Photosynthesis C3 and C4 cycle, Dr.Kamlesh shah, PSSHDA,KADI
- 2. General Mechanism of Bacterial Photosynthesis • Light-harvesting pigments (LHPs) embedded in membranes capture light energy and transfer it to a protein-complex called a reaction center • the energy is converted into excited, low potential electrons • electrons are fed into an electron transport chain, where they "fall" through a series of electron carriers, generating a proton motive force • membrane-bound ATPases then use the proton motive force to make ATP.
- 4. Classification of Photosynthetic Bacteria • Five photosynthetic groups within domain Bacteria (based on 16S rRNA) • Oxygenic Photosynthesis – Cyanobacteria and prochlorophytes • Anoxygenic Photosynthesis – Purple bacteria – Green sulfur bacteria – Heliobacteria – Green gliding bacteria
- 5. Oxygenic Photosynthesis • Occurs in cyanobacteria and prochlorophytes • Synthesis of carbohydrates results in release of molecular O2 and removal of CO2 from atmoshphere • Occurs in lamallae which house thylakoids containing chlorophyll a/b and phycobilisomes pigments which gather light energy • Uses two photosystems (PS): - PS II- generates a proton-motive force for making ATP - PS I- generates low potential electrons for reducing power.
- 7. Anoxygenic Photosynthesis • Uses light energy to create organic compounds, and sulfur or fumarate compounds instead of O2 • Occurs in purple bacteria, green sulfur bacteria, green gliding bacteria and heliobacteria • Uses bacteriochlorophyll pigments instead of chlorophyll • Uses one photosystem (PS I) to generate ATP in “cyclic” manner
- 9. Comparison of electron transport pathways in oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis
- 11. III. Light Dependent Reactions A. Photo-oxidation of Chlorophyll B. Chemiosmotic model of ATP production. IV. Light Independent Reactions A. Calvin Cycle II. How plants harness sunlight I. Anatomy of Photosynthesis
- 13. Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation pH = 4 pH = 8 + charge - charge
- 15. Graph changes in pH of the thylakoid interior over one 24 hr period. Indicate when ATP production during the light reactions is zero. 6AM pH Night Day 7 14 1 Turn to your neighbor and… Night 6 PM 4 9 No ATP No ATP
- 16. The Big Picture What have we produced so far? ATP NADPH CO2 provides the energy provides high energy electron and H+ ions provides the carbon and oxygen Used to make energy rich sugar molecules during the light independent reactions!
- 17. The Calvin Cycle
- 18. (3) CO2 molecules enter Rubisco attaches the CO2 to RuBP CARBON FIXATION
- 19. 6 ATP and 6 NADPH used REDUCTION 1 G3P molecule produced
- 20. Regenerate RuBP Use 3 more ATP
- 21. And boy can plants fix carbon!
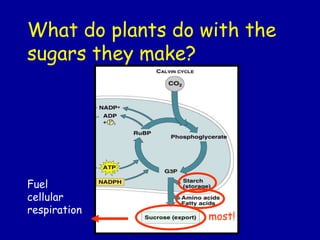
- 22. What do plants do with the sugars they make? most! Fuel cellular respiration
- 23. Similarities between photosynthesis and cellular respiration… Chemiosmosis Energy Coupling Examples
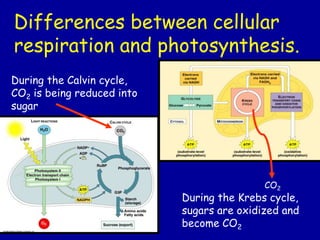
- 24. Differences between cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration In CR electron carriers bring electrons to the ETC, and O2 finally accepts them and is reduced to H2O. In photosynthesis H2O brings electrons to the ETC and becomes O2, an electron carrier finally accepts the electrons.
- 25. Differences between cellular respiration and photosynthesis. During the Calvin cycle, CO2 is being reduced into sugar CO2 During the Krebs cycle, sugars are oxidized and become CO2
- 26. Photosynthetic Adaptations What problems may a plant experience when it is exposed to arid (dry) conditions? Dehydration Elevated O2 levels in the leaves Response Close stomata to prevent dehydration
- 27. Photorespiration Rubisco – an enzyme that catalyzes the addition of CO2 to RuBP. O2 competes with CO2 for the active site on Rubisco. Photorespiration Calvin cycle sometimes called the C3 pathway
- 28. Rubisco RuBp CO2 RuBp Rubisco P G A P G A P G A Later becomes glucose! CO2 CO2 O2 Photorespiration – these CO2’s did not get incorporated into glucose this time!
- 29. Photorespiration can lead to lower photosynthetic output by siphoning carbon from the Calvin cycle! They produce less sugar!!!
- 30. CO2 + RuBP 2 molecules of 3- phosphoglycerate CO2 Competingreactions rubisco Turn to your neighbor and discuss the following questions… 1) What factor determines which reaction below occurs more often? a) The concentration of rubisco b) The relative concentration of CO2 and O2 c) The concentration of RuBp 2) This is most similar to which of the mechanisms of enzyme regulation we discussed earlier in the semester?
- 31. Adaptations to arid climates A) C4 plants - spatial separation of steps B) CAM plants - temporal separation of steps
- 32. Leaf anatomy of plants adapted for hot/arid conditions (C4 plants)… O2 C4 pathway C3 pathwaySeparate CO2 fixation and sugar making into two different cells
- 33. CAM Plants - steps performed at different times • Close their stomata during the day to minimize water loss, and open stomata at night. • Desert plants…cacti, succulent plants, pineapples… • At night they store CO2 in organic acids. Organic acid CO2 CO2 Calvin Cycle sugar • CO2 is released from organic acids in the day and used in the Calvin cycle.
- 34. The Silversword