Physics worksheet lesson 30 standard model 1
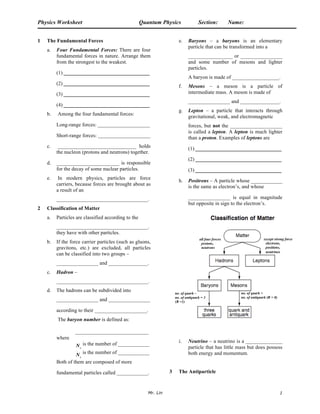
- 1. Physics Worksheet Quantum Physics Section: Name: Mr. Lin 1 1 The Fundamental Forces a. Four Fundamental Forces: There are four fundamental forces in nature. Arrange them from the strongest to the weakest. (1) _________________________________ (2) _________________________________ (3) _________________________________ (4) _________________________________ b. Among the four fundamental forces: Long-range forces: ____________________ Short-range forces: ____________________ c. ______________________________ holds the nucleon (protons and neutrons) together. d. ________________________ is responsible for the decay of some nuclear particles. e. In modern physics, particles are force carriers, because forces are brought about as a result of an ___________________________________. 2 Classification of Matter a. Particles are classified according to the ___________________________________. they have with other particles. b. If the force carrier particles (such as gluons, gravitons, etc.) are excluded, all particles can be classified into two groups ŌĆō ________________ and _______________. c. Hadron ŌĆō ___________________________________. d. The hadrons can be subdivided into ________________ and ________________ according to their ____________________. The baryon number is defined as: ____________________________ where Ōé¼ Nq is the number of ____________ Ōé¼ Nq is the number of ____________ Both of them are composed of more fundamental particles called ____________. e. Baryons ŌĆō a baryons is an elementary particle that can be transformed into a _________________ or ________________ and some number of mesons and lighter particles. A baryon is made of __________________. f. Mesons ŌĆō a meson is a particle of intermediate mass. A meson is made of ________________ and _______________. g. Lepton ŌĆō a particle that interacts through gravitational, weak, and electromagnetic forces, but not the ____________________ is called a lepton. A lepton is much lighter than a proton. Examples of leptons are (1) _________________________________ (2) _________________________________ (3) _________________________________ h. Positrons ŌĆō A particle whose ____________ is the same as electronŌĆÖs, and whose ________________ is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the electronŌĆÖs. i. Neutrino ŌĆō a neutrino is a ______________ particle that has little mass but does possess both energy and momentum. 3 The Antiparticle all four forces protons, neutrons except strong force electrons, positions, neutrinos no. of quark = no. of antiquark (B = 0) no. of quark ŌĆō no. of antiquark = 3 (B =1)