Personal liability of agent
- 1. PERSONAL LIABILITY OF AGENT An agent acts on behalf of his principal but in following cases he is personally liable if there is an agreement to that effect. 1. Where the contract is made by an agent for a merchant living abroad. 2. Where agent doesnot disclose the name of his principal. 3. Where principal though disclosed, but cannot be sued. 4. Where an agent exceeds his authority. 5. Where an agent agrees to be bound personally. In all the above cases, the agent is accountable and can be sued.
- 2. TERMINATION OF AGENCY Termination of agency may take place in two ways *Operation Of Law *Act Of Parties
- 3. TERMINATION OF AGENCY BY THE OPERATION OF LAW: Following are the situations where the agency is terminated by the operation of law. - Expiry of Time: At times, contract of agency may be formed for a particular period. In such a case, after expiry of that agreed period, termination of agency takes place. -Fulfillment of object: At times the contract of agency may be found for a particular objective. In such a case termination of agency takes place after the fulfillment of the objective. -Death or lunacy of either party: Whenever principal or agent come across death or lunacy, agency contract gets terminated. -Insolvency of Principal: Principal should have capacity to contract. When principal becomes insolvent, He foregoes capacity to contract and termination of agency takes place.
- 4. -Destruction of subject matter: When subject matter of contract gets destructed, agency contract comes to an end. -Principal – Alien Enemy: When principal is alien and war breaks out between the countries, then principal becomes alien enemy and agency contract gets terminated. -Liquidation of company: Company as being a legal entity, may act either as principal or agent. Whatever the status may be, if company enters into liquidation, termination of agency takes place.
- 5. TERMINATION OF AGENCY BY THE ACT OF PARTIES: The following are the situations where the agency is terminated by the act of parties. -Termination of agency by the Principal: Principal can terminate the contract of agency by giving notice to agent. By doing so if agent comes across any suffering. Principal has to compensate the agent. -Termination of agency by the Agent: Agent also can terminate the agency contract by giving notice to principal but by doing so if principal comes across any suffering, agent has to compensate. -Termination of agency by both the parties to the contract: By means of mutual understanding between principal and agent, the contract of agency may come to an end.
- 6. SUBSTITUTED AGENT A substituted agent is a person who is only named by the agent but is under the control of the principal. He acts independently for his principal. There is contractual relationship between the substituted agent and the principal. The principal can hold the substituted agent liable. An agent is however not liable for the acts of the substituted agent. While naming substituted agent for the principal, an agent is bound to exercise some amount of discretion as a man of ordinary prudence would exercise in his own case.If the agent does so, he is not responsible to the principal for the acts or negligence of the substituted agent. Example – Mr. Khan appoints Mr. Jhanzeb as his agent for selling his car in auction and requests Mr. Jhanzeb to name some reliable solicitor for that purpose. Mr. Jhanzeb named Miss Saima as a solicitor. There is a direct privity of contract between Mr. Khan and Miss Saima. And so in this scenario Miss Saima is the substituted agent.
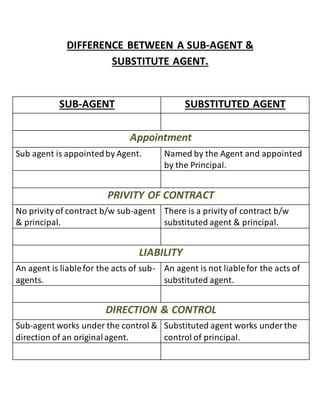
- 7. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A SUB-AGENT & SUBSTITUTE AGENT. SUB-AGENT SUBSTITUTED AGENT Appointment Sub agent is appointed by Agent. Named by the Agent and appointed by the Principal. PRIVITY OF CONTRACT No privity of contract b/w sub-agent & principal. There is a privity of contract b/w substituted agent & principal. LIABILITY An agent is liable for the acts of sub-agents. An agent is not liable for the acts of substituted agent. DIRECTION & CONTROL Sub-agent works under the control & direction of an original agent. Substituted agent works under the control of principal.