Phys lo7
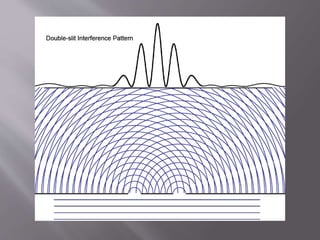
- 2. ’é© When waves propagate from 2 sources, and come in contact with each other, interference occurs ’é© It is a 2D representation of the interference that arise from waves overlapping
- 3. ’é© 2 sound source placed next to each other ’é© Other signals distorting your WiFi
- 4. ’é© Constructive ’éĪ When waves overlap their peaks with peaks, and troughs with troughs ’é© Destructive ’éĪ When waves overlap peaks with troughs, and vice versa
- 6. ’é© As you can see from the previous picture, the waves overlapped ’é© The graph above the waves show areas of constructive and destructive interference ’é© To overlap peaks with peaks and troughs with troughs, the phase difference must be 2 ’é© Destructive interference is caused by phase difference of
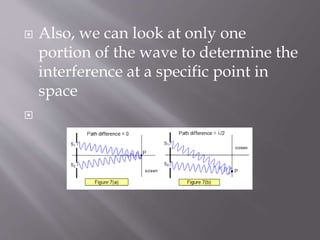
- 7. ’é© Also, we can look at only one portion of the wave to determine the interference at a specific point in space ’é©
- 8. ’é© To determine the path difference and interference pattern at point P on the previous slide, we can solve it by using trigonometry ’é© If the distance and/or angle is given, we will solve for the unknown and after obtaining the distances, we will divide by the wavelength to see the phase difference caused by path difference is
- 9. ’é© In this example, the phase difference can be seen from the graph at the overlapping point ’é© If only numerical info were given, we will need to solve it via trig Practice time!
- 10. ’é© Using the same pic as a reference, the angle that wave 1 is 60 degrees from the slit ’é© Wave 2ŌĆÖs slit is 10m below wave 1 ’é© Point P is 50m away from the wall where the slits are ’é© The wave length of the waves are 5m ’é© What kind of interference occurs at point P?
- 11. ’é© The information that we have are that S1 and S2 are 10m apart, while P is 50m away from the wall, and also that wave 1 propels at a 30 degree angle ’é© From the info we are given we can make a new pic
- 12. ’é© Using trig, we can determine that the distance travelled by Wave 1 is 100m, and the vertical distance from S1 to point P is 86.60m ’é© The vertical distance from S2 to point P will be 86.60 ŌĆō 10 = 76.60m ’é© Once the vertical distance from S2 to point P is obtained, we can calculate the distance travelled by wave 2 ’é© sqrt(76.60^2 + 50^2) = 91.4744m ’é© 91.4744/5 = 18.2949 wavelengths ’é© 100/5 = 20.00 wavelengths ’é© 20-18 = 2 wavelengths apart = Constructive
- 13. ’é© From the calculations on the previous page, it can be seen that at point P, there is constructive interference, because the path difference is an integer number of wavelengths a part ’é© That concludes my LO for this week