PhDretreat2014
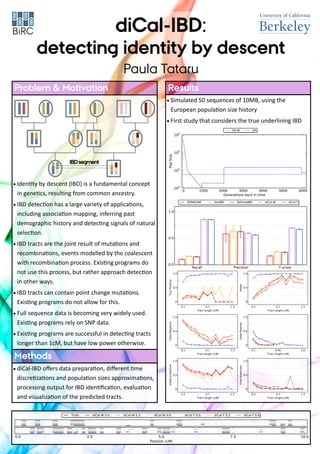
- 1. diCal-IBD: detecting identity by descent Paula Tataru ? diCal-IBD offers data preparation, different time discretizations and population sizes approximations, processing output for IBD identification, evaluation and visualization of the predicted tracts. Methods ? Identity by descent (IBD) is a fundamental concept in genetics, resulting from common ancestry. ? IBD detection has a large variety of applications, including association mapping, inferring past demographic history and detecting signals of natural selection. ? IBD tracts are the joint result of mutations and recombinations, events modelled by the coalescent with recombination process. Existing programs do not use this process, but rather approach detection in other ways. ? IBD tracts can contain point change mutations. Existing programs do not allow for this. ? Full sequence data is becoming very widely used. Existing programs rely on SNP data. ? Existing programs are successful in detecting tracts longer than 1cM, but have low power otherwise. Problem & Motivation ? Simulated 50 sequences of 10MB, using the European population size history ? First study that considers the true underlining IBD Results