Personal characteristics 01
- 1. Personality Type Ladies and Gentlemen, Well IŌĆÖve been in role for a month now and, as discussed and agreed weŌĆÖre about to commence with the one to one sessions throughout the department. Since moving into the role of Facilities General Manager (hard services), weŌĆÖve had the initial meeting followed by the team talk (last Friday), added to this IŌĆÖve held three management meetings in my office (with the next one being next Wednesday at SMH). All of this was in the first information sheet sent out, with the second one due to be issued at the beginning of next month. So whatŌĆÖs this document about? As stated at our first meeting, the biggest problem the department has is communication and I thought that to develop this IŌĆÖd prepare a piece on my personality type. The aim of this is two fold, firstly to give you all an insight into why and how I do things and secondly to show that whilst people do have strengths they also have weaknesses, but as part of a team we learn to use each others strengths and support each others weaknesses and what better place to start than looking at that my personality type. To assist me in putting this over to you, IŌĆÖll be using two publications used on the Raising our Game (RoG) training programmes. The information in the attached is taken from these and are not my words (in most instances) a. Introduction to type (6th Edition) by Isabel Briggs Myers b. Introduction to type and communication by Donna dunning Within the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) there are a total of sixteen types they are as show in the table below; ISTJ ISFJ INFJ INTJ ISTP ISFP INFP INTP ESTP ESFP ENFP ENTP ESTJ ESFJ ENFJ ENTJ I happen to be in the ENTP area. So what does that mean? The aim of this paper is to highlight highs and lows in this type so that you have a better understanding of me, my actions and how to work with me. E- Extraversion. People who prefer extraversion like to focus on the outer world of people and activity. They direct their energy and attention outward and receive energy from interacting with people and from taking action.
- 2. Personality Type Characteristics associated with people who prefer extraversion: ’ā« Attuned to external environment ’ā« Prefer to communicate by talking ’ā« Work out ideas by talking them through ’ā« Learn best through doing or discussing ’ā« Have broad interests ’ā« Sociable and expressive ’ā« Readily take initiative in work and relationships N - Intuition. People who prefer intuition like to take in information by seeing the big picture, focusing on the relationships and connections between facts. They want to grasp patterns and are especially attuned to seeing new possibilities. Characteristics associated with people who prefer intuition: ’ā« Oriented to future possibilities ’ā« Imaginative and verbally creative ’ā« Focus on the pattern and meanings in data ’ā« Remembers details when they relate to a pattern ’ā« Moves quickly to conclusions, follow hunches ’ā« Want to clarify ideas and theories before putting them into practice ’ā« Trust inspiration T - Thinking. People who prefer to use thinking in decision making like to look at the logical consequences of a choice or action. They want to remove themselves mentally from the situation to examine the pros and cons objectively. They are energised by evaluating and analysing to identify whatŌĆÖs wrong with something so they can solve the problem. Their goal is to find a standard or principle that will apply in all similar situations. Characteristics associated with people who prefer thinking: ’ā« Analytical ’ā« Use cause-and-effect reasoning ’ā« Solve problems logically ’ā« Reasonable ’ā« Can be ŌĆ£Tough-mindedŌĆØ ’ā« Fair ŌĆō want everyone treated equally
- 3. Personality Type P - Perceiving. People who prefer to use their perceiving process in the outer world like to live in a flexible, spontaneous way, seeking to experience and understand life, rather than control it. Detailed plans and final decisions feel confining to them; they prefer to stay open to new information and last-minute options. They are energised by their resourcefulness in adapting to the demands of the moment. Characteristics associated with people who prefer perceiving; ’ā« Spontaneous ’ā« Flexible ’ā« Casual ’ā« Open-ended ’ā« Adapt, change course ’ā« Like things loose and open to change ’ā« Feel energised by last minute pressure It then goes on to say about the characteristics ŌĆ£Flexible and tolerant, they take a pragmatic approach focused on immediate results. Theories and conceptual explanations bore them ŌĆō they want to act energetically to solve the problem. Focus on the here-and-now, spontaneous, enjoy each moment that they can be active with others. Enjoy material comforts and style. Learn best through doing. So what is an ENTP personality type like? At their best People with ENTP preferences constantly scan the environment for opportunities and possibilities. They see patterns and connections not obvious to others at the time and at times seem able to see into the future. They are adept at generating conceptual possibilities and the analysing the strategically. ENTPs are good at understanding how systems work and are enterprising and resourceful in manoeuvring within then to achieve their ends. Characteristics of ENTPs ENTPs are enthusiastic innovators. Their world is full of possibilities, interesting concepts and exciting challenges. They are stimulated by difficulties, quickly devising creative responses and plunging into activity, trusting their ability to improvise. They use their intuition primarily externally and enjoy exercising ingenuity in the world. ENTPs are likely to be:
- 4. Personality Type ’ā« Creative, imaginative and clever ’ā« Theoretical, conceptual and curious ENTPs are enterprising, resourceful, active and energetic. They respond to challenging problems by creating complex and global solutions. They are usually adept at ŌĆ£readingŌĆØ other people, seeing how to motivate them, and assuming leadership. They can do almost anything that captures their interest. How others may see them (in this instance me) ENTPs are spontaneous and adaptable. They find schedules and standard operating procedures confining and work around them whenever possible. They possess remarkable insight into the attitudes of others, and their enthusiasm and energy can mobilise people to support their vision. Their conversational style is customarily challenging and stimulating because they love to debate ideas. They are fluent conversationalists, mentally quick, and enjoy verbal sparring. When they express their underlying thinking principles, however, they may with an intensity and abruptness that seem to challenge others. Others usually see ENTPs as: ’ā« Independent, autonomous and creative ’ā« Lively, enthusiastic and energetic ’ā« Assertive and outspoken Potential areas of growth If ENTPs do not find where they can use their gifts and be appreciated for their contribution, they usually feel frustrated and may: ’ā« Become brash, rude and abrasive ’ā« Criticise others, especially those who seem to them to be inefficient or incompetent ’ā« Become rebellious and combative ’ā« Become scattered ŌĆō unable to focus It is natural for ENTPs to give less attention to their non-preferred Sensing and Feeling parts. If they neglect these too much, however, they may: ’ā« Not take care of the detail and routine required to implement insights ’ā« Not give enough weight to the impact on others of their ideas and plans ’ā« Be excessively and inappropriately ŌĆ£challenging and stimulatingŌĆØ.
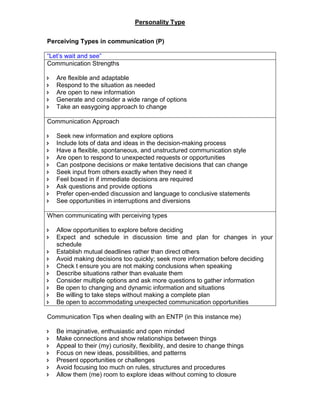
- 5. Personality Type Using type preference combinations Combinations of energy and external orientations: Dealing with change EP ŌĆō Adaptable Extraverts ŌĆō When changes are proposed, they consult their network, talk to people, find out what everyone thinks. If changes allow room for their creativity and action, they gather resources and try to energise everyone to implement the changes Combination of perception and judgement: Career interests Perception (S or N) Judging (T or F) - NT Focus on Possibilities Handling these by applying: Theoretical concepts and systems Thus tend to become: Logical and analytical Find scope for their interests in: Theoretical and technical framework For example: Physical science, research, management, computers, law engineering and technical work Combinations of energy orientation and perception: Uses of information Orientation of energy (E or I) and perception (S or N) ŌĆō EN EN Action-oriented innovators Knowledge is important for changing reality Combination of judgment and external orientation: leading/following styles Combination of judgment function (T or F) and the preferred orientation to the external world (J or P) - TP TP Adaptable problem solving Lead by example. Value and display technical expertise, and create consistent and orderly frameworks for working. Objective, sceptical and curious, will change course as new information comes in. Effective problem solvers, if interested. The Temperaments - NT ŌĆ£RationalŌĆØ Theory-oriented: Seek to understand the principles on which the world and things in it work. Trust logic and reason, sceptical and precise. Think in terms of differences, categories, definitions and structure. Focus on strategies and designs that achieve long-range goals and lead to progress. Want competence and thorough knowledge.
- 6. Personality Type Learning styles Interested in: Theories and global explanations about why the world works the way it does Learn best by: Categorising, analysing, applying logic Need: To be given a big problem to solve, an intellectual challenge, and then to be allowed to work it out. Want from teacher: To be treated with respect, to respect the teacherŌĆÖs competence So as an ENTP how do I function in this arena? Extraversion (E) ŌĆ£LetŌĆÖs talk this overŌĆØ Individuals with a preference for extraversion tend to: ’ā« Focus their energy and process information externally ’ā« Dislike working on one thing for a long time, especially if they must do it on their own ’ā« Learn and work best when able to share, discuss, and process information with others ’ā« Ask questions and think out aloud during activities or while working through decisions ’ā« Understand their world best by acting on it or talking about it Intuition (N) ŌĆ£I can see it all nowŌĆØ Individuals who prefer Intuition tend to: ’ā« Focus first on what facts mean and how they fit together; see links, possibilities, and relationships. ’ā« Pay more attention to connections and implementations between facts than to facts and detail alone ’ā« Prefer information that is introduced with a ŌĆ£big pictureŌĆØ overview; jump around between ideas and tasks ’ā« Have bursts of energy rather than stamina ’ā« Become bored or impatient with tasks that required considerable focus on detail, routines, or sequencing. ’ā« Like creating ideas and possibilities; have a future and change focus
- 7. Personality Type Thinking (T) ŌĆ£Is this logicalŌĆØ Individuals that prefer thinking tend to: ’ā« Evaluate situations by focusing on logic and analysis ’ā« Be most influenced by objective data and cause-and-effect relationships ’ā« Consider pros and cons of ideas, information, and opinions ’ā« Make decisions based mainly on logic ’ā« Prefer calm, objective interactions, often see work and private life as separate ’ā« Spot flaws and provide constructive feedback Perceiving (P) ŌĆ£LetŌĆÖs wait and seeŌĆØ Individuals with a perceiving orientation tend to: ’ā« Defer judgment and gather more information; like to keep their options open ’ā« Act spontaneously and leave things to the last minute ’ā« Prefer starting projects to following through with projects ’ā« Be frustrated by rules, routines, and highly structured tasks ’ā« Be open, flexible and adaptable Extraverts in communication (E) ŌĆ£Lets Talk about itŌĆØ Communication Strengths ’ā« Are active, energetic, and enthusiastic ’ā« Think on their feet ’ā« Establish networks of contacts ’ā« Have breadth of interest ’ā« Provide extensive information and feedback Communication Approach ’ā« Seek interactions and diversions ’ā« Share thoughts freely in lively group discussions ’ā« Can discuss a wide range of topics ’ā« Change topics and opinions as a dialogue progresses ’ā« Think out load ’ā« Share ideas or information immediately ’ā« Respond rapidly ’ā« Talk more than listed ’ā« Overlap air space and interrupt others ’ā« Ask lots of spur-of-the-moment questions
- 8. Personality Type When communicating with Extraverts ’ā« Acknowledge you are listening and use cues to show you are preparing a response ’ā« Provide immediate feedback and verbal acknowledgement ’ā« Express overt interest and enthusiasm; lean forward, nod, smile , and maintain eye contact ’ā« If needed, ask for time to think about something, then set a time to communicate ’ā« Anticipate other will want feedback and be prepared to share more information sooner ’ā« Focus on discussing topics you know well or have had chance to consider ’ā« Seek networking opportunities; find someone to help you make links and contacts ’ā« Take initiative to introduce yourself or start a conversation ’ā« Deal with conflict and be willing to confront issues when they occur ’ā« Remember other often think loud, so donŌĆÖt assume words are well thought out Intuitive Types in communication (N) ŌĆ£I can see it all nowŌĆØ Communication Strengths ’ā« Are open to possibilities ’ā« Anticipate and create change ’ā« Are future oriented; see trends ’ā« Link and integrate information ’ā« Generate Ideas Communication Approach ’ā« Want implications and relationships, not just facts ’ā« Become board or impatient with detail ’ā« Like to brainstorm or play with ideas and imagine what could be ’ā« Focus on future and long-term aspects and impact ’ā« See patterns and understand the big picture ’ā« Are stimulated by possibilities; seek to create, grasp and share new ideas ’ā« Use metaphors, analogies, and other forms of symbolic language ’ā« In conversation, may jump across topics exploring links ’ā« Trust and are eager to apply theories, models and frameworks ’ā« DonŌĆÖt like to be hampered by barriers or limits When communicating with intuitive types ’ā« Consider possibilities that may initially seem farfetched ’ā« Provide an overview or thumbnail sketch first ’ā« Suspend realities when necessary to brainstorm and generate ideas ’ā« DonŌĆÖt get bogged down in facts and detail
- 9. Personality Type ’ā« Share main points, then add some detail as necessary ’ā« Stretch towards taking a longer-term, future focus ’ā« Shoe future possibilities of your ideas ’ā« Trust what works and be open to changing what doesnŌĆÖt work ’ā« Let others share your ideas and dreams ’ā« Provide a reality check without discarding ideas; help intuitive types link ideas to reality Thinking Types in communication (T) ŌĆ£Is this logicalŌĆØ Communication Strengths ’ā« Calm, reasonable, and under control ’ā« Provide honest and frank feedback ’ā« Analyse, evaluate and critique ’ā« Objective and principled ’ā« Clear thinking process using defined criteria Communication Approach ’ā« Use logic and analysis to spot flaws or weaknesses ’ā« Need to know ŌĆ£why?ŌĆØ ’ā« Prefer information that is presented objectively as a matter of fact ’ā« Debate or challenge information ’ā« List and cider pros and cons ’ā« Create or use clearly defined criteria ’ā« Trust competence and expertise ’ā« Like competence and want to win ’ā« Use precise and concise language ’ā« Task and goal focused When communicating with thinking types ’ā« Be calmly objective and demonstrate your competence ’ā« Offer honest and frank feedback as positive comments ’ā« Detach situation and view them logically and objectively ’ā« Support your opinions with logical reasoning and clear thinking ’ā« Avoid becoming overly emotional or passionate when discussing issues ’ā« Be logical, reasonable, clear, precise, and concise ’ā« Focus on tasks and objectives as well as on individuals involved in the situation ’ā« DonŌĆÖt feel threatened or attacked when others like to compete, debate, or challenge ’ā« Show cause-and-effect relationships and pros and cons ’ā« Accept critical feedback without personalising it
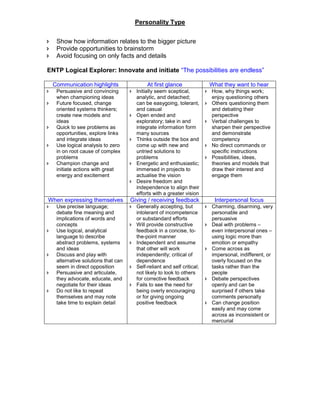
- 10. Personality Type Perceiving Types in communication (P) ŌĆ£LetŌĆÖs wait and seeŌĆØ Communication Strengths ’ā« Are flexible and adaptable ’ā« Respond to the situation as needed ’ā« Are open to new information ’ā« Generate and consider a wide range of options ’ā« Take an easygoing approach to change Communication Approach ’ā« Seek new information and explore options ’ā« Include lots of data and ideas in the decision-making process ’ā« Have a flexible, spontaneous, and unstructured communication style ’ā« Are open to respond to unexpected requests or opportunities ’ā« Can postpone decisions or make tentative decisions that can change ’ā« Seek input from others exactly when they need it ’ā« Feel boxed in if immediate decisions are required ’ā« Ask questions and provide options ’ā« Prefer open-ended discussion and language to conclusive statements ’ā« See opportunities in interruptions and diversions When communicating with perceiving types ’ā« Allow opportunities to explore before deciding ’ā« Expect and schedule in discussion time and plan for changes in your schedule ’ā« Establish mutual deadlines rather than direct others ’ā« Avoid making decisions too quickly; seek more information before deciding ’ā« Check t ensure you are not making conclusions when speaking ’ā« Describe situations rather than evaluate them ’ā« Consider multiple options and ask more questions to gather information ’ā« Be open to changing and dynamic information and situations ’ā« Be willing to take steps without making a complete plan ’ā« Be open to accommodating unexpected communication opportunities Communication Tips when dealing with an ENTP (in this instance me) ’ā« Be imaginative, enthusiastic and open minded ’ā« Make connections and show relationships between things ’ā« Appeal to their (my) curiosity, flexibility, and desire to change things ’ā« Focus on new ideas, possibilities, and patterns ’ā« Present opportunities or challenges ’ā« Avoid focusing too much on rules, structures and procedures ’ā« Allow them (me) room to explore ideas without coming to closure
- 11. Personality Type ’ā« Show how information relates to the bigger picture ’ā« Provide opportunities to brainstorm ’ā« Avoid focusing on only facts and details ENTP Logical Explorer: Innovate and initiate ŌĆ£The possibilities are endlessŌĆØ Communication highlights At first glance What they want to hear ’ā« Persuasive and convincing when championing ideas ’ā« Future focused, change oriented systems thinkers; create new models and ideas ’ā« Quick to see problems as opportunities, explore links and integrate ideas ’ā« Use logical analysis to zero in on root cause of complex problems ’ā« Champion change and initiate actions with great energy and excitement ’ā« Initially seem sceptical, analytic, and detached; can be easygoing, tolerant, and casual ’ā« Open ended and exploratory; take in and integrate information form many sources ’ā« Thinks outside the box and come up with new and untried solutions to problems ’ā« Energetic and enthusiastic; immersed in projects to actualise the vision ’ā« Desire freedom and independence to align their efforts with a greater vision ’ā« How, why things work; enjoy questioning others ’ā« Others questioning them and debating their perspective ’ā« Verbal challenges to sharpen their perspective and demonstrate competency ’ā« No direct commands or specific instructions ’ā« Possibilities, ideas, theories and models that draw their interest and engage them When expressing themselves Giving / receiving feedback Interpersonal focus ’ā« Use precise language; debate fine meaning and implications of words and concepts ’ā« Use logical, analytical language to describe abstract problems, systems and ideas ’ā« Discuss and play with alternative solutions that can seem in direct opposition ’ā« Persuasive and articulate, they advocate, educate, and negotiate for their ideas ’ā« Do not like to repeat themselves and may note take time to explain detail ’ā« Generally accepting, but intolerant of incompetence or substandard efforts ’ā« Will provide constructive feedback in a concise, to- the-point manner ’ā« Independent and assume that other will work independently; critical of dependence ’ā« Self-reliant and self critical; not likely to look to others for corrective feedback ’ā« Fails to see the need for being overly encouraging or for giving ongoing positive feedback ’ā« Charming, disarming, very personable and persuasive ’ā« Deal with problems ŌĆō even interpersonal ones ŌĆō using logic more than emotion or empathy ’ā« Come across as impersonal, indifferent, or overly focused on the tasks rather than the people ’ā« Debate perspectives openly and can be surprised if others take comments personally ’ā« Can change position easily and may come across as inconsistent or mercurial
- 12. Personality Type Communicating effectively with ENTPŌĆÖs Do ’ā« Let them work independently ’ā« Use logic and reason to convince them; be precise when expressing your thoughts ’ā« Know what you are talking about to ensure they perceive you as a competent person ’ā« Expect them to critique and question ’ā« Be prepared for debate and challenges ’ā« Provide time for them to analyse and integrate information ’ā« Present information in global formats such as flow charts and system maps ’ā« Allow them to define how and what they need to do to accomplish goals ’ā« Be patient with open-ended brainstorming, modelling or idea-generating sessions Do not ’ā« Focus on emotional or personal communication at work ’ā« Expect them to overtly appreciate and validate others on a regular basis ’ā« Present information or perspectives that cannot be justified using logical reasoning ’ā« Expect them to give specific direction to or supervise others closely ’ā« Discuss routine or straightforward tasks ’ā« Tell the specifics about what to do or how to do it ’ā« Expect patience when discussing ways to organise people or tasks ’ā« Keep turning the focus to practical details and short-term implications ’ā« Provide the detail until they have had time to see the ŌĆ£big pictureŌĆØ ’ā« Personalise their need to question, critique, challenge and debate Well in twelve pages IŌĆÖve hopefully covered my personality type, which I feel has covered me very well. If you have read through this paper you will have noted my strengths, spotted my weaknesses, and by using my strengths to support you in your daily tasks and giving me support in my weaker areas we can move forward as a fully functional team. You have now seen my personality type - warts and all - and I am sure that over the coming months you will see me in action and be able to take a moment to look back to this indicator and say, yes, I should have expected that reaction or result. Dale Vaughan