Perseieds
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes176 views
The Perseid meteor shower occurs each August when the Earth passes through debris left behind by Comet Swift-Tuttle, causing specks of comet material entering the atmosphere at 140,000 mph to disintegrate and appear as flashes of light radiating from the constellation Perseus. The meteor shower provides a popular night sky attraction each year as viewers on Earth pass through the debris trail remaining from the comet's passage every 133 years.
1 of 4
Download to read offline



Ad
Recommended
Team a
Team asatish kumar
╠²
The document provides an overview of the solar system's structure, detailing the sun as the central star and primary energy source for Earth. It mentions the characteristics of various planets, including Mercury, Venus, Jupiter, Uranus, and the classification of Pluto as a dwarf planet. The information highlights the unique orbital and physical attributes of these celestial bodies.Planet Venus
Planet VenusAmita Vadlamudi
╠²
Venus is the second planet from the sun and the brightest object in the sky after the sun. It appears luminous because it is comprised of dense carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid atmospheres. Venus has the hottest surface temperatures of any planet, averaging around 480┬░C due to extreme greenhouse effects. It revolves slowly, taking almost 225 Earth days to rotate once on its axis.Planet Venus, the Veiled and Hottest Planet
Planet Venus, the Veiled and Hottest PlanetAlma Mae Casabay
╠²
Venus is Earth's closest planetary neighbor with similarities in size, mass, and composition. It has a dense carbon dioxide atmosphere and experiences extreme surface temperatures around 864 degrees F due to greenhouse gas warming. Venus rotates backwards compared to Earth and has no magnetic field. It has been explored by numerous spacecraft but cannot support life due to the hostile conditions.Our Closest Star, the Sun
Our Closest Star, the SunAmita Vadlamudi
╠²
The sun is a crucial celestial body at the center of the solar system, containing 99% of its mass and providing essential energy and light for Earth. It is approximately 93 million miles away from Earth and primarily made of hydrogen, undergoing fusion that produces energy vital for life. The sun's chemical composition and influence have evolved over 4.6 billion years, affecting both scientific understanding and cultural significance.Satellites
SatellitesRileyAntler
╠²
Satellites are objects built and sent into Earth's orbit that transmit information to ground stations via radio waves. Communication satellites made wireless communication cheaper than telephone lines in the early 20th century by using digital systems. Weather satellites in geosynchronous orbit provide 24-hour monitoring of specific areas, while other satellites not in this orbit can track ships and fires from low Earth orbit. Remote sensing satellites in low orbit take images of the Earth's surface to send data on heat, resources, and urbanization. GPS satellites accurately track locations within a few meters via radio signals.Mercury and venus lesson
Mercury and venus lessonsarahdavenport63
╠²
Mercury is the closest planet to the sun and has temperatures ranging from 840┬░F to 4,980┬░F. Most of Mercury's surface is covered in impact craters like the Moon's surface. Its largest impact basin is the 1300 km wide Caloris Basin. Venus is the second closest planet to the sun and similar in size to Earth, but has surface temperatures over 900┬░F due to thick carbon dioxide and sulfur clouds. Venus is also the brightest planet and rotates clockwise unlike the other planets.Venus, the planet
Venus, the planetPatoEva
╠²
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting every 224 Earth days. It is the brightest object in the night sky after the Moon. Venus is closer to the Sun than Earth and orbits between the Earth and Sun. Venus is named after the Roman goddess of beauty and is the only planet named after a woman. While similar in size, mass, and gravity to Earth, Venus has the densest atmosphere of the rocky planets due to atmospheric pressure 92 times that of Earth.The planet venus
The planet venusHeather Huffman
╠²
Venus is Earth's closest planetary neighbor and similar in size, but has extreme environmental conditions. It has a toxic atmosphere of thick clouds and strong winds, with surface temperatures reaching over 900┬░F due to its slow rotation. While once thought an Earth-like planet, it is now known to have volcanoes and landscapes unlike our own, rotating backwards with days lasting four months.Meteors moons asteroids comets
Meteors moons asteroids cometstylerking5
╠²
Comets are icy, small solar system bodies that develop a coma and sometimes tails when close to the sun. They originate from the Kuiper belt and Oort cloud. Asteroids orbit the sun and are remnants of protoplanets. Meteoroids are sand to boulder sized objects in the solar system that produce meteors upon entering atmospheres. Moons orbit planets and dwarf planets. Having multiple moons would affect Earth's tides in complex ways depending on their interactions.The Universe - a great mystery
The Universe - a great mysteryErasmus+
╠²
Our universe contains many structures, including satellites, planets, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, stars, constellations, supernovae, nebulae, dark nebulae, black holes, blazars, quasars, and dark matter. It is largely unknown to us, and we only understand some basic components like satellites that orbit planets, planets that orbit stars, asteroids and meteoroids that orbit within solar systems, and comets that follow elliptical paths. Stars produce their own light, while constellations are groupings of stars, and supernovae are massive exploding stars. Nebulae are clouds of dust and gas where new stars are formed.Origin of-the-solar-system
Origin of-the-solar-systemjoycekim61
╠²
This document discusses theories of how the Solar System formed and describes the planets in our Solar System. It provides several early theories for how the Sun, Earth, and planets formed, including from swirling gases, explosions, collisions, and captured objects. The most widely accepted theory today is the nebular hypothesis, which suggests the Solar System formed from a contracting nebula. It then describes the eight planets - Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune - and some of their key properties.Sophie & char formation of the solar system
Sophie & char formation of the solar systemwhitmers
╠²
The solar system formed from a giant cloud of gas and dust that collapsed under gravity around the sun approximately 4.6 billion years ago. A supernova may have triggered the collapse of the cloud. The planets formed from circling disks of debris left over from the formation of the sun. While the sun contains 99.9% of the mass of the solar system, the planets combined contain 99.7% of its angular momentum due to their orbital motion. Water and other volatiles are found throughout the outer solar system, though Earth has by far the largest stores of liquid water.Astronomy unit 2011 SUN EARTH MOON SYSTEM acloutier copyright
Astronomy unit 2011 SUN EARTH MOON SYSTEM acloutier copyrightAnnie C. Cloutier
╠²
The document provides an overview of concepts in astronomy including:
1) It describes Earth's rotation, the moon's effect on Earth, and how this impacts seasons and timekeeping.
2) It explains how the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the sun cause the seasons and equinoxes and solstices.
3) It discusses technology that has expanded our ability to observe space like telescopes, interferometry, and photography.Solar System Compfor Teachers 1
Solar System Compfor Teachers 1aschae48
╠²
The document is an illustrated guide to the solar system that provides facts about the sun and eight planets in 3 sentences or less per planet. It includes information about the mythology and physical characteristics of each celestial body, and concludes with multiple choice questions about the content.Space[1]
Space[1]BF5040
╠²
This document provides an overview of our solar system, including brief descriptions of each planet and some key facts. It begins with an introduction noting that space is mysterious and unknown, with births and deaths of stars. It then summarizes each planet from Mercury to Pluto, highlighting one or two interesting facts about each, such as Mercury's fast orbit, Venus potentially having once supported life, Earth being the only known life-bearing planet, and Pluto taking 248 years to orbit the sun. The last two paragraphs note that Eris is the most distant known planet and that much remains unknown about it since its discovery in 2006.Venus
VenusMark Mikail
╠²
Venus can be seen from Earth and looks like the morning star before sunrise and the evening star after sunset. It orbits the sun every 225 days, compared to Earth's 365 day orbit. Venus is similar in size to Earth but is the hottest planet due to its dense carbon dioxide atmosphere and greenhouse effect, with surface temperatures over 800┬░F. The first spacecraft to land on Venus in 1975 sent back images, providing the first photos from the surface.Isabelle venus
Isabelle venusMrsCaron
╠²
Venus is the second planet from the sun and is similar in size to Earth. It has a thick, toxic atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide. Venus rotates clockwise and has an extremely hot surface temperature averaging between 480-870 degrees Fahrenheit due to its dense atmosphere. A day on Venus lasts over four Earth months and a year is over eight Earth months.Satellite
Satelliteaveejjeeva
╠²
Man-made satellites orbit Earth and other planets or moons. The idea of artificial satellites was first conceived by Isaac Newton through his thought experiment of firing a cannonball fast enough to achieve orbit. The first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched by the Soviet Union in 1957. There are two main types of satellites: geostationary satellites that orbit above the equator at 35,800 km and have a 24 hour period, and polar satellites that have a lower altitude of 500-800 km and orbit over the north and south poles with a period of 100 minutes. Satellites are used for scientific research, earth observation, communications, navigation, and military purposes.Satellite
Satellite Mudasir soomro
╠²
This document provides information about different types of satellites:
- Natural satellites are heavy bodies that orbit planets and shine by reflecting sunlight. The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. Mars has 2 natural satellites while Jupiter has 16.
- Artificial satellites are man-made satellites that orbit planets or other celestial bodies. Examples include communication and GPS satellites.
- Geostationary satellites orbit directly above the Earth's equator at the same rate that the Earth rotates, allowing them to remain fixed over one position. They are often used for communication.
- Polar stationary satellites orbit north to south over the poles in about 102 minutes at an altitude of 500 to 850 km. One such satellite was launched inThe solar system aimen
The solar system aimenShephali Bose
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and celestial bodies that revolve around it, including eight planets in order of their distance from the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The Sun is the central and largest body in the solar system, and is the primary source of energy for planets. Key facts about some of the planets include Mercury being the smallest and closest planet to the Sun, Venus being Earth's nearest neighbor, and Earth being the only known planet capable of supporting life.02 Venus -Godes of Love or Demon of Hell
02 Venus -Godes of Love or Demon of HellSyed Ali Salman
╠²
Venus is a bright object in the night sky, named after the Roman goddess of love, sex, and beauty, and has a rich history in mythology. NASA's Magellan spacecraft photographed the planet's surface, revealing its volcanoes and impact craters after being launched in 1989. A rare event occurred on June 5, 2012, when Venus crossed in front of the sun, with the next occurrence not expected until 2117.Solar system
Solar systemVaishnavi Sahu
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets, 5 dwarf planets, over 160 moons, 500,000 asteroids, over 3,000 comets, dust and gas. The accepted theory is that the Solar System formed from a giant cloud of gas and dust that collapsed under gravity, with particles in the center forming the Sun and particles in the outer edges forming the planets. Asteroids are minor planets that orbit the Sun in the inner Solar System, especially between Mars and Jupiter. They were historically called planetoids but the term asteroid now specifically refers to the small bodies of the inner Solar System.Planet Uranus
Planet Uranus Hawkesdale P12 College
╠²
Uranus has 27 known moons, with Oberon and Titania being the largest. The surfaces of the four largest moons are covered with craters formed by meteorites, and astronomers believe they are composed of ice and rock. Uranus has 13 dark, faint rings composed likely of ice and dust encircling its equator. Astronomers use telescopes to observe how Uranus orbits the sun in an oval path, taking 84 years to complete one revolution around a distance of approximately 3 billion kilometers from the sun. William Herschel first discovered Uranus in 1781 using a telescope.Solar system
Solar systemMaleeha Fatima
╠²
The document is about the solar system and its planets. It provides information on each planet, including Mercury being both very hot and cold, Venus being the hottest planet with dense clouds, and Mars appearing red due to its iron oxide surface. It also notes that Jupiter is the largest planet, Saturn has iconic rings, Uranus spins on its side, and Neptune appears blue due to methane in its atmosphere. Pluto is identified as the smallest planet that sometimes comes closer to the sun than Neptune.The solar system.
The solar system.SamyJJ
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that orbits around it, including 8 planets, moons, asteroids, comets and other space objects. The Sun contains over 99% of the mass in the solar system and is at the center. It is a medium-sized, yellow dwarf star that is over 4 billion years old. The planets can be divided into inner, rocky planets like Earth and outer gas giants like Jupiter that have rings.The Planet Venus
The Planet VenusHawar Silver
╠²
Venus is the second planet from the sun and is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. It shone the brightest of the five planets known to ancient astronomers. Venus has a dense, toxic atmosphere that causes a runaway greenhouse effect, making surface temperatures over 870 degrees Fahrenheit. The atmosphere is made up primarily of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds, and creates a surface pressure 90 times greater than Earth. Probes sent to Venus can only survive for a few hours on the surface before being destroyed by the extreme heat and acidic conditions.The Eight Planets
The Eight Planetshcudmore
╠²
The document discusses the 8 planets in our solar system - Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. It provides details about each planet's size, distance from the sun, rotation period, number of moons, and other characteristics. The inner planets are smaller and closer to the sun, while the outer planets are gas giants. The document also includes a short quiz about key facts regarding the planets.Cell theory etc ch1 section 1 cells and heredity july 22
Cell theory etc ch1 section 1 cells and heredity july 22Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
This document summarizes a classroom lesson on cells. Students had the option to work inside doing a guided question and answer activity from their textbook, or outside modeling the parts and functions of the cell. Inside, students answered questions about cell structures and the history of cell discovery. Outside, students acted out being different cell parts like the nucleus, mitochondria and cell membrane to demonstrate their functions. The class then discussed what they learned before returning inside to write answers about key cell parts.Study guide soil ecology and nat selection code 3
Study guide soil ecology and nat selection code 3Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document provides information about soil, ecosystems, food chains, natural selection, adaptations, and fossils. It explains that soil consists of living and nonliving materials like rocks, minerals, organisms, and dead plant and animal matter. Soil provides nutrients and support for plant growth. It also describes how food chains demonstrate the transfer of energy between organisms and defines natural selection as how organisms develop traits over generations to better survive in their environments. Adaptations are inherited traits that improve an organism's chances of survival, and fossils show how species have changed over long periods of time. Hands-on activities are suggested to help students understand these concepts.Solid liquid gas foldable
Solid liquid gas foldableMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document outlines instructions for creating a foldable to learn about the states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases. It details the steps for constructing the foldable, including folding techniques and labeling flaps with appropriate terms and drawings. Additionally, there is a requirement to research and include information about shape, volume, motion, color, and temperature of water in each state.More Related Content
What's hot (19)
Meteors moons asteroids comets
Meteors moons asteroids cometstylerking5
╠²
Comets are icy, small solar system bodies that develop a coma and sometimes tails when close to the sun. They originate from the Kuiper belt and Oort cloud. Asteroids orbit the sun and are remnants of protoplanets. Meteoroids are sand to boulder sized objects in the solar system that produce meteors upon entering atmospheres. Moons orbit planets and dwarf planets. Having multiple moons would affect Earth's tides in complex ways depending on their interactions.The Universe - a great mystery
The Universe - a great mysteryErasmus+
╠²
Our universe contains many structures, including satellites, planets, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, stars, constellations, supernovae, nebulae, dark nebulae, black holes, blazars, quasars, and dark matter. It is largely unknown to us, and we only understand some basic components like satellites that orbit planets, planets that orbit stars, asteroids and meteoroids that orbit within solar systems, and comets that follow elliptical paths. Stars produce their own light, while constellations are groupings of stars, and supernovae are massive exploding stars. Nebulae are clouds of dust and gas where new stars are formed.Origin of-the-solar-system
Origin of-the-solar-systemjoycekim61
╠²
This document discusses theories of how the Solar System formed and describes the planets in our Solar System. It provides several early theories for how the Sun, Earth, and planets formed, including from swirling gases, explosions, collisions, and captured objects. The most widely accepted theory today is the nebular hypothesis, which suggests the Solar System formed from a contracting nebula. It then describes the eight planets - Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune - and some of their key properties.Sophie & char formation of the solar system
Sophie & char formation of the solar systemwhitmers
╠²
The solar system formed from a giant cloud of gas and dust that collapsed under gravity around the sun approximately 4.6 billion years ago. A supernova may have triggered the collapse of the cloud. The planets formed from circling disks of debris left over from the formation of the sun. While the sun contains 99.9% of the mass of the solar system, the planets combined contain 99.7% of its angular momentum due to their orbital motion. Water and other volatiles are found throughout the outer solar system, though Earth has by far the largest stores of liquid water.Astronomy unit 2011 SUN EARTH MOON SYSTEM acloutier copyright
Astronomy unit 2011 SUN EARTH MOON SYSTEM acloutier copyrightAnnie C. Cloutier
╠²
The document provides an overview of concepts in astronomy including:
1) It describes Earth's rotation, the moon's effect on Earth, and how this impacts seasons and timekeeping.
2) It explains how the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the sun cause the seasons and equinoxes and solstices.
3) It discusses technology that has expanded our ability to observe space like telescopes, interferometry, and photography.Solar System Compfor Teachers 1
Solar System Compfor Teachers 1aschae48
╠²
The document is an illustrated guide to the solar system that provides facts about the sun and eight planets in 3 sentences or less per planet. It includes information about the mythology and physical characteristics of each celestial body, and concludes with multiple choice questions about the content.Space[1]
Space[1]BF5040
╠²
This document provides an overview of our solar system, including brief descriptions of each planet and some key facts. It begins with an introduction noting that space is mysterious and unknown, with births and deaths of stars. It then summarizes each planet from Mercury to Pluto, highlighting one or two interesting facts about each, such as Mercury's fast orbit, Venus potentially having once supported life, Earth being the only known life-bearing planet, and Pluto taking 248 years to orbit the sun. The last two paragraphs note that Eris is the most distant known planet and that much remains unknown about it since its discovery in 2006.Venus
VenusMark Mikail
╠²
Venus can be seen from Earth and looks like the morning star before sunrise and the evening star after sunset. It orbits the sun every 225 days, compared to Earth's 365 day orbit. Venus is similar in size to Earth but is the hottest planet due to its dense carbon dioxide atmosphere and greenhouse effect, with surface temperatures over 800┬░F. The first spacecraft to land on Venus in 1975 sent back images, providing the first photos from the surface.Isabelle venus
Isabelle venusMrsCaron
╠²
Venus is the second planet from the sun and is similar in size to Earth. It has a thick, toxic atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide. Venus rotates clockwise and has an extremely hot surface temperature averaging between 480-870 degrees Fahrenheit due to its dense atmosphere. A day on Venus lasts over four Earth months and a year is over eight Earth months.Satellite
Satelliteaveejjeeva
╠²
Man-made satellites orbit Earth and other planets or moons. The idea of artificial satellites was first conceived by Isaac Newton through his thought experiment of firing a cannonball fast enough to achieve orbit. The first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched by the Soviet Union in 1957. There are two main types of satellites: geostationary satellites that orbit above the equator at 35,800 km and have a 24 hour period, and polar satellites that have a lower altitude of 500-800 km and orbit over the north and south poles with a period of 100 minutes. Satellites are used for scientific research, earth observation, communications, navigation, and military purposes.Satellite
Satellite Mudasir soomro
╠²
This document provides information about different types of satellites:
- Natural satellites are heavy bodies that orbit planets and shine by reflecting sunlight. The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. Mars has 2 natural satellites while Jupiter has 16.
- Artificial satellites are man-made satellites that orbit planets or other celestial bodies. Examples include communication and GPS satellites.
- Geostationary satellites orbit directly above the Earth's equator at the same rate that the Earth rotates, allowing them to remain fixed over one position. They are often used for communication.
- Polar stationary satellites orbit north to south over the poles in about 102 minutes at an altitude of 500 to 850 km. One such satellite was launched inThe solar system aimen
The solar system aimenShephali Bose
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and celestial bodies that revolve around it, including eight planets in order of their distance from the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The Sun is the central and largest body in the solar system, and is the primary source of energy for planets. Key facts about some of the planets include Mercury being the smallest and closest planet to the Sun, Venus being Earth's nearest neighbor, and Earth being the only known planet capable of supporting life.02 Venus -Godes of Love or Demon of Hell
02 Venus -Godes of Love or Demon of HellSyed Ali Salman
╠²
Venus is a bright object in the night sky, named after the Roman goddess of love, sex, and beauty, and has a rich history in mythology. NASA's Magellan spacecraft photographed the planet's surface, revealing its volcanoes and impact craters after being launched in 1989. A rare event occurred on June 5, 2012, when Venus crossed in front of the sun, with the next occurrence not expected until 2117.Solar system
Solar systemVaishnavi Sahu
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets, 5 dwarf planets, over 160 moons, 500,000 asteroids, over 3,000 comets, dust and gas. The accepted theory is that the Solar System formed from a giant cloud of gas and dust that collapsed under gravity, with particles in the center forming the Sun and particles in the outer edges forming the planets. Asteroids are minor planets that orbit the Sun in the inner Solar System, especially between Mars and Jupiter. They were historically called planetoids but the term asteroid now specifically refers to the small bodies of the inner Solar System.Planet Uranus
Planet Uranus Hawkesdale P12 College
╠²
Uranus has 27 known moons, with Oberon and Titania being the largest. The surfaces of the four largest moons are covered with craters formed by meteorites, and astronomers believe they are composed of ice and rock. Uranus has 13 dark, faint rings composed likely of ice and dust encircling its equator. Astronomers use telescopes to observe how Uranus orbits the sun in an oval path, taking 84 years to complete one revolution around a distance of approximately 3 billion kilometers from the sun. William Herschel first discovered Uranus in 1781 using a telescope.Solar system
Solar systemMaleeha Fatima
╠²
The document is about the solar system and its planets. It provides information on each planet, including Mercury being both very hot and cold, Venus being the hottest planet with dense clouds, and Mars appearing red due to its iron oxide surface. It also notes that Jupiter is the largest planet, Saturn has iconic rings, Uranus spins on its side, and Neptune appears blue due to methane in its atmosphere. Pluto is identified as the smallest planet that sometimes comes closer to the sun than Neptune.The solar system.
The solar system.SamyJJ
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that orbits around it, including 8 planets, moons, asteroids, comets and other space objects. The Sun contains over 99% of the mass in the solar system and is at the center. It is a medium-sized, yellow dwarf star that is over 4 billion years old. The planets can be divided into inner, rocky planets like Earth and outer gas giants like Jupiter that have rings.The Planet Venus
The Planet VenusHawar Silver
╠²
Venus is the second planet from the sun and is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. It shone the brightest of the five planets known to ancient astronomers. Venus has a dense, toxic atmosphere that causes a runaway greenhouse effect, making surface temperatures over 870 degrees Fahrenheit. The atmosphere is made up primarily of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds, and creates a surface pressure 90 times greater than Earth. Probes sent to Venus can only survive for a few hours on the surface before being destroyed by the extreme heat and acidic conditions.The Eight Planets
The Eight Planetshcudmore
╠²
The document discusses the 8 planets in our solar system - Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. It provides details about each planet's size, distance from the sun, rotation period, number of moons, and other characteristics. The inner planets are smaller and closer to the sun, while the outer planets are gas giants. The document also includes a short quiz about key facts regarding the planets.More from Mad Science of Detroit (20)
Cell theory etc ch1 section 1 cells and heredity july 22
Cell theory etc ch1 section 1 cells and heredity july 22Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
This document summarizes a classroom lesson on cells. Students had the option to work inside doing a guided question and answer activity from their textbook, or outside modeling the parts and functions of the cell. Inside, students answered questions about cell structures and the history of cell discovery. Outside, students acted out being different cell parts like the nucleus, mitochondria and cell membrane to demonstrate their functions. The class then discussed what they learned before returning inside to write answers about key cell parts.Study guide soil ecology and nat selection code 3
Study guide soil ecology and nat selection code 3Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document provides information about soil, ecosystems, food chains, natural selection, adaptations, and fossils. It explains that soil consists of living and nonliving materials like rocks, minerals, organisms, and dead plant and animal matter. Soil provides nutrients and support for plant growth. It also describes how food chains demonstrate the transfer of energy between organisms and defines natural selection as how organisms develop traits over generations to better survive in their environments. Adaptations are inherited traits that improve an organism's chances of survival, and fossils show how species have changed over long periods of time. Hands-on activities are suggested to help students understand these concepts.Solid liquid gas foldable
Solid liquid gas foldableMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document outlines instructions for creating a foldable to learn about the states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases. It details the steps for constructing the foldable, including folding techniques and labeling flaps with appropriate terms and drawings. Additionally, there is a requirement to research and include information about shape, volume, motion, color, and temperature of water in each state.Snowflakes with mi benchmarks slideshow draft
Snowflakes with mi benchmarks slideshow draftMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document outlines a highly differentiated chemistry lesson for ninth graders, focused on understanding the states of matter and the behavior of water, including ice and snowflakes. It includes objectives, prerequisite knowledge, and various assessments such as pretests and post-tests, as well as vocabulary related to the topic. The lesson emphasizes concepts like particle arrangement, density, and energy changes during phase transitions.Building molecules
Building moleculesMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document outlines a chemistry lesson plan focused on building molecules, naming ionic and covalent compounds, and associated homework tasks. Students are to utilize a simulation tool and textbook resources to complete quizzes and practice problems, emphasizing both independent and collaborative learning. Instruction includes examples of naming compounds and identifying chemical formulas.Tuesday, april 27, 2010
Tuesday, april 27, 2010Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document is a chemistry teacher's daily lesson plan from April 27, 2010. It includes the daily agenda, assignments due, and a presentation on Avogadro's number. The presentation defines Avogadro's number as 6.02 x 1023, explains how many items are in a mole, and provides examples of moles of carbon atoms and donuts. It also gives background on Amadeo Avogadro and how his constant is calculated using X-ray crystallography of silicon.Tuesday july 27, 2010
Tuesday july 27, 2010Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document summarizes a playdate between two families with young children. It lists activities the children engaged in such as visiting the planetarium, playing in Joey's room, having lunch outside, eating snacks, playing with balloons and paper, reading outside, putting paper dots on a dog, hitting targets, using a baby swing, and playing in compost with pitchforks. It ended up being a long day and now it was time to rest, dedicating the day to both families.100810.ppt
100810.pptMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document provides an agenda for a physics class that will focus on Newton's Three Laws of Motion. It lists homework on the laws due on Monday and a "Do Now" activity rewriting a statement in everyday language. The class will then compare and contrast the three laws through group presentations, with each group responsible for defining one law, providing examples and diagrams, and including relevant math formulas. Presentation 1 is scheduled to start at 8:45 am.100110 chem a gall ihs
100110 chem a gall ihsMad Science of Detroit
╠²
This document contains a chemistry teacher's lesson plan for their 4th and 5th hour classes on October 1, 2010. The lesson plan includes having students answer questions about electron, neutron and proton charges as a "Do Now" activity. It instructs students to study the names and symbols of the first 20 elements for homework. The lesson will focus on teaching students the internal structure of the modern atomic model, and having them apply their knowledge using a model of an atom. It outlines notes, a quiz and assessment activities for students.093010 chem a
093010 chem aMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document is notes from a chemistry lesson discussing the historical development of the atomic theory. It includes homework assignments on the first 20 elements, a smallest piece of paper contest, and questions about early atomic models like the plum pudding model. A post-test reviews key concepts like the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in atoms, different atomic models, and the discoverer of the periodic table.092910 isa ihs
092910 isa ihsMad Science of Detroit
╠²
This document contains notes from an integrated science class taught by Mrs. Gall. It outlines the daily lesson plan which includes reviewing concepts of scientific method, velocity, distance, and time. Students are asked to complete a safety contract and lab demonstration on circular motion as homework. The safety contract must be signed and returned the next day.092810 isa ihs
092810 isa ihsMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document provides an overview of classroom activities for the day, including completing a Do Now activity, reviewing lesson steps, discussing the Do Now, and returning graded work with opportunities for late credit. It mentions an upcoming quiz on how to prepare and that safety contracts will be coming soon. It outlines homework, a response time lab, and a demonstration on circular motion. It asks students to list three forces and identify them as contact or non-contact and to identify forces acting between objects in direct contact or at a distance.Wpa open house science dept 3
Wpa open house science dept 3Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document outlines the science curriculum and requirements for middle and high school students. It details the science classes taken each year from grades 6 through 11, required credits for graduation, teachers and their subjects, assignments, and information about trimesters including length, progress reports, exams, and report cards.Week 6 101110 gall int sci
Week 6 101110 gall int sciMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document discusses a science class lesson on mixtures. It includes instructions for homework on physics equations, a discussion of mixtures versus compounds, and a quiz on mixtures. The class debated whether air or sugar is a mixture, and the quiz asked students how long they remained silent during the quiz and to list two components of air. The document also provides test taking strategy notes.Week 6 101110 gall chem.
Week 6 101110 gall chem.Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document provides instructions and notes for homework, aims of a lesson, and information about atoms and their structure. It discusses how a helium balloon will leak over time as helium atoms escape through the balloon wall. It also lists electron configurations and locations in atoms and provides assignments due on atoms, elements, and atomic structure to be completed.Tuesday july 27, 2010
Tuesday july 27, 2010Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
Gall and Lasky took their sons Joey and Buffy on a playdate that included a visit to the planetarium, playing in Joey's room, having lunch, eating yogurt snacks, playing with balloons and paper, reading outside, playing a target game where Buffy had paper dots put on him, sitting in a baby swing, and working in the compost pile before resting at the end of a long day. The presentation is dedicated to both of their families for helping raise their children.Physics midterm-review-1200447658210237-3
Physics midterm-review-1200447658210237-3Mad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document discusses the scientific method and its connection to investigating a car accident. It describes the stages of observation, developing hypotheses, testing hypotheses through experiments, reinterpreting evidence and revising hypotheses, and reaching a conclusion. It provides examples of how each stage would be applied in investigating a hypothetical car accident.Physics student presentation jan 2010 artifact gall
Physics student presentation jan 2010 artifact gallMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts from chaos theory and fractal geometry. It defines chaos theory as the field studying how dynamical systems can be highly sensitive to initial conditions. The butterfly effect metaphorically describes how small differences in initial conditions can lead to large variations over time. Fractals are geometric shapes that can be split into parts that are reduced-size copies of the whole. Different types of fractals are described including escape-time, iterated function systems, random, and strange attractors.Perseids
PerseidsMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The Perseid meteor shower occurs each August when the Earth passes through debris left behind by Comet Swift-Tuttle, causing specks of comet material entering the atmosphere at over 140,000 mph to disintegrate and appear as flashes of light. The shower is a popular night sky event as debris from the comet intersects with our planet each year.Observatory outreach scripts outlined briefly
Observatory outreach scripts outlined brieflyMad Science of Detroit
╠²
The document provides an outline for tour scripts of the observatory at the University of Michigan Dearborn. It divides the tour into five sections - the atrium, vestibule, observation deck, control room, and dome. For each section, it lists key things to point out and topics to cover such as available assistance, restrooms, presentations, telescope types, equipment used, and typical procedures. The goal is to guide visitors through the observatory spaces and provide an overview of its features and operations.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Wenn alles versagt - IBM Tape sch├╝tzt, was z├żhlt! Und besonders mit dem neust...
Wenn alles versagt - IBM Tape sch├╝tzt, was z├żhlt! Und besonders mit dem neust...Josef Weingand
╠²
IBM LTO10You are not excused! How to avoid security blind spots on the way to production
You are not excused! How to avoid security blind spots on the way to productionMichele Leroux Bustamante
╠²
We live in an ever evolving landscape for cyber threats creating security risk for your production systems. Mitigating these risks requires participation throughout all stages from development through production delivery - and by every role including architects, developers QA and DevOps engineers, product owners and leadership. No one is excused! This session will cover examples of common mistakes or missed opportunities that can lead to vulnerabilities in production - and ways to do better throughout the development lifecycle.FIDO Seminar: Targeting Trust: The Future of Identity in the Workforce.pptx
FIDO Seminar: Targeting Trust: The Future of Identity in the Workforce.pptxFIDO Alliance
╠²
FIDO Seminar: Targeting Trust: The Future of Identity in the WorkforceWar_And_Cyber_3_Years_Of_Struggle_And_Lessons_For_Global_Security.pdf
War_And_Cyber_3_Years_Of_Struggle_And_Lessons_For_Global_Security.pdfbiswajitbanerjee38
╠²
Russia is one of the most aggressive nations when it comes to state coordinated cyberattacksŌĆŖŌĆöŌĆŖand Ukraine has been at the center of their crosshairs for 3 years. This report, provided the State Service of Special Communications and Information Protection of Ukraine contains an incredible amount of cybersecurity insights, showcasing the coordinated aggressive cyberwarfare campaigns of Russia against Ukraine.
It brings to the forefront that understanding your adversary, especially an aggressive nation state, is important for cyber defense. Knowing their motivations, capabilities, and tactics becomes an advantage when allocating resources for maximum impact.
Intelligence shows Russia is on a cyber rampage, leveraging FSB, SVR, and GRU resources to professionally target UkraineŌĆÖs critical infrastructures, military, and international diplomacy support efforts.
The number of total incidents against Ukraine, originating from Russia, has steadily increased from 1350 in 2021 to 4315 in 2024, but the number of actual critical incidents has been managed down from a high of 1048 in 2022 to a mere 59 in 2024ŌĆŖŌĆöŌĆŖshowcasing how the rapid detection and response to cyberattacks has been impacted by UkraineŌĆÖs improved cyber resilience.
Even against a much larger adversary, Ukraine is showcasing outstanding cybersecurity, enabled by strong strategies and sound tactics. There are lessons to learn for any enterprise that could potentially be targeted by aggressive nation states.
Definitely worth the read!FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon.pptx
FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon.pptxFIDO Alliance
╠²
FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - AmazonCrypto Super 500 - 14th Report - June2025.pdf
Crypto Super 500 - 14th Report - June2025.pdfStephen Perrenod
╠²
This OrionX's 14th semi-annual report on the state of the cryptocurrency mining market. The report focuses on Proof-of-Work cryptocurrencies since those use substantial supercomputer power to mint new coins and encode transactions on their blockchains. Only two make the cut this time, Bitcoin with $18 billion of annual economic value produced and Dogecoin with $1 billion. Bitcoin has now reached the Zettascale with typical hash rates of 0.9 Zettahashes per second. Bitcoin is powered by the world's largest decentralized supercomputer in a continuous winner take all lottery incentive network.MuleSoft for AgentForce : Topic Center and API Catalog
MuleSoft for AgentForce : Topic Center and API Catalogshyamraj55
╠²
This presentation dives into how MuleSoft empowers AgentForce with organized API discovery and streamlined integration using Topic Center and the API Catalog. Learn how these tools help structure APIs around business needs, improve reusability, and simplify collaboration across teams. Ideal for developers, architects, and business stakeholders looking to build a connected and scalable API ecosystem within AgentForce.No-Code Workflows for CAD & 3D Data: Scaling AI-Driven Infrastructure
No-Code Workflows for CAD & 3D Data: Scaling AI-Driven InfrastructureSafe Software
╠²
When projects depend on fast, reliable spatial data, every minute counts.
AI Clearing needed a faster way to handle complex spatial data from drone surveys, CAD designs and 3D project models across construction sites. With FME Form, they built no-code workflows to clean, convert, integrate, and validate dozens of data formats ŌĆō cutting analysis time from 5 hours to just 30 minutes.
Join us, our partner Globema, and customer AI Clearing to see how they:
-Automate processing of 2D, 3D, drone, spatial, and non-spatial data
-Analyze construction progress 10x faster and with fewer errors
-Handle diverse formats like DWG, KML, SHP, and PDF with ease
-Scale their workflows for international projects in solar, roads, and pipelines
If you work with complex data, join us to learn how to optimize your own processes and transform your results with FME.OpenACC and Open Hackathons Monthly Highlights June 2025
OpenACC and Open Hackathons Monthly Highlights June 2025OpenACC
╠²
The OpenACC organization focuses on enhancing parallel computing skills and advancing interoperability in scientific applications through hackathons and training. The upcoming 2025 Open Accelerated Computing Summit (OACS) aims to explore the convergence of AI and HPC in scientific computing and foster knowledge sharing. This year's OACS welcomes talk submissions from a variety of topics, from Using Standard Language Parallelism to Computer Vision Applications. The document also highlights several open hackathons, a call to apply for NVIDIA Academic Grant Program and resources for optimizing scientific applications using OpenACC directives."How to survive Black Friday: preparing e-commerce for a peak season", Yurii ...
"How to survive Black Friday: preparing e-commerce for a peak season", Yurii ...Fwdays
╠²
We will explore how e-commerce projects prepare for the busiest time of the year, which key aspects to focus on, and what to expect. WeŌĆÖll share our experience in setting up auto-scaling, load balancing, and discuss the loads that Silpo handles, as well as the solutions that help us navigate this season without failures.Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free Download
Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free DownloadPuppy jhon
╠²
Ō×Ī ¤īŹ¤ō▒¤æēCOPY & PASTE LINK¤æē¤æē¤æē Ō׿ Ō׿Ō׿ https://drfiles.net/
Wondershare Filmora Crack is a user-friendly video editing software designed for both beginners and experienced users.
Edge-banding-machines-edgeteq-s-200-en-.pdf
Edge-banding-machines-edgeteq-s-200-en-.pdfAmirStern2
╠²
ū×ūøūĢūĀū¬ ū¦ūĀūśūÖūØ ūöū×ū¬ūÉūÖū×ūö ū£ūĀūÆū©ūÖūĢū¬ ū¦ūśūĀūĢū¬ ūÉūĢ ūÆūōūĢū£ūĢū¬ (ūøū×ūøūĢūĀū¬ ūÆūÖūæūĢūÖ).
ū×ūōūæūÖū¦ūö ū¦ūĀūśūÖūØ ū×ūÆū£ūÖū£ ūÉūĢ ūżūĪūÖūØ, ūóūō ūóūĢūæūÖ ū¦ūĀūś ŌĆō 3 ū×"ū× ūĢūóūĢūæūÖ ūŚūĢū×ū© ūóūō 40 ū×"ū×. ūæū¦ū© ū×ū×ūĢūŚū®ūæ ūöū×ū¬ū©ūÖūó ūóū£ ū¬ū¦ū£ūĢū¬, ūĢū×ūĀūĢūóūÖūØ ū×ūÉūĪūÖūæūÖūÖūØ ū¬ūóū®ūÖūÖū¬ūÖūÖūØ ūøū×ūĢ ūæū×ūøūĢūĀūĢū¬ ūöūÆūōūĢū£ūĢū¬.Creating Inclusive Digital Learning with AI: A Smarter, Fairer Future
Creating Inclusive Digital Learning with AI: A Smarter, Fairer FutureImpelsys Inc.
╠²
Have you ever struggled to read a tiny label on a medicine box or tried to navigate a confusing website? Now imagine if every learning experience felt that wayŌĆöevery single day.
For millions of people living with disabilities, poorly designed content isnŌĆÖt just frustrating. ItŌĆÖs a barrier to growth. Inclusive learning is about fixing that. And today, AI is helping us build digital learning thatŌĆÖs smarter, kinder, and accessible to everyone.
Accessible learning increases engagement, retention, performance, and inclusivity for everyone. Inclusive design is simply better design.June Patch Tuesday
June Patch TuesdayIvanti
╠²
IvantiŌĆÖs Patch Tuesday breakdown goes beyond patching your applications and brings you the intelligence and guidance needed to prioritize where to focus your attention first. Catch early analysis on our Ivanti blog, then join industry expert Chris Goettl for the Patch Tuesday Webinar Event. There weŌĆÖll do a deep dive into each of the bulletins and give guidance on the risks associated with the newly-identified vulnerabilities. "Database isolation: how we deal with hundreds of direct connections to the d...
"Database isolation: how we deal with hundreds of direct connections to the d...Fwdays
╠²
What can go wrong if you allow each service to access the database directly? In a startup, this seems like a quick and easy solution, but as the system scales, problems appear that no one could have guessed.
In my talk, I'll share Solidgate's experience in transforming its architecture: from the chaos of direct connections to a service-based data access model. I will talk about the transition stages, bottlenecks, and how isolation affected infrastructure support. I will honestly show what worked and what didn't. In short, we will analyze the controversy of this talk.Connecting Data and Intelligence: The Role of FME in Machine Learning
Connecting Data and Intelligence: The Role of FME in Machine LearningSafe Software
╠²
In this presentation, we want to explore powerful data integration and preparation for Machine Learning. FME is known for its ability to manipulate and transform geospatial data, connecting diverse data sources into efficient and automated workflows. By integrating FME with Machine Learning techniques, it is possible to transform raw data into valuable insights faster and more accurately, enabling intelligent analysis and data-driven decision making.Securing Account Lifecycles in the Age of Deepfakes.pptx
Securing Account Lifecycles in the Age of Deepfakes.pptxFIDO Alliance
╠²
Securing Account Lifecycles in the Age of DeepfakesTurning the Page ŌĆō How AI is Exponentially Increasing Speed, Accuracy, and Ef...
Turning the Page ŌĆō How AI is Exponentially Increasing Speed, Accuracy, and Ef...Impelsys Inc.
╠²
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer in content creation, automating tasks that were once very time-consuming and labor-intensive. AI-powered tools are now capable of generating high-quality articles, blog posts, and even poetry by analyzing large datasets of text and producing human-like writing.
However, AIŌĆÖs influence on content generation is not limited to text; it has also made advancements in multimedia content, such as image, video, and audio generation. AI-powered tools can now transform raw images and footage into visually stunning outputs, and are all set to have a profound impact on the publishing industry.Information Security Response Team Nepal_npCERT_Vice_President_Sudan_Jha.pdf
Information Security Response Team Nepal_npCERT_Vice_President_Sudan_Jha.pdfICT Frame Magazine Pvt. Ltd.
╠²
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly changing the face of cybersecurity across the globe. In Nepal, the shift is already underway. Vice President of the Information Security Response Team Nepal (npCERT) and Information Security Consultant at One Cover Pvt. Ltd., Sudan Jha, recently presented an in-depth workshop on how AI can strengthen national security and digital defenses.You are not excused! How to avoid security blind spots on the way to production
You are not excused! How to avoid security blind spots on the way to productionMichele Leroux Bustamante
╠²
Information Security Response Team Nepal_npCERT_Vice_President_Sudan_Jha.pdf
Information Security Response Team Nepal_npCERT_Vice_President_Sudan_Jha.pdfICT Frame Magazine Pvt. Ltd.
╠²
Ad
Perseieds
- 1. PERSEIEDS Public viewingpresented byUniversity of michigandearbornobservatory outreach
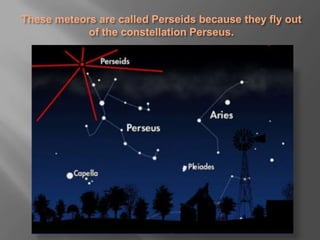
- 2. These meteors are called Perseids because they fly out of the constellation Perseus.
- 3. The Perseid meteor shower is caused by debris from Comet Swift-Tuttle. Every 133 years the huge comet swings through the inner solar system and leaves behind a trail of dust and gravel. When Earth passes through the debris, specks of comet-stuff hit the atmosphere at 140,000 mph and disintegrate in flashes of light.
- 4. The Perseidsare a popular attraction in the night sky in August each year.
