Passenger load factor
- 1. Prateek Garodia PASSENGER LOAD FACTOR
- 2. What is ASK/ASM? ASM stands for Available Seat Miles Countries using kilometers as a measure of distance use ASK (Available Seat Kilometers) ASM is the number of seats available to a passenger for purchase per mile of flight It is used to measure an airline’s passenger carrying capacity 11/10/2011 2
- 3. What is ASK/ASM? It excludes seats not available for passengers due to weight of fuel or other load The higher the ASM the higher the capacity of the airline to carry more passengers This unit can be used to measure carrying capacity of an airline for a route, a region or the entire operation 11/10/2011 3
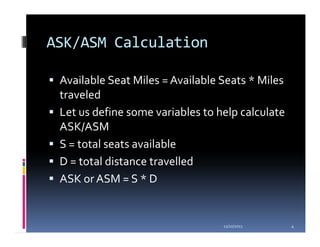
- 4. ASK/ASM Calculation Available Seat Miles = Available Seats * Miles traveled Let us define some variables to help calculate ASK/ASM S = total seats available D = total distance travelled ASK or ASM = S * D 11/10/2011 4
- 5. Example 1 An aircraft has 300 seats available for purchase. It flies for 1,000 miles. What is the ASM? S = 300 D = 1,000 ASM = 300 * 1,000 = 300,000 The airline has 300,000 available seat miles 11/10/2011 5
- 6. What is RPK/RPM? RPM stands for Revenue Passenger Miles Countries using kilometers as a measure of distance use RPK (Revenue Passenger Kilometers) A revenue passenger is one for whose transportation an air carrier receives commercial remuneration RPM is used to measure the number of revenue passengers flown for each mile 11/10/2011 6
- 7. What is RPK/RPM? In conjunction with revenue, this measurement is also used to calculate yield The difference between RPM and ASM is that ASM measures the total carrying capacity of the airline while RPM measures the number of revenue paying passengers actually carried by the airline So, RPM is really a subset of ASM Ideally RPM should always be equal to ASM 11/10/2011 7
- 8. RPK/RPM Calculation Revenue Passenger Mile = Revenue passengers flown * Miles traveled Let us define some variables to help calculate RPK/RPM P = total number of revenue generating passengers D = total distance travelled RPK or RPM = P * D 11/10/2011 8
- 9. Example 2 An airplane flies a distance of 2,962 miles. There are 130 passengers in the flight. What is the RPM? P = 130 D = 2,962 RPM = 130 * 2,962 = 385,060 In this example, the airline has 385,060 revenue passenger miles 11/10/2011 9
- 10. What is PLF? PLF is Passenger Load Factor This is a measure of capacity utilization It is used to calculate the percentage of available capacity used to carry passengers It is also used to calculate financial figures like capacity utilization required to allow the airline to break even PLF = RPM / ASM Ideally this ratio should always be 1 11/10/2011 10
- 11. Example 3 An aircraft has 23 seats in first class, 80 seats in business class and 313 seats in first class. The aircraft flew for 7,733 miles. The RPM of this flight was 2,420,429. What is the load factor? RPM = 2,420,429 ASM = (23 + 80 + 313) * 7733 = 416 * 7733 = 3,216,928 PLF = 2,420,429 / 3,216,928 = 0.7524 The load factor or capacity utilization of this aircraft for this trip is 75.24% 11/10/2011 11
- 12. Exercise 1 An airline in a year had an ASM of 45,610 million. In the same year, its RPM was 36,531 million. What was the airline’s passenger load factor in that year? 11/10/2011 12
- 13. References http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Revenue_passenger _mile http://moneyterms.co.uk/rpk-revenue- passenger-kilometres/ http://icaodata.com/Terms.aspx#RevenuePasse nger http://www.airliners.net/aviation- forums/general_aviation/read.main/3582373/ http://www.linkedin.com/groupAnswers?viewQu estionAndAnswers=&discussionID=76033155&gi d=59519&commentID=55329309&trk=view_disc &ut=1XhPa6HzrtskY1 11/10/2011 13
- 14. References http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Available_seat_miles http://moneyterms.co.uk/ask-available-seat- kilometre/ http://www.wikinvest.com/metric/Available_Seat_M iles_(ASM) http://icaodata.com/Terms.aspx#SeatKilometresAv ailable http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Passenger_load_factor http://moneyterms.co.uk/plf-passenger-load-factor/ 11/10/2011 14