PHEME Project at EDF 2015
- 1. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu PHEME Veracity: The 4th Challenge of Big Data Tom├Īs Pariente tomas.parientelobo@atos.net @tpariente
- 2. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Phemes & social media ŌĆóMemes are thematic motifs that spread through social media in ways analogous to genetic traits ŌĆóWe coined the term phemes to add truthfulness and deception to the mix 2 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pheme PHEME focuses on a fourth crucial, but hitherto largely unstudied, challenge: Veracity
- 3. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Rumour analysis: The Problem Now mostly manual ’é¦ Rumours are challenging ’é¦ Some rumours could take hours, days, weeks or even months to die out ’é¦ Ill-meaning humans can currently outsmart computers (and humans) and appear genuine
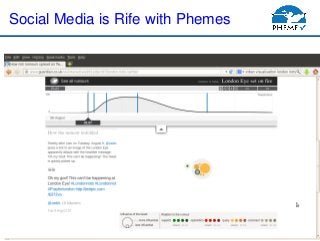
- 4. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Rumour analysis: The Problem ’é¦Mike Brown shot by police in Ferguson ’é¦We have different rumors emerging from the topic ’é¦We donŌĆÖt know if they are true. ’é¦We see the spikes and sometimes they come back (different temporal dynamics) ’é¦We need to understand the overall conversation to see the different points of view and how the rumours go forward
- 5. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Social Media is Rife with Phemes
- 6. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Social Media is Rife with Phemes
- 7. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu From manual to automatic We are investigating... ’é¦Ontologies for modelling phemes ’é¦Use a priori knowledge (LOD) and reasoning to detect contradictions ’é¦Model phemes spread across media, social networks, and time ’é¦Conversational analysis ’é¦Real-time rumour classification ’é¦Pheme visualisation to support veracity checking: media maps, impact maps, geographical mapsŌĆ”
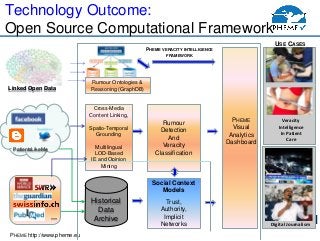
- 8. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu PatientsLikeMe Cross-Media Content Linking, Spatio-Temporal Grounding Multilingual LOD-Based IE and Opinion Mining Rumour Detection And Veracity Classification USE CASES Veracity Intelligence In Patient Care Digital Journalism Linked Open Data Rumour Ontologies & Reasoning (GraphDB) Historical Data Archive PHEME Visual Analytics Dashboard Social Context Models Trust, Authority, Implicit Networks Technology Outcome: Open Source Computational Framework ... ŌĆ” PHEME VERACITY INTELLIGENCE FRAMEWORK
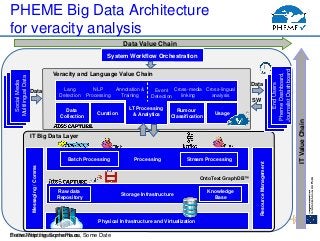
- 9. PHEME http://www.pheme.euSome Meeting, Some Place, Some Date Physical Infrastructure and Virtualization Storage Infrastructure Processing Knowledge Base Stream ProcessingBatch Processing Messaging/Comms MultilingualData Data Collection Rumour Classification UsageCuration Data Value Chain ITValueChain IT Big Data Layer Veracity and Language Value Chain System Workflow Orchestration MultilingualDataSocialMedia MultilingualData Data Data SW LT Processing & Analytics Raw data Repository Lang Detection OntoText GraphDBŌäó MultilingualData MultilingualData EndUsers PhemeDashboard, JournalistDashboard Event Detection NLP Processing Annotation & Training Cross-media linking Cross-lingual analysis ResourceManagement PHEME Big Data Architecture for veracity analysis
- 10. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Application areas ’é¦Open-source social intelligence tools for data journalism ’é¦Involves journalists from SwissInfo.ch, the Guardian, New York Times, and other media ’é¦Improving healthcare ’é¦What health-related rumours are discussed in patient- clinician consultations ’é¦Preventative medical advice, e.g. warn patients not to trust certain rumours, when researching their disease online
- 11. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu PHEME Dashboard And dynamics Over Time/Location 11 vs replies
- 12. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Journalism Dashboard Prototype 12
- 13. PHEME http://www.pheme.eu Acknowledgement The PHEME research project has received funding from the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration under grant agreement No. 611233. 13 This document does not represent the opinion of the European Community, and the European Community is not responsible for any use that might be made of its content Thanks!