perception
- 1. PERCEPTION PLAYS KEY ROLE IN FORMING GROUP Group Members:- Sachdev Tarun 103 Ahuja Nilesh 62 Shadi Sneha 104 Rawlani Sanjay 101 Galani Nitin 66 Dulani Avinash 65 By:- Cognizant Achievers HIGH PERFORMANCE LEADERSHIP
- 2. INTRODUCTION “ WE DON’T SEE THINGS AS THEY ARE, WE SEE THINGS AS WE ARE.”
- 3. PERCEPTION The Nature and Importance of Perception Sensation is not the same as perception External Attention Factors Intensity Size Contrast Motion Internal Attention Factors learning & perception Motivation & perception
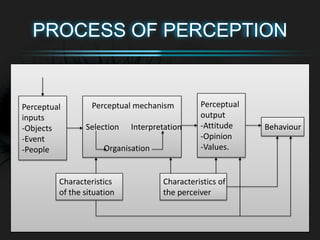
- 4. PROCESS OF PERCEPTION Perceptual inputs -Objects -Event -People Perceptual mechanism Selection Interpretation Organisation Behaviour Perceptual output -Attitude -Opinion -Values. Characteristics of the situation Characteristics of the perceiver
- 5. TYPES OF GROUPS Formal Groups Command groups Task groups Functional groups Informal Group Interest groups Friendship groups Reference groups
- 6. PERCEPTUAL GROUPING Proximity principle Closure principle
- 7. PERCEPTUAL GROUPING Similarity principle Continuity principle
- 8. SHORTCUTS IN JUDGING OTHERS Person Perception the term person perception refers to the different mental processes that we use to form impressions of other people Selective Perception People selectively interpret what they see on the basis of their interests, background, experience and attitudesHalo Effect Drawing a general impressions about an individual on the basis of a single
- 9. SHORTCUTS IN JUDGING OTHERS Contrast Effect Evaluation of a person’s characteristics that are effected by comparisons with other people recently encountered who rank higher or lower on the same characteristics Projection Attributing one's own characteristics to other peopleStereotyping Judging someone on the basis of one’s perception of the group to which that
- 10. THANKYOU