Physiology of sleep
- 1. PHYSIOLOGY OF SLEEP By: RAJNISH KUMAR CIMS BILASPUR
- 2. Definitions â SLEEP: A state of loss of consciousness form which a subject can be aroused by appropriate stimulus. â COMA: A state of unconsciousness form which a subject cannot be aroused.
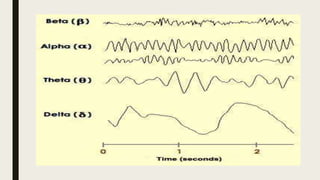
- 3. SLEEP STAGE â According to EEG criteria- 1. NREM(non-rapid eye movement) Stage 1 NREM Stage 2 NREM Stage 3 NREM Stage 4 NREM 2.REM(rapid eye movement)
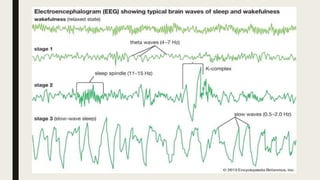
- 6. STAGE 1 NREM â NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep is dreamless sleep. â Occurs at sleep onset or following arousal form another stage of sleep. â 1 to 7 min in the initial cycle. â 2 to 5% of total sleep. â Easily interupted â EEG: Rhythmic alpha wave.
- 7. STAGE 2 NREM â Lasts for 10 to 15 min in initial cycle and lengthens with each successive cycle. â 45 to 55% of total sleep duration. â Arousal requires more intense stimulus then stage 1. â EEG: Sleep spindles.
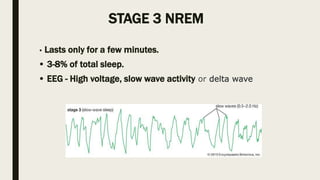
- 8. STAGE 3 NREM âĒ Lasts only for a few minutes. âĒ 3-8% of total sleep. âĒ EEG - High voltage, slow wave activity or delta wave
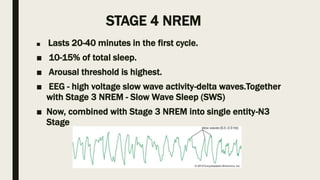
- 9. STAGE 4 NREM â Lasts 20-40 minutes in the first cycle. â 10-15% of total sleep. â Arousal threshold is highest. â EEG - high voltage slow wave activity-delta waves.Together with Stage 3 NREM - Slow Wave Sleep (SWS) â Now, combined with Stage 3 NREM into single entity-N3 Stage
- 11. REM â Desynchronised (low frequency) brain wave activity. â "Sawtooth" waveforms. Theta activity and slow alpha activity also characterise REM sleep. â 1-5 minutes in initial cycle. â Progressively prolonged as sleep progresses.
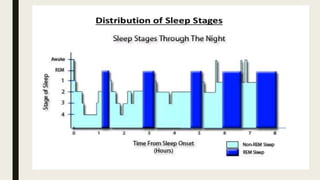
- 12. â 4-5 cycles of these sequential stages â Each cycle -90-110 mins â As sleep progresses delta sleep decreases and REM sleep increases. â REM in initial cycle is only 5-10 mins but in last cycle can be as long as 40 mins â As sleep progresses Stage 2 predominates in NREM sleep and Stage 3 & 4 sometimes disappear altogether.
- 14. THANK YOU âTrue education means fostering the ability to be interested in something.â