Phdpe rationale
- 1. PHDPE RATIONALE The importance of PDHPE in primary schools Miss Naomi Vaughan 5/6N
- 2. WHAT IS PDHPE? The study of PDHPE is an important area within the primary curriculum as it focuses on: ïĒ Physical, social, cognitive and emotional growth ïĒ Developing and maintaining positive interpersonal relationships ïĒ Personal health choices ïĒ Living and learning in a safe secure environment ïĒ Adopting an active lifestyle ïĒ Body movement and co-ordination ïĒ Skills that enable better health and movement (Board of Studies, 2007).
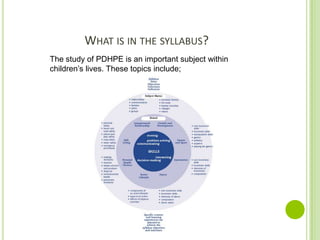
- 3. WHAT IS IN THE SYLLABUS? The study of PDHPE is an important subject within childrenâs lives. These topics include;
- 4. WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF PDHPE? Regular physical activity helps children: ïĒ Have a healthy growth and development ïĒ Build strong bones and muscles ïĒ Improve balance and develop skills ïĒ Maintain and develop flexibility ïĒ Achieve and maintain a healthy weight ïĒ Improve cardiovascular fitness ïĒ Reduce stress and feel more relaxed ïĒ Boost confidence and self-esteem ïĒ have fun with their friends and make new ones Children who donât get enough physical activity are at a greater risk of becoming overweight or obese. This makes it harder for them to be active and keep up in sport or play. Being overweight can also make kids more prone to conditions such as asthma, flat feet and joint sprains. In the long term, it can contribute to conditions such as high blood pressure and cholesterol, heart disease, Type 2 Diabetes and liver disease (NSW Department of Education and Communities, 2011).
- 5. WHAT CAN YOU DO TO HELP? ïĒ Be a good role model and have a positive attitude to being active. ïĒ Make time to be active as a family â walk to the local park, go bike riding or take the dog for a stroll. ïĒ Encourage âactive playâ by buying gifts that get children up and moving, such as balls, bats, skipping ropes and other equipment. ïĒ Limit the amount of time that children spend on âsmall screenâ entertainment â such as watching TV, going online or playing computer games â to no more than 2 hours a day. ïĒ Children should wear hats, appropriate footwear and 30+ sunscreen when theyâre being active outdoors. ïĒ Make sure they drink plenty of water when they are physically active or playing sports. ïĒ An active lifestyle is fuelled by healthy foods â make sure your children make healthy food and drink choices and limit foods that are high in added sugar, salt and saturated fat. (Healthy kids, 2014)
- 6. REFERENCES ïĒ Board of Studies, NSW (2007). PDHPE K â 6 Syllabus ïĒ Healthy kids. (2014) Kids and Teens. Retrieved 24 April, 2014 from http://www.healthykids.nsw.gov.au/kids- teens.aspx ïĒ NSW Department of Education and Communities (2011). Benefits of physical activity. Retrieved 24 April, 2014 from http://www.curriculumsupport.education.nsw.gov.au/pr imary/pdhpe/paschools/pa_benefits.htm