Periodic trends
- 2. How is the periodic table arranged? ’üĄ The modern periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number (protons).
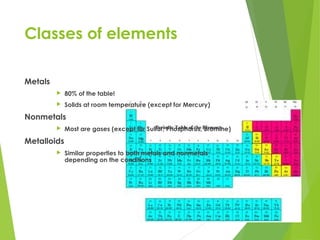
- 3. Classes of elements Metals ’üĄ 80% of the table! ’üĄ Solids at room temperature (except for Mercury) Nonmetals ’üĄ Most are gases (except for Sulfur, Phosphorus, Bromine) Metalloids ’üĄ Similar properties to both metals and nonmetals depending on the conditions
- 4. Periods and Groups ’üĄ The vertical columns are called groups ’üĄ The horizontal rows are called periods
- 5. The Representative Elements ’üĄ Groups ’üĄ For 1A ŌĆō 7A these elements the group number represents the number of electrons in the highest occupied energy level
- 6. Periodic Trends ’üĄ Atomic size (Distance between nuclei) ’üĄ Increases from top to bottom (energy levels increase) ’üĄ Decreases from left to right (electrons get pulled closer to the nucleus)
- 7. Periodic Trends ’üĄ Ionization energy (energy required to remove one electron) ’üĄ Decrease from top to bottom ’üĄ Increases from left to right (more attraction to nucleus makes it harder to get that electron out!)
- 8. Periodic Trends ’üĄ _Ionic Size (size of a charged atom) ’üĄ Cations (+) are always smaller than the atom from which they form ’üĄ Anions (-) are always larger than the atoms from which they form ’üĄ Increases from top to bottom ’üĄ Decreases from left to right
- 9. Periodic Trends ’üĄ Electronegativity (ability of an atom to attract electrons when in a compound) ’üĄ Decreases from top to bottom ’üĄ Increases from left to right
- 10. Vocabulary Cards ’üĄ Periodic Table ’üĄ Metal ’üĄ Nonmetal ’üĄ Metalloid ’üĄ Energy Level ’üĄ Ionization Energy ’üĄ Cation ’üĄ Anion ’üĄ Electronegativity ’üĄ Valence Electrons
- 11. POST IT UP How is electronegativity related to how an element will react in a chemical compound? I S! TH OT IG IN EE DH EL P!