pengertian past dan simple future tense sman 3 nganjuk
- 1. Understanding Past Future Tense Past future tense is a form of the verb to discuss the future from the perspective of the past. More specifically, this form is used to express an action to be performed, either voluntarily or planned, making predictions, and make an appointment in the future at the moment is in the past. Past future tense is often used in reported speech. Formula Future Past Tense Past future tense is formed of capital "would" and bare infinitive or formed from the auxiliary verb "be" (was,were),present participle "going", and infinitive. What is the infinitive? Infinitive is the particle "to" + bare infinitive. formed by using the "capital" and "be" auxiliary verb, "being" present participle and to the infinitive. The formula is as follows: In the sentence Positive (+) Subject + should / would + be + object Subject + should / would + verb + object I In sentence negative (-) Subject + should / would + not + be + object Subject + should / would + not + verb + object In interrogative sentences / Q (?) Should / would + be + subject + object? Should / would + subject + verb + object I? To form the passive voice in the past future tense,you of course use the following pattern: S + would + be + Verb-3 / Past Participle I understood the party would be finished in Paris S + was / were + going to + be + Verb-3 / Past Participle Father thought a new half was going to be finished by John.
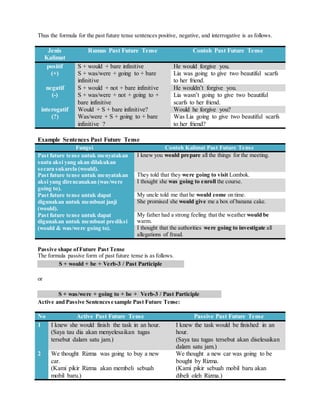
- 2. Thus the formula for the past future tense sentences positive, negative, and interrogative is as follows. Jenis Kalimat Rumus Past Future Tense Contoh Past Future Tense positif (+) S + would + bare infinitive S + was/were + going to + bare infinitive He would forgive you. Lia was going to give two beautiful scarfs to her friend. negatif (-) S + would + not + bare infinitive S + was/were + not + going to + bare infinitive He wouldn’t forgive you. Lia wasn’t going to give two beautiful scarfs to her friend. interogatif (?) Would + S + bare infinitive? Was/were + S + going to + bare infinitive ? Would he forgive you? Was Lia going to give two beautiful scarfs to her friend? Example Sentences Past Future Tense Fungsi Contoh Kalimat Past Future Tense Past future tense untuk menyatakan suatu aksi yang akan dilakukan secara sukarela (would). I knew you would prepare all the things for the meeting. Past future tense untuk menyatakan aksi yang direncanakan (was/were going to). They told that they were going to visit Lombok. I thought she was going to enroll the course. Past future tense untuk dapat digunakan untuk membuat janji (would). My uncle told me that he would come on time. She promised she would give me a box of banana cake. Past future tense untuk dapat digunakan untuk membuat prediksi (would & was/were going to). My father had a strong feeling that the weather would be warm. I thought that the authorities were going to investigate all allegations of fraud. Passive shape ofFuture Past Tense The formula passive form of past future tense is as follows. S + would + be + Verb-3 / Past Participle or S + was/were + going to + be + Verb-3 / Past Participle Active and Passive Sentencesexample Past Future Tense: No Active Past Future Tense Passive Past Future Tense 1 I knew she would finish the task in an hour. (Saya tau dia akan menyelesaikan tugas tersebut dalam satu jam.) I knew the task would be finished in an hour. (Saya tau tugas tersebut akan diselesaikan dalam satu jam.) 2 We thought Rizma was going to buy a new car. (Kami pikir Rizma akan membeli sebuah mobil baru.) We thought a new car was going to be bought by Rizma. (Kami pikir sebuah mobil baru akan dibeli oleh Rizma.)
- 3. Sentence in the form of Future Past Tense is used to: a. Declare an activity, action or situation that will be done or happened in the past. example: - They would come here last week but they were sick. b. Declare an activity, action or situation that will be done in the past when the conditions are met. example: - She would come here if you invited him. c. Declaring a person to do something, namely using Would you ... because this form is considered more subtle and polite compared to the sentence application that uses Will you ... example: - Would you open the window?
- 4. Understanding the Simple Future Tense Simple future tense is a verb form used to express that an action happens in the future, spontaneous or planned. This tense can also be used to form a conditional sentence type 1. Formula Simple Future Tense Simple future tense is formed of capital "will" or "shall" and bare infinitive (basic verb form) or formed from phrasal capital "be going to" and bare infinitive (base form verb). Formula SentencesSimple Future Tense Expressing Future Tense Simple sentences using verbs (VERB) + Subject + WILL / SHALL + Verb 1 + Object - Subject + WILL / SHALL + NOT + Verb 1 + Object ? WILL / SHALL + Subject + Verb 1 + Object ? ? Question Word + WILL / SHALL + Subject + Verb 1 ? Expressing Future Tense Simple sentences that do not use the verb (NON VERB) + Subject + WILL / SHALL + be + Non Verb + Object - Subject + WILL / SHALL + NOT + be + Non Verb + Object ? WILL / SHALL + Subject + be + Non Verb + Object ? ? Question Word + WILL/SHALL + Subject + be + Non Verb + Object ? Using the "To Be Going To" Pattern Simple Future Tense verbal sentence can be replaced by using the phrase to be + going to to replace shall and will. Formula and example sentences using the "To Be Going To" + Subject + To be + going to + Verb 1 + Object - Subject + To be + Not + going to + Verb 1 + Object ? To be + Subject + going to + Verb 1 + Object ? ? Question Word + To be + Subject + going to + verb 1 +? For more information, please read also about the function and use of Will and To Be Going To, may be useful. Remarks time for Simple Future Tense used are: tomorrow morning, tomorrow night, next week,next year and so on. Hopefully this article can be understood and helped to learn English, if useful please be shared. We are sorry if there is a mistake in typing. And for all kinds of questions, suggestions, and criticisms can be included in the comments field. Thus the formula for the simple future tense sentences positive, negative, and interrogative as follows.
- 5. Jenis Kalimat Rumus Contoh Simple Future Tense positif (+) S + will + bare infinitive S + be (am/is/are) going to + bare infinitive You will win They are going to come negatif (-) S + will + not + bare infinitive S + be (am/is/are) + not + going to + bare infinitive You won’t win They aren’t going to come interogatif (?) Will + S + bare infinitive Be (am/is/are) + S + going to + bare infinitive? Will you win Are they going to come Example Sentences Simple Future Tense Some examples of simple future tense sentences with their functions are as follows. Fungsi Contoh kalimat Simple Future Tense Simple future tense (will) untuk membuat keputusan secara spontan untuk melakukan sesuatu (tanpa rencana). Wait a minute. I will change my clothes. You look nervous. I’ll give you a glass of water. Simple future tense (will) untuk memerediksi masa depan (tanpa rencana). The doom will not happen in 2014. Which hotels do you think will offer the best service? He’ll be angry. The sandstorm will come. I think he will pass. Present continuous tense digunakan untuk menyatakan arrangement (rencana yang sudah dipikirkan dan dibahas dengan orang lain). I’m visiting South Korea tomorrow. She’s going to the physiotherapist next monday. Simple future tense dengan “going+to” untuk menyatakan intention (rencana dimasa depan yang sudah dipikirkan sebelumnya). I’m going to send this letter tomorrow. He is going to go to French to continue his study. Simple future tense digunakan untuk membentuk conditional sentence 1 I will come if they invite me. Functions ofthe simple future tenseThe simple future refers to a time later than now, and expresses facts or certainty. In this case there is no 'attitude'. The simple future is used:  To predict a future event: It will rain tomorrow.  With I or We, to express a spontaneous decision: I'll pay for the tickets by credit card.  To express willingness: I'll do the washing-up. He'll carry your bag for you.
- 6. ď‚· In the negative form, to express unwillingness: The baby won't eat his soup. I won't leave until I've seen the manager! ď‚· With I in the interrogative form using "shall", to make an offer: Shall I open the window? ď‚· With we in the interrogative form using "shall", to make a suggestion: Shall we go to the cinema tonight? ď‚· With I in the interrogative form using "shall", to ask for advice or instructions: What shall I tell the boss about this money? ď‚· With you, to give orders: You will do exactly as I say. ď‚· With you in the interrogative form, to give an invitation: Will you come to the dance with me? Will you marry me? Note:In modern English will is preferred to shall. Shall is mainly used with I and we to make an offer or suggestion, or to ask for advice (see examples above). With the other persons (you, he, she, they) shall is only used in literary or poetic situations, e.g. "With rings on her fingers and bells on her toes, She shall have music wherever she goes." Forming the simple future The simple future tense is composed of two parts: will / shall + the infinitive without to Subject will infinitive without to Affirmative I will go I shall go Negative They will not see They won't see Interrogative Will she ask? Interrogative negative Won't they try? To see:Simple future tense Affirmative Negative Interrogative Interrogative Negative I will see I won't see Will I see? Won't I see? *I shall see *Shall I see? You will see You won't see Will you see? Won't you see? He will see He won't see Will he see? Won't he see? We will see We won't see Will we see? Won't we see? *We shall see *Shall we see? They will see They won't see Will they see? Won't they see?