Photosynthesis process, Sucrose formation
- 2. RASHIDUL ISLAM 20121107007 Department of Applied Chemistry and Chemical Engineering. BSMRSTU
- 3. COURSE TITLE: CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY-II COURSE NO: ACCE-462
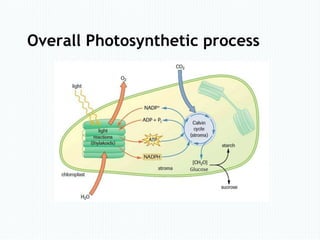
- 4. Sucrose Formation in Sugar cane • Sucrose forms in sugar cane mainly by photosynthetic process. • The photosynthetic process is divided into two stage − Photo stage and − Synthesis stage
- 5. Sucrose Formation in Sugar cane • The photo stage proceeds in the presence of light • Synthesis stage is taken place in the darkness. • The chlorophyll catalyses this process.
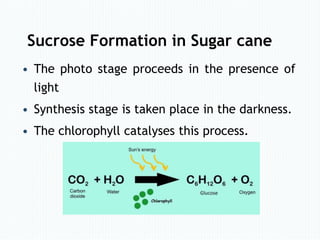
- 6. Photo Stage • In this stage light energy is convert to chemical energy. • In leaves, water (H2O) molecules break down and form oxygen (O2), NADPH and ATP (energy carriers) in the presence of light and chloroplast. [ATP= Adenosine triphosphate] [NADPH= Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate]
- 8. Photo Stage
- 9. Synthesis Stage • CO2 is Converted into glucose. • The CO2 react with RuBP and energy from ATP and NADPH to form G3P (an energy-rich glucose) • The G3P is then converted into glucose. [RuBP= Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate] [G3P= Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate]
- 13. Constituent of Sugar cane Name of Constituents Wt. Percentage Water 73-76 Solid substance 24-27 Fiber 3-5 Soluble solid substance 11-16 Juice constituent sugar 10-16
- 14. Constituent of Sugar cane juice Name of constituents Percentage Glucose 70-88 Fructose 2-4 Salt 2-4 Protein 0.1-0.5 Gums 0.506 Wax, fats, phosphates 0.3-0.5





![Photo Stage
• In this stage light energy is convert to
chemical energy.
• In leaves, water (H2O) molecules break down
and form oxygen (O2), NADPH and ATP
(energy carriers) in the presence of light and
chloroplast.
[ATP= Adenosine triphosphate]
[NADPH= Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sucroseformationconstituentofsugarcaneand-170102063607/85/Photosynthesis-process-Sucrose-formation-6-320.jpg)

![Synthesis Stage
• CO2 is Converted into glucose.
• The CO2 react with RuBP and energy from
ATP and NADPH to form G3P (an energy-rich
glucose)
• The G3P is then converted into glucose.
[RuBP= Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate]
[G3P= Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sucroseformationconstituentofsugarcaneand-170102063607/85/Photosynthesis-process-Sucrose-formation-9-320.jpg)