Pedagogy.pptx
- 2. Let us brush up 1. Definition of implant and components 2. Classification 3. Advantages and disadvantages of implant
- 3. Which is best ?? Tooth Or Implant
- 4. Comparison between tooth and implant Under the headings 1. Composition 2. Surrounding supporting tissue 3. Proprioception 4. Mobility 5. Biomechanical design 6. Load bearing characteristics
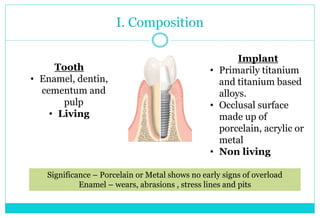
- 5. I. Composition Tooth âĒ Enamel, dentin, cementum and pulp âĒ Living Implant âĒ Primarily titanium and titanium based alloys. âĒ Occlusal surface made up of porcelain, acrylic or metal âĒ Non living Significance â Porcelain or Metal shows no early signs of overload Enamel â wears, abrasions , stress lines and pits
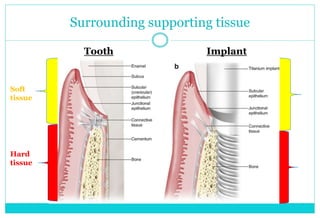
- 6. Surrounding supporting tissue Tooth Implant Soft tissue Hard tissue
- 7. Significance ï Soft tissue - probing cautiously only when indicated ï Hard tissue attachment Periodontal membrane Direct bone implant Shock absorber Higher impact force Longer force duration Short force duration Distribution of force around teeth Force primarily to crest Tooth mobility can be related to force Implant is always rigid Mobility dissipates lateral force Lateral force increases strain to bone Fremitus related to force No fremitus Radiographic changes related to force are reversible Radiographic changes are at crest - not reversible
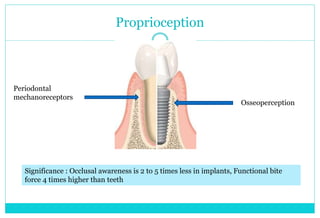
- 8. Proprioception Periodontal mechanoreceptors Osseoperception Significance : Occlusal awareness is 2 to 5 times less in implants, Functional bite force 4 times higher than teeth
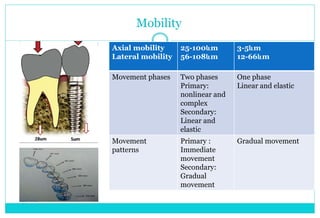
- 9. Mobility Axial mobility Lateral mobility 25-100Öm 56-108Öm 3-5Öm 12-66Öm Movement phases Two phases Primary: nonlinear and complex Secondary: Linear and elastic One phase Linear and elastic Movement patterns Primary : Immediate movement Secondary: Gradual movement Gradual movement
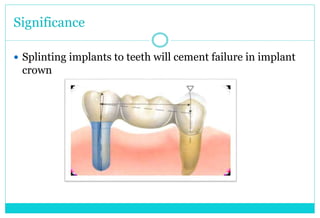
- 10. Significance ï Splinting implants to teeth will cement failure in implant crown
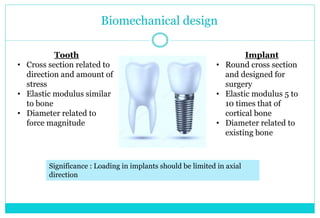
- 11. Biomechanical design Tooth âĒ Cross section related to direction and amount of stress âĒ Elastic modulus similar to bone âĒ Diameter related to force magnitude Implant âĒ Round cross section and designed for surgery âĒ Elastic modulus 5 to 10 times that of cortical bone âĒ Diameter related to existing bone Significance : Loading in implants should be limited in axial direction
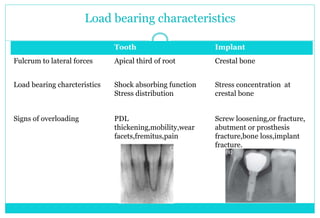
- 12. Load bearing characteristics Tooth Implant Fulcrum to lateral forces Apical third of root Crestal bone Load bearing charcteristics Shock absorbing function Stress distribution Stress concentration at crestal bone Signs of overloading PDL thickening,mobility,wear facets,fremitus,pain Screw loosening,or fracture, abutment or prosthesis fracture,bone loss,implant fracture.
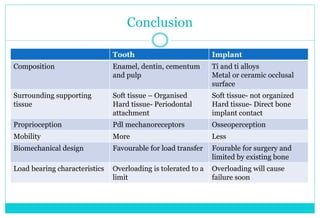
- 13. Conclusion Tooth Implant Composition Enamel, dentin, cementum and pulp Ti and ti alloys Metal or ceramic occlusal surface Surrounding supporting tissue Soft tissue â Organised Hard tissue- Periodontal attachment Soft tissue- not organized Hard tissue- Direct bone implant contact Proprioception Pdl mechanoreceptors Osseoperception Mobility More Less Biomechanical design Favourable for load transfer Fourable for surgery and limited by existing bone Load bearing characteristics Overloading is tolerated to a limit Overloading will cause failure soon
- 14. Which is best ?? Tooth Or Implant