Particulate seminar
- 1. Airborne Particulate Particle Size: Statistical Description Initial Physiological Deposition Site Airborne Sampling Simulation & Bias Sampling Devices PSP and Lung Effects Michael A. Jayjock, Ph.D. CIH 1
- 3. Site of Deposition Depends on Aerodynamic Particle Size or Aerodynamic Diameter (AD) ŌĆó AD is determined by the settling velocity of the particle in normal air. ŌĆó Any Particle with aerodynamic diameter of X falls at the same speed as a UNIT DENSITY SPHERE with X diameter. 3
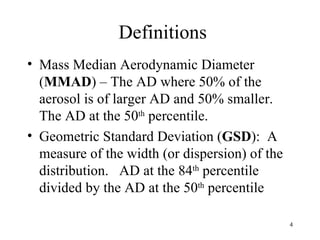
- 4. Definitions ŌĆó Mass Median Aerodynamic Diameter (MMAD) ŌĆō The AD where 50% of the aerosol is of larger AD and 50% smaller. The AD at the 50th percentile. ŌĆó Geometric Standard Deviation (GSD): A measure of the width (or dispersion) of the distribution. AD at the 84th percentile divided by the AD at the 50th percentile 4
- 5. Example: Typical In-plant aerosol from a ŌĆ£dustyŌĆØ Plastic Powder ŌĆó MMAD = 10 microns ŌĆó GSD = 2 ŌĆó 50th percentile AD = 10 microns ŌĆó 84th percentile AD = 20 microns ŌĆó 16th percentile AD = 5 microns Compare to 50% ŌĆ£cut point for respirable particulate of 4 or 5 microns ŌĆō only about 10% of the airborne K120n is respirable 5
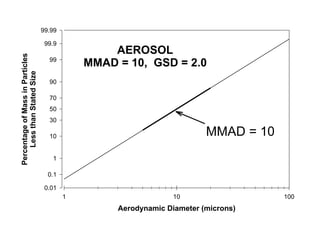
- 6. 99.99 99.9 AEROSOL Percentage of Mass in Particles 99 MMAD = 10, GSD = 2.0 Less than Stated Size 90 70 50 30 10 MMAD = 10 1 0.1 0.01 1 10 100 Aerodynamic Diameter (microns) 6
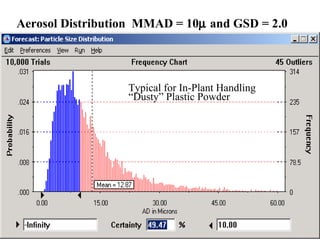
- 7. Aerosol Distribution MMAD = 10┬Ą and GSD = 2.0 Typical for In-Plant Handling ŌĆ£DustyŌĆØ Plastic Powder 7
- 8. Definitions/Classifications ŌĆó PNOC ŌĆō airborne particulate not otherwise classified ŌĆó PSP ŌĆō poorly soluble airborne particulate ŌĆó Lung Overload ŌĆō dose rate of particulate that exceeds the normal rate of clearance leading to an even lower rate (or cessation) of clearance and secondary toxicity as a result. ŌĆó Particulate with Inherent Toxicity ŌĆō particulate that when in contact with pulmonary tissue can injure that tissue irrespective of overload. 8
- 9. Initial Physiological Deposition Site 9
- 10. 10
- 11. 11
- 12. Airborne Sampling Simulation 12
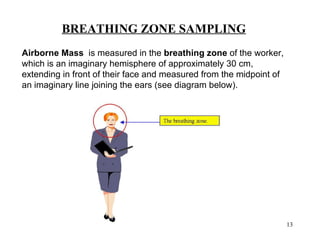
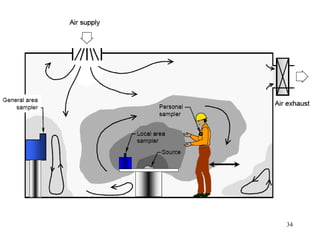
- 13. BREATHING ZONE SAMPLING Airborne Mass is measured in the breathing zone of the worker, which is an imaginary hemisphere of approximately 30 cm, extending in front of their face and measured from the midpoint of an imaginary line joining the ears (see diagram below). 13
- 14. 14
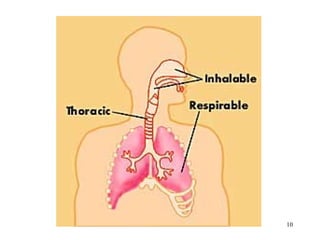
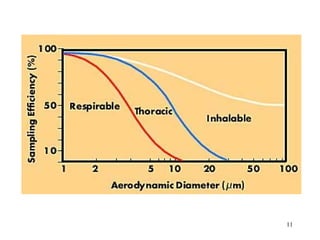
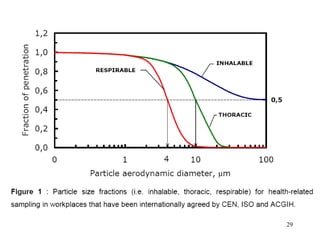
- 15. THREE MEASUREMENT/SIMULATION CLASSES OF AIRBORNE PARTICULATE DOSE/EXPOSURE ŌĆó INHALABLE: any particle that penetrates/deposits past the nose and mouth. ŌĆó THORACIC: particles that penetrate/deposit anywhere within the lung airways and the gas- exchange region ŌĆó RESPIRABLE: particles that penetrate/deposit exclusively into the gas-exchange region or pulmonary region of the deep lung. 15
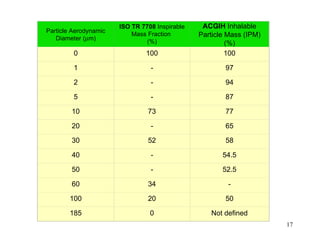
- 16. INHALABLE MASS ACGIH operational definition of the proportion of TOTAL Airborne Aerosol Mass in the breathing zone (BZ) for any aerodynamic diameter that will be Deposited anywhere in the respiratory tree including the nose and mouth. SI(d) = 50% x (1 + e-0.06d ) for 0 < d Ōēż 100┬Ąm where SI(d) = collection efficiency for particles with aerodynamic diameter d in ┬Ąm. 16
- 17. ISO TR 7708 Inspirable ACGIH Inhalable Particle Aerodynamic Mass Fraction Particle Mass (IPM) Diameter (┬Ąm) (%) (%) 0 100 100 1 - 97 2 - 94 5 - 87 10 73 77 20 - 65 30 52 58 40 - 54.5 50 - 52.5 60 34 - 100 20 50 185 0 Not defined 17
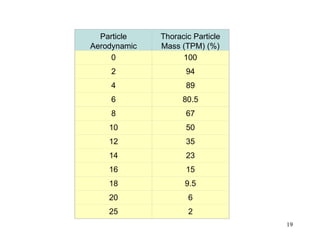
- 18. THORACIC DUST ACGIH Mathematical definition of proportion of inhalable particulate per AD size that is deposited anywhere within the lung airways and the gas- exchange region. 18
- 19. Particle Thoracic Particle Aerodynamic Mass (TPM) (%) Diameter (┬Ąm) 0 100 2 94 4 89 6 80.5 8 67 10 50 12 35 14 23 16 15 18 9.5 20 6 25 2 19
- 20. RESPIRABLE PARTICULATE MASS ACGIH operational definition for proportion of inhalable particulate per AD size class that will be deposited deposited in the gas-exchange region. 20
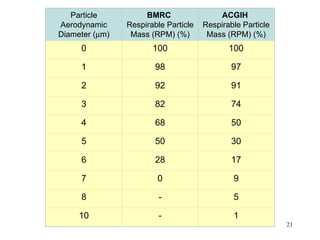
- 21. Particle BMRC ACGIH Aerodynamic Respirable Particle Respirable Particle Diameter (┬Ąm) Mass (RPM) (%) Mass (RPM) (%) 0 100 100 1 98 97 2 92 91 3 82 74 4 68 50 5 50 30 6 28 17 7 0 9 8 - 5 10 - 1 21
- 22. Sampling Devices 22
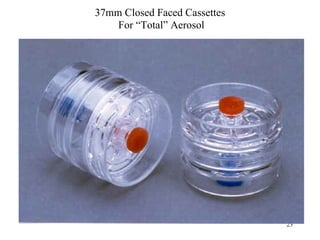
- 23. 37mm Closed Faced Cassettes For ŌĆ£TotalŌĆØ Aerosol 23
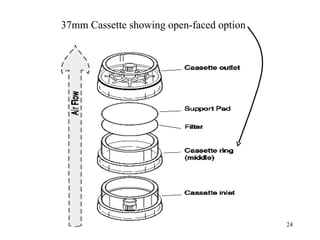
- 24. 37mm Cassette showing open-faced option 24
- 25. Inlet of an open-faced filter 25
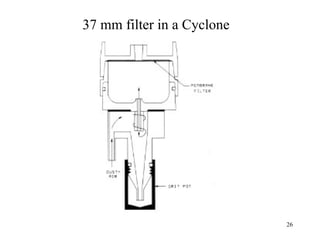
- 26. 37 mm filter in a Cyclone 26
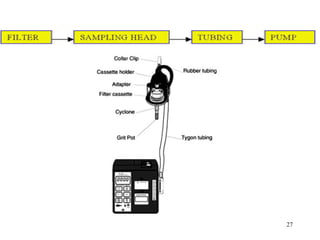
- 27. 27
- 28. Inhalable Dust Sampler 28
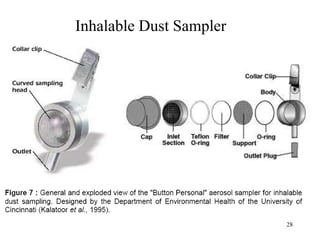
- 29. 29
- 30. 30
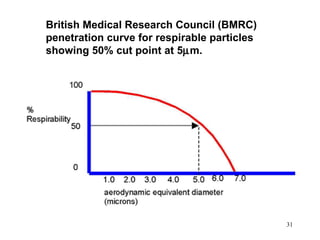
- 31. British Medical Research Council (BMRC) penetration curve for respirable particles showing 50% cut point at 5┬Ąm. 31
- 32. Sampling Bias 32
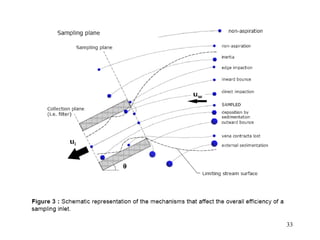
- 33. 33
- 34. 34
- 35. PSP and Lung Effects 35
- 36. PSP RESPIRABLE vs. Non-Respirable Aerosol Particulate ŌĆó NON-RESPIRABLE: Insoluble Airborne Particulate that is deposited in Upper Respiratory Track (ciliated region and above) will go to GI track and be excreted quickly. ŌĆó RESPIRABLE: Insoluble Airborne particulate that penetrates to the deep lungs (pulmonary region) has a much longer residence time in the lung; thus, chronic exposure is more subject to lung ŌĆ£over-loadŌĆØ effect. 36
- 37. Oberdorster, G: Toxicokinetics and Effects of Fibrous and Nonfibrous Particles, Inhalation Toxicology, 14: 29-56, 2002 Pulmonary Retention Kinetics and Effects of Poorly Soluble Particulate of Low Toxicity (PSP) ŌĆ£ŌĆ”if the deposition rate of the inhaled particles exceeds their mechanical clearance rateŌĆ”, the retention half-time is significantly increased, reflecting an impaired or prolonged alveolar macrophage-mediated clearance function with accumulation of lung burden.ŌĆØ 37
- 38. Oberdorster (op. cit.) ŌĆ£Morrow (1988) hypothesized ŌĆō based on a thorough evaluation of a number of long- term inhalation studies with particles in rats ŌĆō that the impairment of alveolar macrophage- mediated clearance is due to a volumetric overloading of the macrophages resulting eventually in a failure to actively move particles toward the mucociliary escalator.ŌĆØ {emphasis added} 38
- 39. Oberdorster (op. cit.) ŌĆ£He [Morrow] estimated that a phagocytized particle volume of about 6% of the normal macrophage volume signals the beginning of the impaired function, and when 60% of the normal alveolar macrophage volume is filled with phagocytized particles its clearance function will completely cease.ŌĆØ 39
- 40. Oberdorster (op. cit.) ŌĆ£Indeed, plotting the retained particle volume in lungs of rats after long-term exposure to different particle types against measured clearance rates demonstrated the correlation between clearance rate and retained dust volume convincingly, as is show in Figure 3.ŌĆØ {emphasis added} 40
- 41. Oberdorster (op. cit.) 41
- 42. What Specifically Does Morrow Say About the Data and its Implications for PNOC ŌĆō WELs ? ŌĆó ŌĆ£The results illustrate a progressive decrease in alveolar clearance rates once an excessive pulmonary burden is attained.ŌĆØ ŌĆó ŌĆ£In this context, loss of mobility represents a failure of particulate clearance to proceed, leading to increased intersitialization of particles and to the induction of a host of dysfunctional and pathologic conditions of a seemingly generic nature.ŌĆØ [emphasis added] Morrow, P.E. et al: Chronic Inhalation Study Findings as the basis for Proposing a New Occupational Dust Exposure Limit, J of Am. Coll. Tox, 10, 2, 1991 42
- 43. Morrow (op. cit.) ŌĆó ŌĆ£ŌĆ”dust overloading represents a serious, confounding complication to the toxicological assessment, one in which the intrinsic toxicity of the test material is either masked or modified by the nonspecific effects of dusts on macrophage transport.ŌĆØ ŌĆó ŌĆ£The foregoing resume of studies indicates that overloading effects on dust clearance can be expected to occur with any persistently retained dustŌĆ”ŌĆØ 43
- 44. MorrowŌĆÖs Arguments for a PNOC Respirable Mass WEL of less than 1 mg/m3 (Morrow op. cit.) ŌĆó For UNIT DENSITY Particles (1 mg/m3)(7.2m3/day)(240days/365days) = 4.7 mg/day ŌĆó Assuming a clearance half life of 200 days (k = 0.0035/day) THEN (0.0035/day) (Burden) = 4.7 mg/day ŌĆó Lung Burden = 1340 mg/1000g Lung ŌĆó Values > 1mg/g lung are associated with overload in the Rat. 44
- 45. Continuation of MorrowŌĆÖs Arguments for a PNOC Respirable Mass WEL of less than 1 mg/m3 (Morrow op. cit.) ŌĆó Breathing rate of 7.2 m3/day is NOT conservative. ŌĆó Clearance rate assumed for humans is typical but it is NOT conservative. ŌĆó Xerox CorporationŌĆÖs HHRC recommended and Xerox Corporation implemented an internal respirable PNOC limit of 0.4 mg/m3 in 1990. 45
- 46. Morrow Recommendation Modify any unit density PNOC WEL relative to the density of the material in question. For example, Portland Cement has a density of about 3.15 g/cc. Any PNOC WEL for these particles should be increased by the density of the particle; that is, the 8 hour WEL should be 3.1 times higher than the unit density WEL of 3.1 mg/m3. 46




















![Oberdorster (op. cit.)
ŌĆ£He [Morrow] estimated that a phagocytized
particle volume of about 6% of the normal
macrophage volume signals the beginning of
the impaired function, and when 60% of the
normal alveolar macrophage volume is filled
with phagocytized particles its clearance
function will completely cease.ŌĆØ
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/particulateseminar-120423074931-phpapp01/85/Particulate-seminar-39-320.jpg)


![What Specifically Does Morrow Say About the
Data and its Implications for PNOC ŌĆō WELs ?
ŌĆó ŌĆ£The results illustrate a progressive decrease in
alveolar clearance rates once an excessive
pulmonary burden is attained.ŌĆØ
ŌĆó ŌĆ£In this context, loss of mobility represents a
failure of particulate clearance to proceed,
leading to increased intersitialization of particles
and to the induction of a host of dysfunctional and
pathologic conditions of a seemingly generic
nature.ŌĆØ [emphasis added]
Morrow, P.E. et al: Chronic Inhalation Study Findings as the basis for
Proposing a New Occupational Dust Exposure Limit, J of Am. Coll. Tox,
10, 2, 1991 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/particulateseminar-120423074931-phpapp01/85/Particulate-seminar-42-320.jpg)



