Php
- 2. Contents ŌĆó Introduction ŌĆó What is PHP? ŌĆó Features ŌĆó Uses of PHP ŌĆó Where it is used? ŌĆó History of PHP ŌĆó Implementations ŌĆó Basics of PHP ŌĆó An Example ŌĆó Security Issues ŌĆó Conclusion
- 3. What is PHP?What is PHP? ŌĆó PHP ŌĆó PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor ŌĆó Originally called ŌĆ£Personal Home Page ToolsŌĆØ ŌĆó Popular server-side scripting technology ŌĆó Open-source ŌĆó Anyone may view, modify and redistribute source code ŌĆó Supported freely by community ŌĆó Platform independent 3
- 4. ŌĆó Source-code not visible by client ŌĆó ŌĆśView SourceŌĆÖ in browsers does not display the PHP code ŌĆó Various built-in functions allow for fast development ŌĆó PHP supports many databases (MySQL, Informix, Oracle, Sybase, Solid, PostgreSQL, Generic ODBC, etc.) ŌĆó PHP is compatible with almost all servers used today (Apache, IIS, etc.)
- 5. PHP FeaturesPHP Features ŌĆó Easy learning ŌĆó Syntax Perl- and C-like syntax. Relatively easy to learn. ŌĆó Large function library ŌĆó Embedded directly into HTML ŌĆó Interpreted, no need to compile ŌĆó Open Source server-side scripting language designed specifically for the web.
- 6. PHP Features(cont.)PHP Features(cont.) ŌĆó Conceived in 1994, now used on +10 million web sites. ŌĆó Outputs not only HTML but can output XML, images (JPG & PNG), PDF files and even Flash movies all generated on the fly. Can write these files to the file system. ŌĆó PHP also has support for talking to other services using protocols such as LDAP, IMAP, SNMP, NNTP, POP3, HTTP.
- 7. Using PHP you.. ŌĆó Can performs system functions, i.e. from files on a system it can create, open, read, write, and close them. ŌĆó Can handle forms, i.e. gather data from files, save data to a file, thru email you can send data, return data to the user. ŌĆó Can add, delete, modify elements within your database thru PHP. ŌĆó Access cookies variables and set cookies. ŌĆó Can restrict users to access some pages of website. ŌĆó Can encrypt data.
- 8. Where it is used..? ŌĆó E-Commerce ŌĆó Project Management Tools ŌĆó Graphical User Interface ŌĆó Building an Online Community ŌĆó Developing Facebook Applications ŌĆó Generating PDF Files ŌĆó Mailing Lists ŌĆó Image Processing and Generation
- 10. History of PHPHistory of PHP ŌĆó PHP began in 1995 when Rasmus Lerdorf developed a Perl/CGI script toolset he called the Personal Home Page or PHP ŌĆó PHP 2 released 1997 (PHP now stands for Hypertext Processor). Lerdorf developed it further, using C instead ŌĆó PHP3 released in 1998 (50,000 users) ŌĆó PHP4 released in 2000 (3.6 million domains). Considered debut of functional language and including Perl parsing, with other major features ŌĆó PHP5.0.0 released July 13, 2004 (113 libraries>1,000 functions with extensive object-oriented programming) ŌĆó PHP 6 is yet to released
- 11. Implementations ŌĆó The PHP language was originally implemented as an interpreter ŌĆó Several compilers have been developed which decouple the PHP language from the interpreter. ŌĆó Advantages of compilation include better execution speed, static analysis, and improved interoperability with code written in other languages. ŌĆó Phalanger, which compiles PHP into Common Intermediate Language (CIL) byte code, and HipHop, developed at Facebook and now available as open source, which transforms the PHP Script into C++, then compiles it, reducing server load up to 50% ŌĆó PHP scripts can also be deployed in executable format using a PHP compiler.
- 12. Basics
- 13. Basic applications ŌĆó Structurally similar to C/C++ ŌĆó Supports procedural and object-oriented paradigm (to some degree) ŌĆó Scripting delimiters ŌĆó <? php ?> ŌĆó Must enclose all script code ŌĆó Variables preceded by $ symbol ŌĆó Case-sensitive ŌĆó End statements with semicolon ŌĆó Comments ŌĆó // for single line ŌĆó /* */ for multiline ŌĆó Filenames end with .php by convention 13
- 14. PHP Operators ŌĆóOperators are used to operate on values. There are four classifications of operators: ŌĆó Arithmetic ŌĆó Assignment ŌĆó Comparison ŌĆó Logical
- 15. PHP Arrays In PHP, there are three kind of arrays: ŌĆó Numeric array ŌĆó Associative array ŌĆó Multidimensional array
- 16. Control Structures ŌĆó Wide Variety available ŌĆó if, else, elseif ŌĆó while, do-while ŌĆó for, foreach ŌĆó break, continue, switch ŌĆó require, include, require_once, include_once
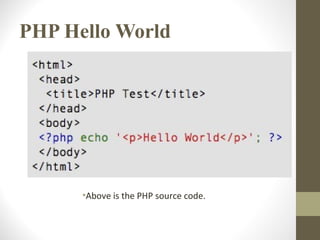
- 17. PHP Hello World ŌĆóAbove is the PHP source code.
- 18. PHP Hello World ŌĆóIt renders as HTML that looks like this:
- 20. Security issues ŌĆó About 30% of all vulnerabilities listed on the National Vulnerability Database are linked to PHP. ŌĆó These are caused mostly by not following best practice programming rules; technical security flaws of the language itself or of its core libraries are not frequent (23 in 2008, about 1% of the total). ŌĆó Recognizing that programmers make mistakes, some languages include taint checking to automatically detect the lack of input validation which induces many issues.
- 21. Conclusion