Part-2.pptx
- 2. Human resource accounting Human Resource Accounting is a term applied by the Accountancy Profession to quantify the cost and value of employees of their employing organization. Human resource accounting is accounting and recognition of expenses related to employees of the organization and involves costs related to recruitment, selection, training, hiring etc. it is the process of identifying and measuring data about Human Resources and communicating this information to the interested parties. It is an attempt to identify and report the Investments made in Human Resources of an organization that are currently not accounted for in the Conventional Accounting Practices. According to Flamholtz â âHuman resource accounting is accounting for people as an organizational resource. It involves measuring the costs incurred by business firms and other organizations to recruit, select, hire, train, and develop human assets. It also involves measuring the economic value of people to the organizations.â
- 3. Objectives of human resource accounting The objectives of Human resource accounting are as follows â âĒMeasuring cost related to the human resource of the organization. âĒEnabling management to properly plan and budget for training and other services for the human resource. âĒTo ensure proper utilization of resources is done or not. âĒIncreasing awareness and value about human resources. âĒTo proper accounting of retiring benefits and other benefits over the service period; âĒTo determine whether an organization has gained from inputs put on human resources, training, recruitment, and other facilities.
- 4. Step-1 HRA Objectives Step-2 Developing HRA Measurements Step-3 Developing HR Accounting Database Step-4 Pilot Testing the System Step-5 Implementing the Human Resource Accounting System Human resource accounting process
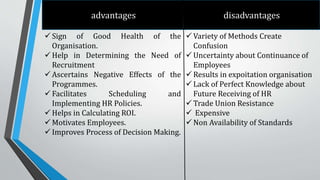
- 5. advantages disadvantages ïž Sign of Good Health of the Organisation. ïž Help in Determining the Need of Recruitment ïž Ascertains Negative Effects of the Programmes. ïž Facilitates Scheduling and Implementing HR Policies. ïž Helps in Calculating ROI. ïž Motivates Employees. ïž Improves Process of Decision Making. ïž Variety of Methods Create Confusion ïž Uncertainty about Continuance of Employees ïž Results in expoitation organisation ïž Lack of Perfect Knowledge about Future Receiving of HR ïž Trade Union Resistance ïž Expensive ïž Non Availability of Standards
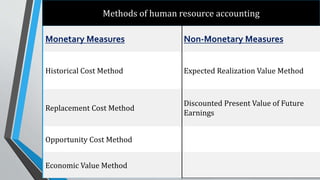
- 6. Methods of human resource accounting Monetary Measures Non-Monetary Measures Historical Cost Method Expected Realization Value Method Replacement Cost Method Discounted Present Value of Future Earnings Opportunity Cost Method Economic Value Method
- 7. Monetary Measures:- 1.Historical Cost Method:-This method was developed in 1967 by William C. Pyle. The historical cost approach means the actual cost experienced by the organization in hiring, developing, and training of the employees is capitalized over for the useful period of human resources. ïą The expenses made in all the selection, recruitment, and development of employees is recorded in written form during which human resource will provide the service. ïą The advantage of this method is it is easy to understand and implement but its disadvantage is it is hard to determine how long employees will carry on his/her job. 2.Replacement Cost Method:-The replacement cost method was first introduced by Eric, G Flamholtz. In this method, the cost of replacing employees is calculated. It is based on the assumption that it will cost the organization if the current human resource is replaced by new employees having the same talent and experience. 3.Opportunity Cost Method:-The opportunity cost method of human resource accounting, also referred to as the competitive bidding model, assigns value to an employee based on what each department would be willing to pay him. This method envisions a fictitious situation in which a company suddenly finds labor and talent scarce and individual divisions or departments within the company must bid on existing employees.
- 8. 4.Economic Value Method:-The economic value model of human resource accounting involves estimating the total inflow of cash that will be produced by an employee over the course of his service to the company. Subtract the total cost of hiring, training, developing and paying an employee from the estimate of the cash he will generate for the company, and you have arrived at his net worth according to the economic value method of HR accounting. Non-Monetary Measures:- 1. Expected Realization Value Method:-The above methods discussed so far are based on cost consideration. Therefore these methods may provide information for record purpose but do not reflect the true value of human assets. As against these methods. Expected realizable value is based on the assumption. And this is true also. That there is no direct relationship between cost incurred on an individual and his value to organization can be defined as the present worth of the set of future services that he is expected to provide during the period he remains in the organization. 2. Discounted Present Value of Future Earnings:-This Model of human resource accounting was developed by Lev and Schwartz in the year 1971 and involves determining the value of human resources as per the present value of estimated future earnings discounted by the rate of return on Investment (Cost of Capital). The assumptions in this method are realistic and scientific. The method has practical applicability when availability of quantifiable and analyzable data is concerned, but this model is unable to give any method to record the value of human resources in the Books of Accounts.
- 9. According to this model, the value of human capital embodied in a person who is âyâ years old, is the present value of his/her future earnings from employment and can be calculated by using the following formula â E (Vy) = Py (t + 1) I (T)/(I + R) Where, E (Vy) = expected value of a âyâ year old personâs human capital T = the personâs retirement age Py (t) = probability of the person leaving the organization I (t) = expected earnings of the person in period I r = discount rate t-y
- 10. Thank you