[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 7. PostgreSQL DB Tuning ???? - ???
4 likes4,420 views
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 7. PostgreSQL DB Tuning ???? - ???
1 of 14
Downloaded 78 times



![?? ?? ?? ?? ??
? ?? ?? ?? ??
? Master data 285?? ? 1?6???, 37? ??
? Master data size 25 GB ? 1 TB, 40? ??
? ???? ?? ??
? 651 msec ? 10? 17?, 948 ? ?? (ID)
? 1.2 ? ? 7? 20?, 367 ? ?? (name)
? 773 msec ? 10?, 776 ? ?? (smiles)
? Chemical data ???
? IUPAC Name
? (3R,6R,7R)-2,3,7-trimethyl-6-(propan-2-yl)tetradecane
? N'-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]-2-phenylacetohydrazide
? Smiles
? CC(C)CCCC(C)C3CCC4C2CC=C1CC(O)CCC1(C)C2CCC34C
? Formula
? C27H46O
? C11H14O3S2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cjsongpostgresqldbtuningexam-20171102-171106043044/85/Pgday-Seoul-2017-7-PostgreSQL-DB-Tuning-4-320.jpg)








Ad
Recommended
[Pgday.Seoul 2021] 2. Porting Oracle UDF and Optimization
[Pgday.Seoul 2021] 2. Porting Oracle UDF and OptimizationPgDay.Seoul
?
The document discusses porting functions from Oracle to PostgreSQL and optimizing performance, including different function types in PostgreSQL like SQL functions and PL/pgSQL functions, as well as volatility categories. It also provides examples of test data created for use in examples and covers strategies for analyzing inefficient Oracle functions and improving them to leverage the PostgreSQL optimizer.[Pgday.Seoul 2021] 1. ??? ???? ????????? ??? SQL
[Pgday.Seoul 2021] 1. ??? ???? ????????? ??? SQLPgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2021] 1. ??? ???? ????????? ??? SQL - ???[pgday.Seoul 2022] ?????? PostgreSQL ??? - ??? & ???
[pgday.Seoul 2022] ?????? PostgreSQL ??? - ??? & ???PgDay.Seoul
?
[pgday.Seoul 2022] ?????? PostgreSQL ??? - ??? & ???[Pgday.Seoul 2019] Citus? ??? ?? ??????
[Pgday.Seoul 2019] Citus? ??? ?? ??????PgDay.Seoul
?
This document summarizes how to set up and use Citus, an open-source PostgreSQL-based distributed database. It explains how to install Citus, add worker nodes, create distributed tables, and use features like reference tables to perform distributed queries across the cluster.[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 8. PostgreSQL 10 ??? ?? - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 8. PostgreSQL 10 ??? ?? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 8. PostgreSQL 10 ??? ?? - ???Mvcc in postgreSQL ???
Mvcc in postgreSQL ???PgDay.Seoul
?
This document summarizes a presentation on Multi Version Concurrency Control (MVCC) in PostgreSQL. It begins with definitions and history of MVCC, describing how it allows transactions to read and write without blocking each other. It then discusses two approaches to MVCC - storing old versions in the main database (PostgreSQL) vs a separate area (Oracle). The rest of the document does a deep dive on how MVCC is implemented in PostgreSQL specifically, showing how tuple headers track transaction IDs and pointers to maintain multiple versions of rows.[???????]Day #1 MySQL ????, ??, ?? ? ??, ???????
[???????]Day #1 MySQL ????, ??, ?? ? ??, ???????Ji-Woong Choi
?
MySQL ??
??? ??
version history
MySQL ???
?? ? ??
?? ??
MySQL ??
MySQL ????? / ?? ??
????? ????
MySQL ??
MySQL ??
MySQL ??
MySQL ?? ??
????, ?? ??
MySQL ???? ?? ??
MySQL tuning ?? ? ??
??? ??/?? ??
??
??
MySQL UpgradePostgreSQL WAL for DBAs
PostgreSQL WAL for DBAs PGConf APAC
?
Devrim Gunduz gives a presentation on Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) in PostgreSQL. WAL logs all transactions to files called write-ahead logs (WAL files) before changes are written to data files. This allows for crash recovery by replaying WAL files. WAL files are used for replication, backup, and point-in-time recovery (PITR) by replaying WAL files to restore the database to a previous state. Checkpoints write all dirty shared buffers to disk and update the pg_control file with the checkpoint location.[pgday.Seoul 2022] POSTGRES ?????? ???? - ???
[pgday.Seoul 2022] POSTGRES ?????? ???? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
[pgday.Seoul 2022] POSTGRES ?????? ???? - ???[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 6. GIN vs GiST ??? ??? - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 6. GIN vs GiST ??? ??? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
B-tree is ideal for unique values while GIN is ideal for indexes with many duplicates. GIST can index most data types and is useful for operations like containment and overlap. A comparison found that GIN indexes have faster search times but slower update times than GiST indexes, and GIN indexes are larger in size and take longer to build. In summary, the best index type depends on the data characteristics and query operations.[Pgday.Seoul 2018] ??? DB?? PostgreSQL?? Migration? ?? DB2PG
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] ??? DB?? PostgreSQL?? Migration? ?? DB2PGPgDay.Seoul
?
This document discusses DB2PG, a tool for migrating data between different database management systems. It began as an internal project in 2016 and has expanded its supported migration paths over time. It can now migrate schemas, tables, data types and more between Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, MySQL and other databases. The tool uses Java and supports multi-threaded imports for faster migration. Configuration files allow customizing the data type mappings and queries used during migration. The tool is open source and available on GitHub under the GPL v3 license.[2018] MySQL ??? ???
[2018] MySQL ??? ???NHN FORWARD
?
24?? 365? ???? ?? MySQL DB ???.
MySQL ??? ???? ?? ???? ????? ?? ???? ???? ???.
??
1. DB ??? ???
2. ??? ??
- HW ???
- MySQL Replication ???
3. ??? ?? ??
4. DNS? VIP
5. MySQL ??? ??? ??
??
- MySQL? ????? ?? ??? ???
- MySQL ???? ?? ?? ???MySQL Administrator 2021 - ?????
MySQL Administrator 2021 - ?????NeoClova
?
MySQL Administrator
Basic course
- MySQL ??
- MySQL ?? / ??
- MySQL ????
- MySQL ???? ??
- MySQL ??
- MySQL ?? / ??
- MySQL ????
Advanced course
- MySQL Optimization
- MariaDB / Percona
- MySQL HA (High Availability)
- MySQL troubleshooting
?????
http://neoclova.co.kr/[Cloud OnAir] Google Cloud §ÿ§Œ•«©`•ø“∆–– 2019ƒÍ1‘¬24»’ ∑≈ÀÕ
[Cloud OnAir] Google Cloud §ÿ§Œ•«©`•ø“∆–– 2019ƒÍ1‘¬24»’ ∑≈ÀÕGoogle Cloud Platform - Japan
?
•«©`•ø§Œ“∆––œ»§Œflxík°¢“∆––•—•π§‰“∆––∑Ω∑®§Ú’h√˜§∑§fi§π°£§fi§ø BigQuery°¢Cloud Storage°¢Data Transfer Appliance § §…§Œ•µ©`•”•π •’•°•fl•Í©`§Ú π”√§∑§∆•«©`•ø§Ú GCP §À“∆––§π§Î•ƒ©`•Î§‚ΩBΩȧ∑§fi§π°£Get to know PostgreSQL!
Get to know PostgreSQL!Oddbj?rn Steffensen
?
This document provides an agenda and background information for a presentation on PostgreSQL. The agenda includes topics such as practical use of PostgreSQL, features, replication, and how to get started. The background section discusses the history and development of PostgreSQL, including its origins from INGRES and POSTGRES projects. It also introduces the PostgreSQL Global Development Team.MariaDB 10.5 binary install (???? ??)
MariaDB 10.5 binary install (???? ??)NeoClova
?
MariaDB? MySQL? ???? ?? ?? ?????? ?????, ?? ??? ???? ???? ??. ? ??? MariaDB? ?? ??, ?? ? ?? ??? ?? ??? ???? ???, ?? OS ??? ?? ??? ??? ?? ? ??? ???? ??, MariaDB ????? ?? ?? ?? ??? ????. ?????, MariaDB? ?? ? ?? ??? ??? ?? ??? ????.Postgresql database administration volume 1
Postgresql database administration volume 1Federico Campoli
?
The document is 'PostgreSQL Database Administration Volume 1' by Federico Campoli, released under a Creative Commons license, making it freely available for sharing and adaptation. It serves as a comprehensive guide for database administrators, covering essential topics from installation to maintenance and provides insights into PostgreSQL's features and functionality. The author aims to spread knowledge by keeping the book free and acknowledges potential grammatical errors as a non-native English speaker.Deep dive into PostgreSQL statistics.
Deep dive into PostgreSQL statistics.Alexey Lesovsky
?
This document discusses PostgreSQL statistics and how to use them effectively. It provides an overview of various PostgreSQL statistics sources like views, functions and third-party tools. It then demonstrates how to analyze specific statistics like those for databases, tables, indexes, replication and query activity to identify anomalies, optimize performance and troubleshoot issues.Oracle database performance tuning
Oracle database performance tuningAbishek V S
?
The document discusses Oracle Database performance tuning. It begins by defining performance as the accepted throughput for a given workload. Performance tuning is defined as optimizing resource use to increase throughput and minimize contention. A performance problem occurs when database tasks do not complete in a timely manner, such as SQL running longer than usual or users facing slowness. Performance problems can be caused by contention for resources, overutilization of the system, or poorly written SQL. The document discusses various performance diagnostics tools and concepts like wait events, enqueues, I/O performance, and provides examples of how to analyze issues related to these areas.Advanced MySQL Query Tuning
Advanced MySQL Query TuningAlexander Rubin
?
- The document discusses advanced techniques for optimizing MySQL queries, including topics like temporary tables, file sorting, order optimizations, and calculated fields.
- It provides examples of using indexes and index optimizations, explaining concepts like index types, index usage, key lengths, and covering indexes.
- One example shows how to optimize a query involving a calculated year() expression by rewriting the query to use a range on the date field instead.AWS 6? ??? | AWS?? MS SQL ?? ???? (??? ????????)
AWS 6? ??? | AWS?? MS SQL ?? ???? (??? ????????)Amazon Web Services Korea
?
AWS 6? ??? | AWS?? MS SQL ?? ???? (??? ????????)More Related Content
What's hot (20)
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 8. PostgreSQL 10 ??? ?? - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 8. PostgreSQL 10 ??? ?? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 8. PostgreSQL 10 ??? ?? - ???Mvcc in postgreSQL ???
Mvcc in postgreSQL ???PgDay.Seoul
?
This document summarizes a presentation on Multi Version Concurrency Control (MVCC) in PostgreSQL. It begins with definitions and history of MVCC, describing how it allows transactions to read and write without blocking each other. It then discusses two approaches to MVCC - storing old versions in the main database (PostgreSQL) vs a separate area (Oracle). The rest of the document does a deep dive on how MVCC is implemented in PostgreSQL specifically, showing how tuple headers track transaction IDs and pointers to maintain multiple versions of rows.[???????]Day #1 MySQL ????, ??, ?? ? ??, ???????
[???????]Day #1 MySQL ????, ??, ?? ? ??, ???????Ji-Woong Choi
?
MySQL ??
??? ??
version history
MySQL ???
?? ? ??
?? ??
MySQL ??
MySQL ????? / ?? ??
????? ????
MySQL ??
MySQL ??
MySQL ??
MySQL ?? ??
????, ?? ??
MySQL ???? ?? ??
MySQL tuning ?? ? ??
??? ??/?? ??
??
??
MySQL UpgradePostgreSQL WAL for DBAs
PostgreSQL WAL for DBAs PGConf APAC
?
Devrim Gunduz gives a presentation on Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) in PostgreSQL. WAL logs all transactions to files called write-ahead logs (WAL files) before changes are written to data files. This allows for crash recovery by replaying WAL files. WAL files are used for replication, backup, and point-in-time recovery (PITR) by replaying WAL files to restore the database to a previous state. Checkpoints write all dirty shared buffers to disk and update the pg_control file with the checkpoint location.[pgday.Seoul 2022] POSTGRES ?????? ???? - ???
[pgday.Seoul 2022] POSTGRES ?????? ???? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
[pgday.Seoul 2022] POSTGRES ?????? ???? - ???[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 6. GIN vs GiST ??? ??? - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 6. GIN vs GiST ??? ??? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
B-tree is ideal for unique values while GIN is ideal for indexes with many duplicates. GIST can index most data types and is useful for operations like containment and overlap. A comparison found that GIN indexes have faster search times but slower update times than GiST indexes, and GIN indexes are larger in size and take longer to build. In summary, the best index type depends on the data characteristics and query operations.[Pgday.Seoul 2018] ??? DB?? PostgreSQL?? Migration? ?? DB2PG
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] ??? DB?? PostgreSQL?? Migration? ?? DB2PGPgDay.Seoul
?
This document discusses DB2PG, a tool for migrating data between different database management systems. It began as an internal project in 2016 and has expanded its supported migration paths over time. It can now migrate schemas, tables, data types and more between Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, MySQL and other databases. The tool uses Java and supports multi-threaded imports for faster migration. Configuration files allow customizing the data type mappings and queries used during migration. The tool is open source and available on GitHub under the GPL v3 license.[2018] MySQL ??? ???
[2018] MySQL ??? ???NHN FORWARD
?
24?? 365? ???? ?? MySQL DB ???.
MySQL ??? ???? ?? ???? ????? ?? ???? ???? ???.
??
1. DB ??? ???
2. ??? ??
- HW ???
- MySQL Replication ???
3. ??? ?? ??
4. DNS? VIP
5. MySQL ??? ??? ??
??
- MySQL? ????? ?? ??? ???
- MySQL ???? ?? ?? ???MySQL Administrator 2021 - ?????
MySQL Administrator 2021 - ?????NeoClova
?
MySQL Administrator
Basic course
- MySQL ??
- MySQL ?? / ??
- MySQL ????
- MySQL ???? ??
- MySQL ??
- MySQL ?? / ??
- MySQL ????
Advanced course
- MySQL Optimization
- MariaDB / Percona
- MySQL HA (High Availability)
- MySQL troubleshooting
?????
http://neoclova.co.kr/[Cloud OnAir] Google Cloud §ÿ§Œ•«©`•ø“∆–– 2019ƒÍ1‘¬24»’ ∑≈ÀÕ
[Cloud OnAir] Google Cloud §ÿ§Œ•«©`•ø“∆–– 2019ƒÍ1‘¬24»’ ∑≈ÀÕGoogle Cloud Platform - Japan
?
•«©`•ø§Œ“∆––œ»§Œflxík°¢“∆––•—•π§‰“∆––∑Ω∑®§Ú’h√˜§∑§fi§π°£§fi§ø BigQuery°¢Cloud Storage°¢Data Transfer Appliance § §…§Œ•µ©`•”•π •’•°•fl•Í©`§Ú π”√§∑§∆•«©`•ø§Ú GCP §À“∆––§π§Î•ƒ©`•Î§‚ΩBΩȧ∑§fi§π°£Get to know PostgreSQL!
Get to know PostgreSQL!Oddbj?rn Steffensen
?
This document provides an agenda and background information for a presentation on PostgreSQL. The agenda includes topics such as practical use of PostgreSQL, features, replication, and how to get started. The background section discusses the history and development of PostgreSQL, including its origins from INGRES and POSTGRES projects. It also introduces the PostgreSQL Global Development Team.MariaDB 10.5 binary install (???? ??)
MariaDB 10.5 binary install (???? ??)NeoClova
?
MariaDB? MySQL? ???? ?? ?? ?????? ?????, ?? ??? ???? ???? ??. ? ??? MariaDB? ?? ??, ?? ? ?? ??? ?? ??? ???? ???, ?? OS ??? ?? ??? ??? ?? ? ??? ???? ??, MariaDB ????? ?? ?? ?? ??? ????. ?????, MariaDB? ?? ? ?? ??? ??? ?? ??? ????.Postgresql database administration volume 1
Postgresql database administration volume 1Federico Campoli
?
The document is 'PostgreSQL Database Administration Volume 1' by Federico Campoli, released under a Creative Commons license, making it freely available for sharing and adaptation. It serves as a comprehensive guide for database administrators, covering essential topics from installation to maintenance and provides insights into PostgreSQL's features and functionality. The author aims to spread knowledge by keeping the book free and acknowledges potential grammatical errors as a non-native English speaker.Deep dive into PostgreSQL statistics.
Deep dive into PostgreSQL statistics.Alexey Lesovsky
?
This document discusses PostgreSQL statistics and how to use them effectively. It provides an overview of various PostgreSQL statistics sources like views, functions and third-party tools. It then demonstrates how to analyze specific statistics like those for databases, tables, indexes, replication and query activity to identify anomalies, optimize performance and troubleshoot issues.Oracle database performance tuning
Oracle database performance tuningAbishek V S
?
The document discusses Oracle Database performance tuning. It begins by defining performance as the accepted throughput for a given workload. Performance tuning is defined as optimizing resource use to increase throughput and minimize contention. A performance problem occurs when database tasks do not complete in a timely manner, such as SQL running longer than usual or users facing slowness. Performance problems can be caused by contention for resources, overutilization of the system, or poorly written SQL. The document discusses various performance diagnostics tools and concepts like wait events, enqueues, I/O performance, and provides examples of how to analyze issues related to these areas.Advanced MySQL Query Tuning
Advanced MySQL Query TuningAlexander Rubin
?
- The document discusses advanced techniques for optimizing MySQL queries, including topics like temporary tables, file sorting, order optimizations, and calculated fields.
- It provides examples of using indexes and index optimizations, explaining concepts like index types, index usage, key lengths, and covering indexes.
- One example shows how to optimize a query involving a calculated year() expression by rewriting the query to use a range on the date field instead.Similar to [Pgday.Seoul 2017] 7. PostgreSQL DB Tuning ???? - ??? (20)
AWS 6? ??? | AWS?? MS SQL ?? ???? (??? ????????)
AWS 6? ??? | AWS?? MS SQL ?? ???? (??? ????????)Amazon Web Services Korea
?
AWS 6? ??? | AWS?? MS SQL ?? ???? (??? ????????)Amazon Redshift? ??? ?? (???) - AWS DB Day
Amazon Redshift? ??? ?? (???) - AWS DB DayAmazon Web Services Korea
?
2016? 4? 27? DB Day ?? ??? ???? ???? ?? ???? °∞Amazon Redshift? ??? ?? °∞ ???????.Big query at GDG Korea Cloud meetup
Big query at GDG Korea Cloud meetupJude Kim
?
2015-01-27 GDG Korea meetup ?? ??? ?????.
???? ?? ??? ?? ?
AppEngine ??? BigQuery? ???? ???? ??? ??? ???????.SQream DB, GPU-accelerated data warehouse
SQream DB, GPU-accelerated data warehouseNAVER Engineering
?
1. SQream ?? ? Use Cases:??? ??
- Why GPU
- How SQream works on GPU
- Use cases
2. Edge Technology : Ami Gal, CEO at SQream
- IoT, and ???? ??AWS Partner ConneXions Online ®C New Year Edition - AWS re:Invent 2020 Tech Re...
AWS Partner ConneXions Online ®C New Year Edition - AWS re:Invent 2020 Tech Re...Amazon Web Services Korea
?
AWS Partner ConneXions Online ®C New Year Edition ? AWS re:Invent Re:Cap ?? ?? ????.
Graviton2 ??? EC2 ???? ?? ?? - ??? :: AWS Unboxing ??? ???
Graviton2 ??? EC2 ???? ?? ?? - ??? :: AWS Unboxing ??? ???Amazon Web Services Korea
?
?? ?? - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GHQMFVLRl4U
Amazon EC2 T4g, M6g, C6g ? R6g ????? ?????? ??, ???? ???? ??? ???? ????? ?? ??? x86 ?? ?????? ?? 40% ? ?? ?? ?? ??? ?????.?????? 1??? 2??? ??????? ????? ????? ????.pptx
?????? 1??? 2??? ??????? ????? ????? ????.pptxyeongkikim2
?
?????? 1??? 2??? ??????? ????? ????? ????.pptxDEVIEW 2013 Presentation
DEVIEW 2013 PresentationWon Gil Kim
?
Presentation for DEVIEW 2013, developer conference by NHN.
This session have introduced encryption technology, engine-level encryption for MySQL & MariaDB.
This is main technology of MyDiamo.
Although this is Korean one, you can understand what we said.
See more at http://www.mydiamo.com
Thanks.AWS Partner ConneXions Online ®C New Year Edition - AWS re:Invent 2020 Tech Re...
AWS Partner ConneXions Online ®C New Year Edition - AWS re:Invent 2020 Tech Re...Amazon Web Services Korea
?
Ad
More from PgDay.Seoul (17)
[pgday.Seoul 2022] PostgreSQL with Google Cloud
[pgday.Seoul 2022] PostgreSQL with Google CloudPgDay.Seoul
?
Google Cloud offers several fully managed database services for PostgreSQL workloads, including Cloud SQL and AlloyDB.
Cloud SQL provides a fully managed relational database service for PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQL Server. It offers 99.999% availability, unlimited scaling, and automatic failure recovery.
AlloyDB is a new database engine compatible with PostgreSQL that provides up to 4x faster transactions and 100x faster analytics queries than standard PostgreSQL. It features independent scaling of storage and computing resources.
Google Cloud aims to be the best home for PostgreSQL workloads by providing compatibility with open source PostgreSQL and enterprise-grade features, performance, reliability, and support across its database services.[Pgday.Seoul 2019] AppOS ??? I/O ?? ??? ?? 10? ?????
[Pgday.Seoul 2019] AppOS ??? I/O ?? ??? ?? 10? ?????PgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2019] AppOS ??? I/O ?? ??? ?? 10? ????? - ???[Pgday.Seoul 2018] PostgreSQL ??? ?? ??? ????? OS ?? apposha
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] PostgreSQL ??? ?? ??? ????? OS ?? apposhaPgDay.Seoul
?
This document introduces AppOS, an operating system specialized for database performance. It discusses how AppOS improves on Linux by being more optimized for database workloads through techniques like specialized caching, I/O scheduling based on database priorities, and atomic writes. It also explains how AppOS is portable, high performing, and extensible to support different databases through its modular design. Future plans include improving cache management, parallel query optimization, and cooperative CPU scheduling.[Pgday.Seoul 2018] PostgreSQL Authentication with FreeIPA
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] PostgreSQL Authentication with FreeIPAPgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] PostgreSQL Authentication with FreeIPA - ???[Pgday.Seoul 2018] AWS Cloud ???? PostgreSQL ????
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] AWS Cloud ???? PostgreSQL ????PgDay.Seoul
?
The document discusses setting up PostgreSQL in an AWS cloud environment. It provides information on using PostgreSQL with AWS services like RDS, Aurora, EC2 and EBS. It compares IaaS vs PaaS deployment options and discusses features of AWS databases like backups, read replicas, high availability and security. The document also summarizes benefits of Aurora over traditional databases like faster crash recovery, continuous backups and independent scaling of database layers.[Pgday.Seoul 2018] Greenplum? ?? ?? ??
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] Greenplum? ?? ?? ??PgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] Greenplum? ?? ?? ?? - ??? ??? ??[Pgday.Seoul 2018] replacing oracle with edb postgres
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] replacing oracle with edb postgresPgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2018] replacing oracle with edb postgres - EDB ??? ??
from oracle to edb postgres
???: ?? ??, ?? ?? ?? ??
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 5. ?????(???) PostgreSQL ???? - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 5. ?????(???) PostgreSQL ???? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 5. ?????(???) PostgreSQL ???? - ???[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 1. PostGIS? ??? ? PostgreSQL ?? - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 1. PostGIS? ??? ? PostgreSQL ?? - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
PostGIS? ??? ? PostgreSQL ?? ???[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 4. Composite Type/JSON ????? ??? TVP??(with C#, JAVA) - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 4. Composite Type/JSON ????? ??? TVP??(with C#, JAVA) - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 4. Composite Type/JSON ????? ??? TVP??(with C#, JAVA) - ???[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 3. PostgreSQL WAL Buffers, Clog Buffers Deep Dive - ???
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 3. PostgreSQL WAL Buffers, Clog Buffers Deep Dive - ???PgDay.Seoul
?
This document provides technical details about PostgreSQL WAL (Write Ahead Log) buffers. It describes the structure and purpose of WAL segments, WAL records, and their components. It also explains how the WAL is used to safely recover transactions after a server crash by replaying the log.PostgreSQL 9.6 ? ?? ??
PostgreSQL 9.6 ? ?? ??PgDay.Seoul
?
? ??? PostgreSQL 9.6? ??? ??? ?? ???? ????. ?? ????? ?? ?? ??, ?? ?? ? ??? ??? ???, ?? ??, ???? ? ?? ??, ? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?????. ?? ?? ?? ? ????? ????? ???? ??? ??? ?????.pg_hba.conf ???
pg_hba.conf ???PgDay.Seoul
?
PostgreSQL ?? ??? ?? ?? ??????.
Copyright: ??(???) search5@gmail.com
License CC BY-NC-NDAd
[Pgday.Seoul 2017] 7. PostgreSQL DB Tuning ???? - ???
- 1. PostgreSQL DB Tuning ???? PGDay.Seoul 2017 ???(cjsong@naver.com)
- 2. ??? cjsong@naver.com ? ChemEssen,Inc ????? ? ????? ?????????? ???????? ? °Æ16 PostgreSQL DB ?? ? °Æ99 web program ?? ? °Æ97 Oracle Process Monitoring tool ?? by PB ? °Æ96 OCP-DBA 7.3 ?? ? °Æ93 UNIX & C System program ??
- 3. About ChemEssen, Inc ? 2006 ??, 40? ????, ??? ???? ? ????? ????? ?? ??? ?? ? Chemical Quantum Application + Mathematical Modeling + IT
- 4. ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ? ?? ?? ?? ?? ? Master data 285?? ? 1?6???, 37? ?? ? Master data size 25 GB ? 1 TB, 40? ?? ? ???? ?? ?? ? 651 msec ? 10? 17?, 948 ? ?? (ID) ? 1.2 ? ? 7? 20?, 367 ? ?? (name) ? 773 msec ? 10?, 776 ? ?? (smiles) ? Chemical data ??? ? IUPAC Name ? (3R,6R,7R)-2,3,7-trimethyl-6-(propan-2-yl)tetradecane ? N'-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]-2-phenylacetohydrazide ? Smiles ? CC(C)CCCC(C)C3CCC4C2CC=C1CC(O)CCC1(C)C2CCC34C ? Formula ? C27H46O ? C11H14O3S2
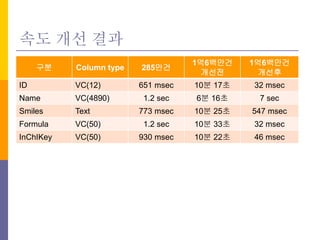
- 5. ?? ?? ?? ?? Column type 285?? 1?6??? ??? 1?6??? ??? ID VC(12) 651 msec 10? 17? 32 msec Name VC(4890) 1.2 sec 6? 16? 7 sec Smiles Text 773 msec 10? 25? 547 msec Formula VC(50) 1.2 sec 10? 33? 32 msec InChIKey VC(50) 930 msec 10? 22? 46 msec
- 6. ?????? ? ?????? ???? SQL query ?? ? ???? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ? Index ??? ? Text Search ?? ?? ? DBMS Parameter ??
- 7. Text Search ?? ?? ?? ? ?? ?? tsvector ?? ?? ALTER TABLE chemicalsc.tb_chem_info ADD COLUMN textsearchable_index_col tsvector; ? Data update UPDATE chemicalsc.tb_chem_info SET textsearchable_index_col = to_tsvector('english', coalesce(replace(upper(iupac_name), ' ', ''), '')); ? Gin ??? ?? CREATE INDEX idx_chem_info_textsearchable_index_col ON chemicalsc.tb_chem_info USING gin (textsearchable_index_col) TABLESPACE tbs_chemical_idx00;
- 8. Sql query - ?? ? SELECT chem_info_id, iupac_name, (length('Benzene') - length(iupac_name) + 100) as jaro FROM chemicalsc.tb_chem_info WHERE iupac_name_upper_stuck like replace(upper( '%Benzene%' ), ' ', '' ) ORDER BY jaro desc, iupac_name asc LIMIT 2000;
- 9. Sql query - ?? ? SET work_mem to '100MB'; SELECT chem_info_id, iupac_name, (length('benzen°Ø) - length(iupac_name)+100) as jaro FROM chemicalsc.tb_chem_info WHERE textsearchable_index_col @@ to_tsquery('english', 'benzen') ORDER BY jaro desc, iupac_name asc LIMIT 2000;
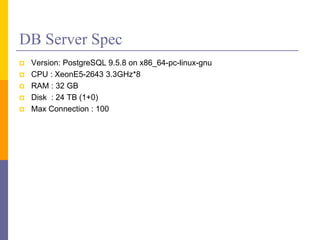
- 10. DB Server Spec ? Version: PostgreSQL 9.5.8 on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu ? CPU : XeonE5-2643 3.3GHz*8 ? RAM : 32 GB ? Disk : 24 TB (1+0) ? Max Connection : 100
- 11. postgresql.conf ? effective_cache_size ? ??? ??? ??? ? ?? ??? ? ? ??? ???? ?? ? shaed_buffers?????+?????OS?? ??? ? ??? ????? *(50% ~ 75%) ? 32GB * 50% = 16GB, 32GB * 75% = 24GB ? maintenance_work_mem ? Vacuum, create index ??? ?? ? 1GB?50MB ? 32 * 50MB = 1,600 MB ? shared_buffers ? Disk IO??? ?? ? ??? ?? ??? *25% ? 32 GB * 0.25 = 8 GB
- 12. postgresql.conf ? work_mem ? sort, bitmap??,hash join, merge join?? ? ????=total RAM /max_connections/ 4 ? ????=total RAM /max_connections/ 16 ? ???? ??? ?? ?? ? 32 GB / 100 / 4 = 0.08 GB = 80 MB ? 32 GB / 100 / 16 = 0.02 GB = 20 MB ? wal_buffers ? DB????? ?? ???? ?? ? 16MB ? max_wal_size / min_wal_size ? 2GB / 1GB ? stats_temp_directory ? /run/shm
- 13. Data update???°≠ ? ??? ??? data insert / update ?? ?? ? ??? ??? ???? data file 301? update ???? 42? ?? ? Vaccum ?? check ?? ®C 1?? ?? ? data file 301? auto vaccum ?? 10? ?? ? ??? insert ? COPY command ?? ? set command ?? copy command ? Source data ?? ?? ? ???? COPY ?? ? ?? ??? ??? ???
- 14. Q & A ?????
