Physiology spotters
- 2. *The sensory fibres from anterior 2/3rds run in lingual nerve, general sensations(touch,pain,pres sure,temp)pass through chorda tympani. * both sensations from posterior 1/3rd run in glossopharyngeal nerve.
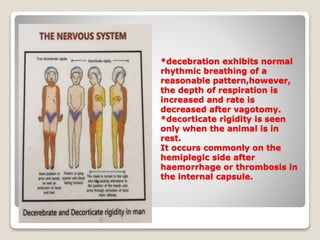
- 3. *decebration exhibits normal rhythmic breathing of a reasonable pattern,however, the depth of respiration is increased and rate is decreased after vagotomy. *decorticate rigidity is seen only when the animal is in rest. It occurs commonly on the hemiplegic side after haemorrhage or thrombosis in the internal capsule.
- 4. Retina has 10 layers,except in the blindspot and fovea centralis,photorecepto rs are placed outwards towards choroid. 1.pigmented epithelium 2.rodes and cones 3.external limiting memb 4.outer nuclear layer 5. outer synaptic layer 6. inner nuclear layer 7.inner synaptic layer 8. ganglion cell layer 9.optic nerve 10. inner limiting memb
- 5. Causes: 1. independent of ACTH *high dose of glucocorti *adrenal cortex tumour 2. ACTH DEPENDENT *tumours of pituitary *ectopic ACTH production.
- 6. Advanced hypothyroidism in adults by swelling of skin and subcutaneous tissues. Features: *goiter *puffiness of face with periorbital swelling *coarsening and loss of scalp hair *ptosis,dropping of upper eyelid. *impaired fertility *menstrual disturbances
- 7. Due to acidophillic cell tumour of anterior pituitary which produces excess of growth hormone (after epiphyseal closure).enlargement of peripheral region. Elongation and widening of mandible is prognathism.
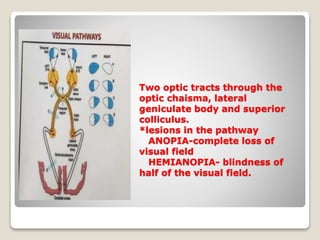
- 8. Two optic tracts through the optic chaisma, lateral geniculate body and superior colliculus. *lesions in the pathway ANOPIA-complete loss of visual field HEMIANOPIA- blindness of half of the visual field.
- 9. IODINE DEFICIENCY swelling in the neck resulting from a enlarged thyroid gland. 2 types: nodular and diffuse hyperthyroid and hypothyroid
- 10. GRAVES DISEASE is the most common hyperthroid disorder.overproduction of t3 and t4. weight loss,weakness,irregular heartbeat and dificulty sleeping.
- 11. Growth hormone deficiency this results in achilds slow groeth pattern and unusual small stature. Normal indivudual
- 12. Its a neuroendocrine reflex when the babby sucks the nipple the reflex starts and passes , pituitary hormones secreted and the milk is ejected.
- 13. Rickets: a softening and weakening of bones in children. Bowlegs: vit d deficient , legs apart.
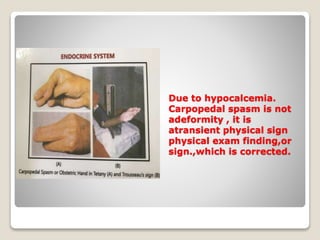
- 14. Due to hypocalcemia. Carpopedal spasm is not adeformity , it is atransient physical sign physical exam finding,or sign.,which is corrected.
- 15. Three neurons dorsal column:fasciculus gracilis(lower limbs) fasciculus cuneatus(upper limbs) ventrolateral spinothalamic: skin to thalamus. Ventroposterior nucleus of the thalamus to the post central gyrus.
- 16. In female reproductive system,an ovarian follicle is afluid filled sac that contains an immature egg or oocyte.these follicles are found in ovaries. Estrogen and progeterone are the female hormones.
- 17. Is a condition of severely stunted physical or mental growth . Due to congenital hypothyroidism.
- 18. The primary motor cortex is a brain region that in humans is located in the dorsal portion of the frontal lobe. Its function is to generate neural impulses that control the execution of the movement.
- 19. A sensory homunculus is a pictorial representation of the primary somatosensory cortex. Located in the parietal lobe , post central gyrus.
- 20. Transection below medulla stops all respiration called apnoea respiratory centres are present in between upper2/3rds of the medulla and pons.
- 21. Micturition reflex normally produces a series ofcontractions of the urinary bladder. The flow of urine through the urethra has an excitatory role in micturition which sustains voiding until the bladder is empty.
- 22. A record or display of a persons heartbeat produced by electrocardiography. P wave-depolarisation of atria in response to Sanode triggering. T WAVE-ventricular repolarisation. QRScomplex- ventricular depolarisation.
- 23. * Also known as Forced vital capacity. * The person is asked to inspire as deeply as possibleand then to breath out as hard and as fast as he can. * The expiration continues till he expired all the air out and thus obtained as forced vital capacity.
- 24. Lung volumes measure the amount of air for a specific function. Lung capacities are the sum of the two or three volumes. Lung volumes include TV,IRV,ERV,RV.
- 25. The four ABO blood groups A,B,AB,O,arise from inheriting one or more of the alternative forms of this gene. The A and B alleles are codominant so both A and B antigens will be expressed on the red cells whenever either allele is present.
- 26. Falling blood pressure stimulates increased sympathetic activity, which leads to increased heart rate,contractility,vasoconstricti on and blood pressure. Longterm regulation involves renal mechanism.
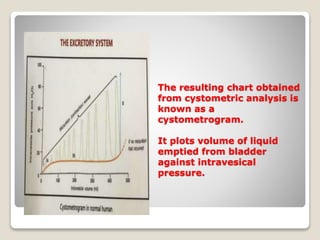
- 27. The resulting chart obtained from cystometric analysis is known as a cystometrogram. It plots volume of liquid emptied from bladder against intravesical pressure.
- 28. Juxtaglomerular apparatus is formed by DCT and glomerular afferent arteriole. It is located near the vascular pole of the glomerulus and its main function is to regulate blood presure and the filtration rate of glomerulus.
- 29. Normal range- 60 to 100 beats per min. It is regulated by the medullary centres of the brain. Sympathetic increases,vice versa
- 30. Obstructive: conditions that hinder a persons ability to exhale all air from their lungs. Restrictive: have difficulty in expanding their lungs