Phylum Arthropoda M.Ishaq ICP
- 1. Group ŌĆ£CŌĆØ ’āś Members ’āś Mohammad Ishaq ’āś Saman Wahab ’āś Ameena Zaman ’āś Madeeha Sardar ’āś Malghalara Iftikhar ’āś Sajida Naeem ’āś Farah Naeem ’āś Farman Ali ’āś Robi
- 2. TOPIC Phylum Arthropoda & Phylum Annelida
- 3. Phylum Arthropoda ’āś Greek ├Īrthron, "joint , pod├│s "legŌĆ£ ’āś have 1,170,000 described species ’āś include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans ’āś The first arthropods appeared during the early Cambrian Period. (543 to 505 million years ago) ’āś The first land animal was a myriapod arthropod.
- 4. Phylum Arthropoda ’āś Definition: A taxonomic group of animals that includes spiders, crabs, insects, and centipedes and whose bodies posess pairs of jointed limbs and in most cases an exoskeleton
- 5. Phylum Arthropoda ’éŚ Characteristics of Arthropods ’éŚ All arthropods have the following characteristics ’éŚ A hard outer body covering called an exoskeleton. ’éŚ Specialized mouth parts ’éŚ Jointed legs
- 6. Phylum Arthropoda ’éŚ Charactristics ’éŚ Compound Eyes ’éŚ Segmented body ’éŚ the circulatory system an open one ’éŚ The sexes nearly always separate.
- 7. Phylum Arthropoda (Charactristics) 1)Exoskeleton (2)joint legs(3)segmented Body 4)Compound Eyes (5)specialized mouth
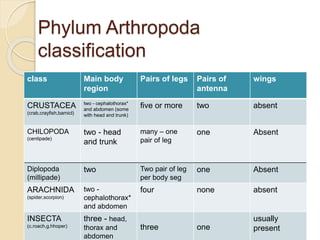
- 8. Phylum Arthropoda classification class Main body region Pairs of legs Pairs of antenna wings CRUSTACEA (crab,crayfish,barnicl) two - cephalothorax* and abdomen (some with head and trunk) five or more two absent CHILOPODA (centipade) two - head and trunk many ŌĆō one pair of leg one Absent Diplopoda (millipade) two Two pair of leg per body seg one Absent ARACHNIDA (spider,scorpion) two - cephalothorax* and abdomen four none absent INSECTA (c.roach,g.hhoper) three - head, thorax and abdomen three one usually present
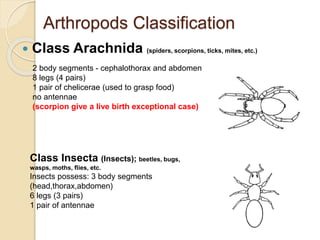
- 9. Arthropods Classification ’éŚ Class Arachnida (spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, etc.) 2 body segments - cephalothorax and abdomen 8 legs (4 pairs) 1 pair of chelicerae (used to grasp food) no antennae (scorpion give a live birth exceptional case) Class Insecta (Insects); beetles, bugs, wasps, moths, flies, etc. Insects possess: 3 body segments (head,thorax,abdomen) 6 legs (3 pairs) 1 pair of antennae
- 10. Arthropods Classification ’éŚ Class Crustacea(crustaceans): crabs, shrimp, barnacles, spiny lobster, etc ’éŚ 2 pairs of antennae ’éŚ 2 body segmentedŌĆö(cephalothorax* and abdomen ) ’éŚ 5 pairs of legs ’éŚ Coconut crab found on land not an aquatic environment
- 11. Arthropoda Classes ’éŚ Class Chilopoda (centipedes) Chilipods possess: many body segments ’éŚ 1 pair of legs per body segment ’éŚ 1 pair of antennae ’éŚ 1st pair of legs modified into venomous Class Diplopoda (millipedes) Diplopods possess: >Many body segments >2 pair of legs per body segment >1 pair of antennae
- 12. phylum Arthropoda (classification) 1) crustecea (2) chilopod (3) diplopoda 3)Arachnids (4) insecta
- 13. Phylum Arthropoda ’éŚ Protection Arthropods are protected by fast movement, an exoskeleton, pinchers, camouflage, and poison glands. ’éŚ Movement The fast movements of arthropods are the combined result of jointed appendages, a hard skeleton, and fast acting striated muscle. o Digestion ’éŚ Digestion is extracellular in the gut
- 14. Phylum Arthropoda ’éŚ Circulation Arthropods have an open circulatory system. They have a dorsal heart ’éŚ Excretion Crustaceans excrete through nephridia or green glands. Others use a network of Malpigian tubes which collects liquid wastes in the gut.
- 15. Phylum Arthropoda ’éŚ Respiration Crustaceans use gills. Insecta, chilopoda, and diplopoda use trachea and spiricles. Arachnids use book lungs. ’éŚ Nervous System Arthropods have a highly complex nervous system with a brain and a ventral nerve cord. They also have compound eyes,touch receptors, chemoreceptors, and auditory receptors.
- 16. Phylum arthropoda ’éŚ Reproduction Most have separate sexes and internal fertilization. Most undergo some form of metamorphosis.
- 17. Exp.Cockroach ’éŚ Kingdom: Animalia ’éŚ Phylum: Arthropoda ’éŚ Subphylum: Hexapoda ’éŚ Class: Insecta ’éŚ Superorder: Dictyoptera ’éŚ Order: Blattodea
- 18. Cockroach ’éŚ four kinds of cockroaches ’éŚ Including ’éŚ i) German cockroach,ii) brownbanded cockroach,iii) American cockroach, and iv)Oriental cockroach.
- 19. cockroach ’éŚ Habitate ’éŚ Cockroaches are nocturnal. They hide in dark, warm areas, especially narrow spaces where surfaces touch them on both sides.
- 20. Cockroach Anatomy and Physiology brown or black insects that are usually between half an inch and two inches long (12-50 millimeters) ’āślong antennae ’āśMales usually have wings ’āśbut females often don't ’āśusually have vestigial wings
- 21. Cockroach body ’éŚ bodies have three primary regions ŌĆōi) the head,ii) the thorax and iii) the abdomen. ’éŚ three pairs of jointed legs,(18 knees) ’éŚ one pair of antennae (sensory organs)and a rigid exoskeleton ’éŚ HEAD ’éŚ Head have eyes,antennae brain,
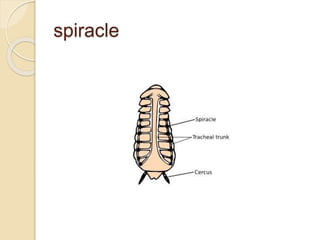
- 22. Head ’éŚ much of their nervous system activity takes place in nerve ganglia located throughout their bodies. This is one of the reasons why a headless roach can live for more than a week. The other is that roaches don't breathe through a nose or mouth. Instead, they draw air through spiracles, or holes in their sides. Tubes called tracheae deliver oxygen from the spiracles to organs and tissues. When a headless roach finally dies, it dies of thirst.
- 23. spiracle
- 24. Cockroach ’éŚ The Thorax ’éŚ attachments for three pairs of legs ’éŚ two pairs of wings ’éŚ prothoracic legs are closest to the head. ’éŚ The middle legs are the mesothoracic legs. ’éŚ The very long metathoracic legs are the roach's back legs,
- 25. Cockroach ’éŚ The Abdomen ’éŚ contains most of their internal organs, ’éŚ tube-like heart moves blood to organs and tissues. ’éŚ much of the blood travels through a network of spaces called a hemocoel.
- 26. cockroach ’éŚ Biology An adult female cockroach produces an egg capsule ’éŚ A cockroach has three stages during its life cycle: egg, nymph, and adult. Adults lay eggs contained within egg cases that are dark-colored and roughly the same size and shape as a dry kidney bean. Depending on the species, an egg case contains between 16 - 50 eggs. Eggs hatch into young cockroaches called nymphs. In a normal cockroach population, nymphs are more numerous than adults.
- 27. Amazing Cockroach facts ’éŚ 1. Cockroach can live up to nine days without its head ’éŚ 2. If a cockroach breaks a leg it can grow a new one ’éŚ 3. A cockroach can change directions up to 25 times in a second ’éŚ 4. Cockroaches can run up to 3km/hr (0.8 m/s)
- 28. cockroach ’éŚ 5. A cockroach can hold its breath for up to 40 minutes if necessary ’éŚ 6. Cockroaches can survive without food for a month and a week without water ’éŚ 7. Coakroaches spend at least 75% of their time in resting
- 29. cockroch ’éŚ 8. Some of the female cockroaches can mate once and remain pregnant for the rest of lives ’éŚ 9. Young cockroaches only need a crack ~ 0.5mm wide to crawl into the house. Adult can squeeze into a space of 1.6mm while pregnant female require 4.5mm of space ’éŚ 10. A cockroach does not have blood vessels ’éŚ Prepared & Presented by ’éŚ M.Ishaq Sagar