parkinson disease -defination ,etiology,clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment.
- 1. PARKINSON DISEASE PRESENTED BY : R.ANUSHA PHARM D 2ND YEAR GEETHANJALI COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
- 2. INTRODUCTION âĒ Parkinson's disease is a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves. âĒ In the early stages of Parkinson's disease, your face may show little or no expression. Your arms may not swing when you walk. Your speech may become soft or slurred. Parkinson's disease symptoms worsen as your condition progresses over time. âĒ Although Parkinson's disease can't be cured, medicines might significantly improve your symptoms.
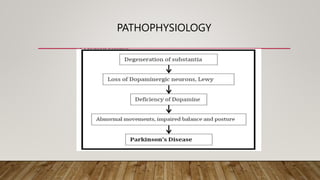
- 3. CAUSES âĒ Many of the symptoms of Parkinson's are due to a loss of neurons that produce a chemical messenger in your brain called dopamine. When dopamine levels decrease, it causes irregular brain activity, leading to problems with movement and other symptoms of Parkinson's disease. âĒ The cause of Parkinson's disease is unknown, but several factors appear to play a role, including: âĒ Genes- These are uncommon except in rare cases with many family members affected by Parkinson's disease.
- 4. Environmental triggers. Exposure to certain toxins or environmental factors. The presence of Lewy bodies. Clumps of specific substances within brain cells are microscopic markers of Parkinson's disease. These are called Lewy bodies. Alpha-synuclein found within Lewy bodies. Although many substances are found within Lewy bodies, scientists believe that an important one is the natural and widespread protein called alpha-synuclein, also called a- synuclein.
- 5. RISK FACTORS âĒ Risk factors for Parkinson's disease include: âĒ Age:People usually develop the disease around age 60 or older. âĒ Heredity. Having a close relative with Parkinson's disease increases the chances that you'll develop the disease. âĒ Sex. Men are more likely to develop Parkinson's disease than are women. âĒ Exposure to toxins. Ongoing exposure to herbicides and pesticides may slightly increase your risk of Parkinson's disease.
- 7. SYMPTOMS âĒ Parkinson's disease symptoms can be different for everyone. Early symptoms may be mild and go unnoticed. Symptoms often begin on one side of the body and usually remain worse on that side, even after symptoms begin to affect the limbs on both sides. âĒ Parkinson's symptoms may include: âĒ Tremor. Rhythmic shaking, called tremor, usually begins in a limb, often your hand or fingers. You may rub your thumb and forefinger back and forth. This is known as a pill-rolling tremor. Your hand may tremble when it's at rest. The shaking may decrease when you are performing tasks. âĒ Slowed movement, known as bradykinesia. Over time, Parkinson's disease may slow your movement, making simple tasks difficult and time-consuming. Your steps may become shorter when you walk. It may be difficult to get out of a chair. You may drag or shuffle your feet as you try to walk. âĒ Rigid muscles. Muscle stiffness may occur in any part of your body. The stiff muscles can be painful and limit your range of motion.
- 8. âĒ Impaired posture and balance. Your posture may become stooped. Or you may fall or have balance problems as a result of Parkinson's disease. âĒ Loss of automatic movements. You may have a decreased ability to perform unconscious movements, including blinking, smiling or swinging your arms when you walk. âĒ Speech changes. You may speak softly or quickly, slur, or hesitate before talking. Your speech may be more of a monotone rather than have the usual speech patterns.
- 9. DIAGNOSIS âĒ Diagnosing Parkinson's disease is primarily clinical, based on the patient's history and neurological examination. Key diagnostic criteria include: âĒ Presence of two or more cardinal motor symptoms (tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability). âĒ Response to dopaminergic medications (e.g., Levodopa). âĒ Imaging tests such as MRI or PET scans
- 10. TREATMENT âĒ Medications 1.Levodopa: The most effective treatment. It is converted to dopamine in the brain. Often combined with Carbidopa to prevent peripheral metabolism. Mechanism of Action: Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA, is a precursor to dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is deficient in Parkinson's disease due to the loss of dopamine- producing neurons in the brain. Levodopa crosses the BBB and is converted into dopamine in the brain, thereby replenishing dopamine levels.
- 11. âĒ DOPAMINE AGONIST : mimic dopamine effect in the brain[ex : paramipexole ,ropinirole] âĒ MAO-B INHIBITORS : prevent breakdown of brain dopamine [ex : selegiline , rasagiline ] âĒ COMT INHIBITOR : prolong the effect of levodopa by inhibiting its breakdown [ex : entacapone ] âĒ ANTI CHOLINERGICS : help reduce tremor and rigidity but are less commonly used due to side effects .
- 12. âĒ Surgical Treatment âĒ Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Electrodes are implanted in specific brain areas (typically the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus) to deliver electrical impulses, modulating abnormal brain activity. DBS can significantly reduce motor symptoms and medication needs in advanced Parkinson's. âĒ Supportive Therapies âĒ Physical Therapy: Focuses on improving mobility, balance, and flexibility. âĒ Occupational Therapy: Helps patients maintain independence in daily activities. âĒ Speech Therapy: Addresses speech and swallowing difficulties.
- 13. COMPLICATIONS âĒ Thinking difficulties. You may experience cognitive problems, such as dementia, and thinking difficulties. These usually occur in the later stages of Parkinson's disease. âĒ Depression and emotional changes. You may experience depression, sometimes in the very early stages. Receiving treatment for depression can make it easier to handle the other challenges of Parkinson's disease.
- 14. âĒ Swallowing problems. You may develop difficulties with swallowing as your condition progresses. Saliva may accumulate in your mouth due to slowed swallowing, leading to drooling. âĒ Chewing and eating problems. Late-stage Parkinson's disease affects the muscles in the mouth, making chewing difficult. This can lead to choking and poor nutrition. âĒ Sleep problems and sleep disorders. People with Parkinson's disease often have sleep problems, including waking up frequently throughout the night, waking up early or falling asleep during the day.
- 15. PATIENT COUNSELLING âĒ Stay healthy by eating nutritious foods and not smoking. âĒ Make changes in what you eat or drink if you have swallowing problems. âĒ Use speech therapy to help you adjust to changes in your swallowing and speech. âĒ Stay active as much as possible when you feel good. Do not overdo it when your energy is low. âĒ Rest as needed during the day and avoid stress.
- 16. âĒ Use physical therapy and occupational therapy to help you stay independent and reduce the risk of falls. âĒ Place handrails throughout your house to help prevent falls. Place them in bathrooms and along stairways. âĒ Use assistive devices, when needed, to make movement easier. These devices may include special eating utensils, wheelchairs, bed lifts, shower chairs, and walkers. âĒ Talk to a social worker or other counseling service to help you and your family cope with the disorder. These services can also help you get outside help, such as Meals on Wheels









![âĒ DOPAMINE AGONIST : mimic dopamine effect in the brain[ex : paramipexole
,ropinirole]
âĒ MAO-B INHIBITORS : prevent breakdown of brain dopamine [ex : selegiline ,
rasagiline ]
âĒ COMT INHIBITOR : prolong the effect of levodopa by inhibiting its breakdown [ex
: entacapone ]
âĒ ANTI CHOLINERGICS : help reduce tremor and rigidity but are less commonly
used due to side effects .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsondisease-anushafinal-240716070054-65e9369d/85/parkinson-disease-defination-etiology-clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-treatment-11-320.jpg)






