevention focuses on reducing stress, maintaining proper temperature and positioning, while treatment involves stopping any stimuli, loosening clothes, placing the patient head-low with legs elevated, and administeringPhonetics



PhoneticsSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
1. Phonetics refers to the sounds of speech and their production. Normal speech relies on the proper functioning of the lungs, vocal cords, oral cavity, and brain.
2. Consonant sounds are important for dentistry and can be classified based on their place of articulation. Sounds like S, T, and D involve the tongue and hard palate, while sounds like TH use the tongue and teeth.
3. Several aspects of denture design can affect speech, such as denture thickness, the vertical dimension of occlusion, and the positioning of teeth. For example, teeth that are too far back can cause difficulties producing F and V sounds. Phonetics is useful for evaluating denture fitCompomer



CompomerSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
Compomers, also known as polyacid-modified composite resins (PAMCRs), combine properties of glass ionomer cements (GICs) and composites. They set through both light-activated polymerization and a slower acid-base reaction between carboxyl groups and glass filler ions. This gives compomers fluoride release capabilities from the glass ionomer component and durability from the composite resin component. Compomers are easy to use, esthetic materials suitable for various restorative applications like sealants, liners/bases, and class III/V restorations. However, they have less fluoride release than GICs and less strength than composites.Cleft lip & cleft palate



Cleft lip & cleft palateSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
The document provides information on cleft lip and cleft palate including definitions, incidence rates, development, classifications, problems associated, and treatment protocols. It defines cleft lip as an opening in the upper lip and cleft palate as an opening in the roof of the mouth. Treatment is a multidisciplinary approach involving surgery to repair the cleft, orthodontics to align teeth and jaws, and speech therapy. Management occurs over many years from infancy through adulthood to address dental, esthetic, speech and other issues.Residual Ridge Resorption



Residual Ridge ResorptionSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
This document discusses residual ridge resorption (RRR), which is the ongoing loss of jawbone that occurs after tooth extraction. It begins with definitions and an overview of the extraction healing process. It then covers the basic bone structure, cells involved in bone remodeling, and the mechanisms of bone resorption. The pathology, pathophysiology, and pathogenesis of RRR are explained. Changes to the maxilla and mandible due to RRR are described. The document lists anatomical, metabolic, functional, and prosthetic factors that contribute to RRR and discusses its epidemiology and etiology.Comparative study of removable & fixed orthodontic appliance



Comparative study of removable & fixed orthodontic applianceSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
The document discusses removable and fixed orthodontic appliances. Removable appliances can tip teeth but cannot perform complex movements like fixed appliances. Removable appliances are easier to construct and manage, require less chair time, and allow for oral hygiene. However, they rely more on patient compliance and cannot move teeth as precisely as fixed appliances. While removable appliances can address mild to moderate malocclusions, fixed appliances offer better control and are needed for more complicated cases.Dentin bonding agents



Dentin bonding agentsSk Aziz Ikbal
Ėý
The document discusses the history and generations of dentin bonding agents. It describes the challenges of bonding to dentin due to its composition and structure. Early bonding agents bonded weakly to the smear layer rather than dentin. Current bonding agents condition and prime the dentin surface to allow resin infiltration and strong bonding. They are classified based on their treatment of the smear layer and number of clinical steps.Recently uploaded (20)
Regulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdf



Regulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdfMedicoseAcademics
Ėý
Title: Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption â A Comprehensive Overview
Description:
This lecture provides a detailed and structured explanation of the mechanisms regulating tubular reabsorption in the kidneys. It explores how different physiological and hormonal factors influence glomerular filtration and reabsorption rates, ensuring fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
ð Who Should Read This?
This presentation is designed for:
âïļ Medical Students (MBBS, BDS, Nursing, Allied Health Sciences) preparing for physiology exams.
âïļ Medical Educators & Professors looking for structured teaching material.
âïļ Healthcare Professionals (doctors, nephrologists, and physiologists) seeking a refresher on renal physiology.
âïļ Postgraduate Students & Researchers in the field of medical sciences and physiology.
ð What Youâll Learn:
â
Local Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
âïļ Glomerulo-Tubular Balance â its mechanism and clinical significance
âïļ Net reabsorptive forces affecting peritubular capillaries
âïļ Role of peritubular hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressures
â
Hormonal Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
âïļ Effects of Aldosterone, Angiotensin II, ADH, and Natriuretic Peptides
âïļ Clinical conditions like Addisonâs disease & Conn Syndrome
âïļ Mechanisms of pressure natriuresis and diuresis
â
Nervous System Regulation
âïļ Sympathetic Nervous System activation and its effects on sodium reabsorption
ðĐš Clinical Correlations & Case Discussions
âïļ How renal regulation is altered in hypertension, hypotension, and proteinuria
âïļ Comparison of Glomerulo-Tubular Balance vs. Tubulo-Glomerular Feedback
This presentation provides detailed diagrams, flowcharts, and calculations to enhance understanding and retention. Whether you are studying, teaching, or practicing medicine, this lecture will serve as a valuable resource for mastering renal physiology.
ðĒ Keywords for Easy Search:
#Physiology #RenalPhysiology #TubularReabsorption #GlomeruloTubularBalance #HormonalRegulation #MedicalEducation #NephrologyNeurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptx



Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptxdribnibrahem164
Ėý
neurological complications of infective endocarditisDigestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing Students



Digestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing StudentsViresh Mahajani
Ėý
This educational PowerPoint presentation is designed to equip GNM students with a solid understanding of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. It explores the anatomical structures, physiological processes, and clinical significance of these vital organs. Key topics include:
Liver functions: detoxification, metabolism, and bile synthesis.
Gallbladder: bile storage and release.
Pancreas: exocrine and endocrine functions, including digestive enzyme and hormone production. This presentation is ideal for GNM students seeking a clear and concise review of these important digestive system components."E Book Daniya Sanal.pdf#healthy books.com



E Book Daniya Sanal.pdf#healthy books.comDaniyaSanal
Ėý
good health for good life good heart for safe and secure life..the good quality of life will makes good and #haelthy vibes...FAO's Support Rabies Control in Bali_Jul22.pptx



FAO's Support Rabies Control in Bali_Jul22.pptxWahid Husein
Ėý
What is FAO doing to support rabies control programmes in Bali, Indonesia, using One Health approach with mass dog vaccination and integrated bite case management as main strategiesRabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptx



Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptxWahid Husein
Ėý
A decade of rabies control programmes in Bali with support from FAO ECTAD Indonesia with Mass Dog Vaccination, Integrated Bite Case Management, Dog Population Management, and Risk Communication as the backbone of the programmesAdvancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý
Co-Chairs and Presenters, Gerald Appel, MD, and Dana V. Rizk, MD, discuss kidney disease in this CME activity titled âAdvancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Pathway Therapies.â For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/48UHvVM. CME credit will be available until February 25, 2026.BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptx



BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptxdrnidhimnd
Ėý
The shoulder complex acts as in coordinated fashion to provide the smoothest and greatest range of motion possible of the upper limb.
Combined motion of GH and ST joint of shoulder complex helps in:
Distribution of motion between other two joints.
Maintenance of glenoid fossa in optimal position.
Maintenance of good length tension
Although some amount of glenohumeral motion may occur while the other shoulder articulations remain stabilized, movement of the humerus more commonly involves some movement at all three shoulder joints.
Solubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...



Solubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...KHUSHAL CHAVAN
Ėý
This presentation provides an in-depth understanding of solubilization and its critical role in pharmaceutical formulations. It covers:
Definition & Mechanisms of Solubilization
Role of surfactants, micelles, and bile salts in drug solubility
Factors affecting solubilization (pH, polarity, particle size, temperature, etc.)
Methods to enhance drug solubility (Buffers, Co-solvents, Surfactants, Complexation, Solid Dispersions)
Advanced approaches (Polymorphism, Salt Formation, Co-crystallization, Prodrugs)
This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical scientists, formulation experts, regulatory professionals, and students interested in improving drug solubility and bioavailability.Research Problems - Nursing Research....



Research Problems - Nursing Research....Dr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
Ėý
Research Problems - Nursing Researchphysiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ØģØĪاŲ.pptx



physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ØģØĪاŲ.pptxamralmohammady27
Ėý
ŲŲ ØđŲØŊŲ ŲاØĻ ØŠŲØĻ ØĢŲ ؊اØĻŲØŠ ŲاŲ
power point show
ŲŲŲŲØđŲ ØŽØŊا ŲŲ Ų
ØąØ§ØŽØđØĐ ØģØąŲØđØĐ ŲŲŲØĐ Ø§ŲاŲ
ØŠØاŲ
ŲاŲŲŲ ŲŲØŊØą ŲØđŲ
Ų Øا؎ØĐ ŲØđŲ
ŲŲا
ŲØīŲØąØ§ ŲŲØŊŲØŠŲØąØĐ ŲŲاŲ ØđŲŲ ØŠØŽŲ
ŲØđØĐ ØĢØģØĶŲØĐ Ø§ŲØĻŲŲCharacteristics and Criteria of Good Research.pptx



Characteristics and Criteria of Good Research.pptxDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
Ėý
Characteristics and Criteria of Good ResearchCreatineâs Untold Story and How 30-Year-Old Lessons Can Shape the Future



Creatineâs Untold Story and How 30-Year-Old Lessons Can Shape the FutureSteve Jennings
Ėý
Creatine burst into the public consciousness in 1992 when an investigative reporter inside the Olympic Village in Barcelona caught wind of British athletes using a product called Ergomax C150. This led to an explosion of interest in â and questions about â the ingredient after high-profile British athletes won multiple gold medals.
I developed Ergomax C150, working closely with the late and great Dr. Roger Harris (1944 â 2024), and Prof. Erik Hultman (1925 â 2011), the pioneering scientists behind the landmark studies of creatine and athletic performance in the early 1990s.
Thirty years on, these are the slides I used at the Sports & Active Nutrition Summit 2025 to share the story, the lessons from that time, and how and why creatine will play a pivotal role in tomorrowâs high-growth active nutrition and healthspan categories.PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...



PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...ABHAY INSTITUTION
Ėý
Personality theory is a collection of ideas that explain how a person's personality develops and how it affects their behavior. It also seeks to understand how people react to situations, and how their personality impacts their relationships.
Key aspects of personality theory
Personality traits: The characteristics that make up a person's personality.
Personality development: How a person's personality develops over time.
Personality disorders: How personality theories can be used to study personality disorders.
Personality and environment: How a person's personality is influenced by their environment. legal Rights of individual, children and women.pptx



legal Rights of individual, children and women.pptxRishika Rawat
Ėý
A legal right is a claim or entitlement that is recognized and protected by the law. It can also refer to the power or privilege that the law grants to a person. Human rights include the right to life and liberty, freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to work and educationIMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINE



IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINERelianceNwosu
Ėý
This presentation emphasizes the role of immunodiagnostics and Immunotherapy. The influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcome



The influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcomeLokesh Kumar Sharma
Ėý
this content related to birth companionship, role of birth companion in care of mother and neonatal Increased Clinical Trial Complexity | Dr. Ulana Rey | MindLumina



Increased Clinical Trial Complexity | Dr. Ulana Rey | MindLuminaUlana Rey PharmD
Ėý
Increased Clinical Trial Complexity. By Ulana Rey PharmD for MindLumina. Dr. Ulana Rey discusses how clinical trial complexityâendpoints, procedures, eligibility criteria, countriesâhas increased over a 20-year period.Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý


