PDXPortland - Dockerize Django
- 1. Dockerizing Django PDX PortlandŌĆ© October 27th, 2016
- 2. Who are we? Michael DoughertyŌĆ© @maackleŌĆ© Senior Front-end EngineerŌĆ© CrowdStreet, Inc. Hannes HapkeŌĆ© @hanneshapkeŌĆ© Software EngineerŌĆ© Talentpair, Inc.
- 3. Our pre-Docker World ŌĆ” ŌĆó Single instance worldŌĆ© (e.g. celery ran on the web server) ŌĆó Outdated Amazon machine image ŌĆó No documentation about the setup, consultancy work ŌĆó Live data monkey patching ŌĆó Scaling/Recovery time > 8 hours ŌĆó Clunky QA setup > bottleneck
- 4. Our post-Docker World ŌĆ” ŌĆó Single instance worldŌĆ© (e.g. celery ran on the web server) ŌĆó Outdated Amazon machine image ŌĆó No documentation about the setup, consultancy work ŌĆó Live data monkey patching ŌĆó Scaling/Recovery time > 8 hours ŌĆó Clunky QA setup > bottleneck ŌĆó One service per container, redundancy of instances ŌĆó One common base image shared across all instances ŌĆó Explicit, declarative server setup ŌĆó Immutable infrastructure (mostly) ŌĆó Scaling/Recovery time ~ 20min ŌĆó As many QA instances as we want
- 5. What is Docker? Docker ŌĆó Compose ŌĆó Machine ŌĆó Swarm
- 6. Docker containers ŌĆ” ŌĆ” wrap a piece of software in a complete ’¼ülesystem that contains everything needed to run: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries ŌĆō anything that can be installed on a server. This guarantees that the software will always run the same, regardless of its environment. * Basically a virtual env for your operating system. * from https://www.docker.com/what-docker
- 8. Where is the difference? Images from https://www.docker.com/what-docker VM includes OS No OS needed
- 10. ŌĆó Create a Docker’¼üle ŌĆó Build the Docker image and push it to the docker registry Plain Docker FROM ubuntu:16.04 RUN apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y RUN pip install Django COPY requirements.txt . WORKDIR /dev $ docker build -t your_project/your-whale . $ docker imagesŌĆ© $ docker tag {image_hash} your_project/your-whale:latestŌĆ© $ docker push
- 11. Plain Docker ŌĆó Run a shell in a docker containerŌĆ© ŌĆ© -i start an interactive containerŌĆ© -t creates ŌĆ£Pseudo interfaceŌĆØ with stdin and stdout ŌĆó Run the Django server in a containerŌĆ© ŌĆ© -d run container in detached modeŌĆ© -P maps all ports to the host machine $ docker run -i -t ubuntu /bin/bash $ docker run -d -P my-container python manage.py run server
- 12. What if we need multiple services? Docker ŌĆó Compose ŌĆó Machine ŌĆó Swarm
- 13. Docker Compose Compose is a tool for orchestrating the building, running, and intercommunication of multi-container Docker applications.
- 14. How does it work? 1) De’¼üne a Docker’¼üle for every service 2) De’¼üne a Docker compose description of the environment 3) Use docker-compose build/up to start all services version: '2' services: web: build: . ports: - "5000:5000" volumes: - .:/code redis: image: redis
- 15. How can I easily provision a server with the containers? Docker ŌĆó Compose ŌĆó Machine ŌĆó Swarm
- 16. Docker Machine ŌĆ” is a great tool which creates Docker hosts anywhere.ŌĆ© Yes, anywhere.ŌĆ© Locally, AWS EC2, Digital Ocean, MS Azure, you name it. No Ansible, Puppet, Chef, fabric, etc. required.
- 17. What if I need multiple instances with multiple services? Docker ŌĆó Compose ŌĆó Machine ŌĆó Swarm
- 18. Docker Swarm
- 19. Dockerize for real ŌĆ”
- 20. If you start from scratch ŌĆ” ŌĆó Docker documentation includes a great Django setup ŌĆó Too much work? The Django Cookie Cutter template includes a great Docker setupŌĆ© Other projects: ŌĆó django-docker on github
- 21. If you convert a project like us ŌĆ”
- 23. Normalize folders ŌĆó Create folders for every service ŌĆó docker-compose-{env}.yml go into the project root ŌĆó Docker’¼üles go into every service folder ŌĆó startup.sh scripts go into the service folders ŌĆó Keep your local folder structure similar to the folder structure within the container(s) - for sanity
- 24. Reorganized folders Project RootŌĆ© |-appsŌĆ© |-settingsŌĆ© |-staticŌĆ© |-templatesŌĆ© |-manage.pyŌĆ© |-fab’¼üle.pyŌĆ© |-urls.pyŌĆ© requirements.txt Project RootŌĆ© |-djangoŌĆ© | |-appsŌĆ© | |- ŌĆ”ŌĆ© | |-Docker’¼üleŌĆ© | |-startup-django.shŌĆ© | -manage.pyŌĆ© |-nginxŌĆ© |-webpackŌĆ© |-docker-compose.ymlŌĆ© |-urls.pyŌĆ© requirements.txt
- 25. Build a base image
- 26. Base Image ŌĆó Create one (or more) base Docker’¼üle(s) with all common packages ŌĆó Service containers can use this base image - this will increase build speed ŌĆó If you store the base image(s) in a separate git repo, the docker registry will build them automatically for you
- 27. Base Image FROM ubuntu:16.04 RUN apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y RUN apt-get install -y vim # Install some useful editor RUN apt-get install -y build-essential git software-properties-common RUN apt-get install -y python python-dev python-setuptools build-essential RUN apt-get install -y nodejs npm RUN npm install -g n # upgrading the npm version RUN n stable ...
- 28. Base Image Add image of the Docker registry
- 29. Set up Docker compose for the different environments
- 30. Docker Compose ŌĆó For every environment, local, QA, staging, production, de’¼üne a docker-compose-{env}.yml ’¼üle ŌĆó The ’¼üles describe the environment stack ŌĆó Each service within the docker-compose ’¼üle can have itŌĆÖs own Docker’¼üle
- 31. Docker Composeversion: '2' volumes: postgres_data_dev: {} redisdata: {} webpack_data: {} services: postgres: image: postgres:9.5 volumes: - postgres_data_dev:/var/lib/postgresql/data restart: always environment: - POSTGRES_USER=postgres_user - POSTGRES_DB=my_fancy_db - POSTGRES_PASSWORD= webpack: image: crowdstreet/crowdstreet-whale:latest command: npm run watch environment: - NODE_PATH=/node_modules volumes: - ./webpack/frontend-src:/frontend-src - ./django:/crowdstreet-src - webpack_data:/webpack_data/ ports: - "3000:3000" restart: always
- 32. Docker Composedjango: build: context: . dockerfile: ./django/Dockerfile-dev command: python /crowdstreet-src/manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 --settings=settings.dev depends_on: - postgres environment: - ENV=dev - DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=settings volumes: - ./django:/crowdstreet-src - ./webpack/frontend-src:/frontend-src - webpack_data:/webpack_data/ ports: - "8000:8000" - "80:8000" links: - postgres - redis - webpack - memcached redis: restart: always image: redis:latest volumes: - redisdata:/data restart: always
- 33. Docker Compose ŌĆó Build your service stack with ŌĆó Start the container stack with ŌĆó Access a single container with $ docker-compose -f docker-compose-{env}.yml build $ docker-compose -f docker-compose-{env}.yml up $ docker-compose -f docker-compose-{env}.yml run django bash $ docker-compose -f docker-compose-{env}.yml ŌĆ© run container name command
- 35. Set up Docker machine and deploy to the world
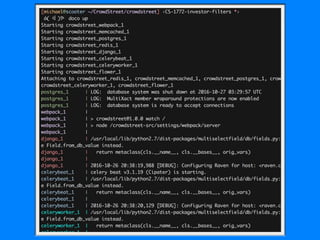
- 38. Docker Machine ŌĆó WithŌĆ© ŌĆ© ŌĆ© ŌĆ© ŌĆ© will provision you an AWS instance ŌĆó ŌĆ£ActivateŌĆØ the instance withŌĆ© ŌĆó Afterwards, any docker-compose command will be executed on the active machine ŌĆó Easy to start/stop/terminate machines $ docker-machine create --driver amazonec2 ŌĆ© --amazonec2-region [e.g. us-west-2] ŌĆ© --amazonec2-vpc-id [YOUR_VPC_ID vpc-xxxxxx] ŌĆ© --amazonec2-instance-type [e.g. t2.small] [INSTANCE_NAME] $ docker-machine env [INSTANCE_NAME]
- 39. Lessons Learned
- 41. Or... how to cowboy code with Docker ŌĆó Sometimes you just need to manually change something ŌĆó Docker provides ways to get a shell inside a running instance and copy ’¼üles back and forth ŌĆó Your changes will of course be lost next time you spin up a new container
- 42. The Disciplined Way: The Cowboy Way: $ docker-compose run django bash $ docker exec -it {container_id} bash
- 43. How does QA work with Docker? ŌĆó No QA bottleneck anymore ŌĆó No database gridlock anymore ŌĆó Each feature branch gets its own instance ŌĆó Once feature is tested, instance gets terminated
- 44. How can I access the manage.py shell/migrate? ŌĆó Access the bash of the django container withŌĆ© ŌĆ© ŌĆó Continue as usual withŌĆ© ŌĆ© ŌĆ© Some for migrations, make_migrations, etc. ŌĆó Or run it from outside of the container stack with $ docker-compose -f docker-compose-{env}.yml run django bash # ./manage.py shell docker-compose -f ŌĆ” run django python manage.py migrate
- 45. Help, ipdb doesnŌĆÖt work anymore ŌĆ” ŌĆó Start the Django container with the service ports enabledŌĆ© ŌĆó If no command is speci’¼üed, then Docker will default to the command in the docker-compose.yml ’¼üle $ docker-compose -f dev.yml run --service-ports django
- 46. How to run tests? ŌĆó Start the Django container with your test commandŌĆ© ŌĆ© $ docker-compose -f ŌĆ” run django manage.py test
- 47. CI Testing is convenient ŌĆó Setup for Circle CI machine: pre: - curl -sSL https://s3.amazonaws.com/circle-downloads/install-circleci-docker.sh | bash -s -- 1.10.0 services: - docker dependencies: override: - sudo pip install docker-compose - docker login -e $DOCKER_EMAIL -u $DOCKER_USER -p $DOCKER_PASS - docker-compose -f docker-compose-circle.yml build - npm install -g jshint test: pre: - sudo killall postgres # not sure why, but port 5432 is already taken up sometimes! - docker-compose -f docker-compose-circle.yml up -d postgres override: - jshint ~/your_project/django/static/js/your_project* - docker-compose -f docker-compose-circle.yml run django /your_project/manage.py test --verbosity=2
- 48. WTF, the ’¼üles I copied into my container are missing?? ŌĆó If a volume is mounted at the same directory where you copied other ’¼üles, you will essentially overwrite those ’¼üles
- 49. Sharing Docker Machine credentials ŌĆó Docker machine is great, but there is no concept of sharing credentials ŌĆó All credentials are simple text ’¼üles, no magic ŌĆó npm tool `machine-share` solved the problem ŌĆó LetŌĆÖs you export and import machine credentials
- 50. General Troubleshooting ŌĆó Con’¼ürm that the correct docker-machine environment is active ŌĆó Rebuild your container stack ŌĆó Rebuild with the --pull and/or --no-cache options ŌĆó Restart the docker daemon ŌĆó Restart your docker machine with docker-machine restart [INSTANCE NAME] ŌĆó Restart your docker machine VirtualBox VM ŌĆó Remove and recreate your docker machine (essentially recreates your dev environment from scratch)
- 51. So, what does our setup look like now?
- 52. Dev Environment ŌĆó You can use the same image as in your production builds ŌĆó All services run at once, all output piped to a single log stream (which we saw earlier) ŌĆó You can still have live reloading via Docker Volumes (but be careful!)
- 53. How does the deployment work now? ŌĆó Create AWS instance with docker-machine ŌĆó Activate the docker machine ŌĆó Use docker-compose to build the stack ŌĆó Use docker-compose up -d ŌĆó Switch the load balancer
- 54. Summary of technologies ŌĆó Learned about Docker ŌĆó How to use docker to de’¼üne images and containers ŌĆó Learned about Docker-compose to de’¼üne relationships between containers ŌĆó Learned about Docker-machine to seamlessly work with containers on local/remote machines
- 55. Summary of bene’¼üts ŌĆó Explicit, declarative server setup ŌĆó Zero down time deployments ŌĆó All dev services in one "window" and start with one command ŌĆó Easy provisioning of multiple QA instances ŌĆó Quick onboarding for new devs
- 56. Thank you!
- 57. Q&A



































![Docker Machine
ŌĆó WithŌĆ©
ŌĆ©
ŌĆ©
ŌĆ©
ŌĆ©
will provision you an AWS instance
ŌĆó ŌĆ£ActivateŌĆØ the instance withŌĆ©
ŌĆó Afterwards, any docker-compose command will be
executed on the active machine
ŌĆó Easy to start/stop/terminate machines
$ docker-machine create --driver amazonec2 ŌĆ©
--amazonec2-region [e.g. us-west-2] ŌĆ©
--amazonec2-vpc-id [YOUR_VPC_ID vpc-xxxxxx] ŌĆ©
--amazonec2-instance-type [e.g. t2.small]
[INSTANCE_NAME]
$ docker-machine env [INSTANCE_NAME]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2e9813-0665-4646-bd20-8bd986f9cf95-161029164502/85/PDXPortland-Dockerize-Django-38-320.jpg)









![General Troubleshooting
ŌĆó Con’¼ürm that the correct docker-machine environment is active
ŌĆó Rebuild your container stack
ŌĆó Rebuild with the --pull and/or --no-cache options
ŌĆó Restart the docker daemon
ŌĆó Restart your docker machine with docker-machine restart
[INSTANCE NAME]
ŌĆó Restart your docker machine VirtualBox VM
ŌĆó Remove and recreate your docker machine (essentially recreates
your dev environment from scratch)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2e9813-0665-4646-bd20-8bd986f9cf95-161029164502/85/PDXPortland-Dockerize-Django-50-320.jpg)






