Payroll Concepts
- 1. 1 Payroll Concepts By Shailesh Nema Greytip Software Pvt. Ltd
- 2. 2 Salary Components(Heads) in Salary Earnings Deductions Statutory: Basic DA HRA Conv. All Statutory: ESI PF PT TDS Others: Medical All. Edc All. etc Others: Canteen Dedn. Qrtr Rent. etc Gross Earnings Gross Deductions Gross Earnings - Gross Deductions = Net Earnings
- 3. 3 Organizational Structure Managing Director/CEO Dept.Head General Manager Dept.Head Dept.Head Dept.Head General Manager Executives / Operators / Assistants
- 4. 4 Acts influencing Payroll Processing Major Acts âĒThe Employee's Provident Funds Act ,1952 âĒThe Employee's State Insurance Act,1948 âĒProfessional Tax Act âĒThe Income Tax Act, 1961 âĒPayment of Bonus Act,1965 âĒPayment of Gratuity Act,1998 âĒMinimum Wages Act âĒMaternity Benefit Act âĒAnd many more
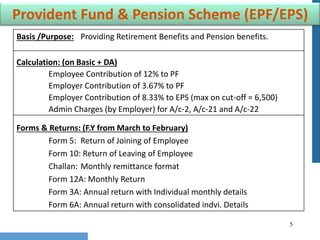
- 5. 5 Provident Fund & Pension Scheme (EPF/EPS) Basis /Purpose: Providing Retirement Benefits and Pension benefits. Calculation: (on Basic + DA) Employee Contribution of 12% to PF Employer Contribution of 3.67% to PF Employer Contribution of 8.33% to EPS (max on cut-off = 6,500) Admin Charges (by Employer) for A/c-2, A/c-21 and A/c-22 Forms & Returns: (F.Y from March to February) Form 5: Return of Joining of Employee Form 10: Return of Leaving of Employee Challan: Monthly remittance format Form 12A: Monthly Return Form 3A: Annual return with Individual monthly details Form 6A: Annual return with consolidated indvi. Details
- 6. 6 Employee State Insurance (ESI) Basis /Purpose: Providing Medical, Hospitalization, Maternity facilities to the eligible Employees Calculation: (on Gross Earnings) Employee Contribution of 1.75% Employer Contribution of 4.75% Calculation can be restricted to cut-off which is 15,000 if Earnings exceeds within a half year. (Cut-off : This is the max salary below which, the Employee will be eligible for ESI. But if an employee comes out of cut-off (salary increased more than 15,000) still, till the completion of half year, the deduction and contribution should be done) Forms & Returns: (period - 1st half from April to Sept, 2nd half from October to March) Challan: Monthly remittance format Form 5: Half yearly return of each Employee details of his attended days, wages earned, contribution, dispensary. Form 6: Half yearly return of contribution and remittances.
- 7. 7 Income Tax (for A.Y.2014-15) Basis /Purpose: It is a major Central Government Revenue collected from all who has any kind of income. Calculation: (on Taxable Income) (Rupees in Lakh) Forms & Returns: (period - April to March) Form 16: Certificate of Tax Deducted at Source from Salary Form 12BA:Statement of Perquisites Form 24:Return of Salary TDS by a company Exempt 10% 20% 30% General 0-2.0 2.0-5.0 (Less Rs. 2000 as tax credit) 5.0-10.0 10.0 & Above Sr. Citizen (60-80 yrs) 0-2.5 2.5-5.0 5.0-10.0 10.0 & Above Sr. Citizen (80 yrs & Abv) 0-5.0 (Exempt) 5.0-10.0 10.0 & Above
- 8. 8 Bonus Basis /Purpose: Generally a share of profit given to the Employees. Calculation: (on Basic + DA earned for the year) Min of 8.33% and Max of 20% Eligibility: Min 30 days of service & (Basic + DA) less than Rs. 10000 per month If Basic + DA is between 3,500 and 10000, it should be restricted to 3,500 as calculation amount. If the Basic + DA is less than or equal to 3500, then it will be calculated on actual Basic + DA This is to be paid before completion of 8 months from the date of closing the books of accounts. Forms & Returns: (period - April to March) Form C: Slip with the complete details of the bonus paid attested by signature of the Employee as a proof of receipt of Bonus.
- 9. 9 Gratuity Basis /Purpose: Providing a compensatory amount on separation of an employee from an organization. Calculation: Eligibility: Employee should have completed min 5 years of service in the organization. Amount: 15 days equivalent Basic wages x number of years of service Calculated as: ((((Basic wages)/26)*15)*No. of years served)
- 10. 10 Other Acts Minimum Wages Act: This specifies the minimum wage that has to be paid to any employee based on his skills classified as Skilled, Semi-Skilled and Un-Skilled . The minimum wages for different industry is defined and notified by the State Governments Maternity Benefit Act: This is to facilitate an woman with the Maternity facilities, who is out of ESI coverage.
- 11. 11 Attendance in Payroll Basis / Purpose: Attendance is nothing but the availability of an Employee for completing the work assigned to him. Usage: Attendance is the basic thing on which salary calculation depends and without which salary calculation is not possible. Types: Physically present, On Official Duty (OOD), Deputation, Paid Leave. Terminologies used: Salary Calendar Days: Actual Number of Days in a month NWD: Number of declared working days in a month (NOD - holidays) NDP: Number of days Present LOP: Loss of Pay. (If any day is not considered for salary calculation due to absenteeism, it will be termed as LOP.
- 12. 12 Attendance Management System There are various types of Attendance Management System followed in organizations. * Manual Recording (Register maintaining) * Spread Sheet System (preferable in MS - Excel) * Mechanized Systems * Bio-Metric : * Finger Print Reader * Face Reader * Voice Reader *Eye-ball Reader * Non Bio-Metric : * Punch Card Reader * Smart Card Reader * Proximity Reader Purpose of all the above systems is to create a log-sheet which contains info of in/ out movement of employees with time and date. All these details are very much important to import into any Payroll Processing Software.
- 13. 13 Leave provided to an Employee Basis / Purpose: Leave is nothing but an exemption given to an Employee from Attendance. It is the permitted absence of an employee which will not be having any adverse effect on his services. This will be allotted to any employee or a particular period and the employee can opt any working day for availing the same. General types of Paid Leaves followed in various organizations: Type of Leave Allotable (Y/N) Carry Forwarable (Y/N) Effect on Salary (Y/N) CL â Casual Leave Y N N SL â Sick Leave Y N N EL â Earned Leave Y Y N PL â Privileged Leave Y Y N RH â Restricted Holiday Y N N
- 14. 14 Payroll Records to be maintained by the employer Attendance Register (Muster Roll) Record of Attendance for a said period for a set of Employees Pay Slip Record of Salary for a month for a particular employee Salary Sheet Record of Salary for a particular month for a set of Employees PF / ESI Register Register containing all the necessary details of the Employees registered under PF / ESI. Leave Register Register of Leaves allotment, used and balance of every Employee Advance Register Register of Payment, receipt, recovery of Advance of all the Employees. ESI - Accident Report (Form 16) Record / details of any accidents occurred in the Company premises during the working hours
- 15. 15 Payroll Records to be maintained by the employer Ex-Gratia Similar to Bonus. But normally paid to the non-eligible employees. Increment & Arrears Increase in the Salary is Increment. Any Salary amount pending to be paid is Arrears. Standing Instructions Any Deductions and Earnings based on certain Instructions from the Employee for a specified period (Ex:- LIC, Loan, Advance, SSS etc) Over Time Extra time worked by an employee is termed as Over time and the compensation for the same is the Over Time Allowance. Leave Encashment Exchange of un-used leaves to money Salary Extrapolation Approximation of Future Salary based on present salary. This is required for the purpose of TDS Estimation. Service Register Record of Service proceedings of an Employee containing, performances, salary, increments, promotions and more details
- 16. 16 For Demo in Payroll Contact : shailesh@greytip.com