Pidgin & creoles
- 1. Pidgin & Creoles Contact languages
- 2. ÔÄ™ Introduction ÔÄ™ History/origin ÔÄ™ Characteristics ÔÄ™ Developmental stages ÔÄ™ Comparison ÔÄ™ Conclusion Outlines:
- 3. ÔÄ™ Sociolinguistic terms ÔÄ™ Contact languages Introduction:
- 4.  Some of the geographical meanings for pidgin are: In Chinese means business In Portuguese means ‘job or occupation’ In South American language means ‘people’ In Hebrew word ‘barter’ Definition: Pidgin is a simple speech-form used as a means of communication among people who do not share a common language. Pidgin:
- 5.  Creole is a French word means ‘native to a locality or country’ Definition: Creole is a stable natural language that has developed from a pidgin. Creole:
- 6. History/Origin of pidgin and creole ÔÄ™ Originated from temporary events: trade seafaring tourism ÔÄ™ Traumatic social situation: wars slavery
- 7. ÔÄ™ Baby talk theory ÔÄ™ Independent parallel development theory ÔÄ™ Nautical jargon theory ÔÄ™ Monogenetic/relaxification theory ÔÄ™ Universalist theory Theories of origin:
- 8. Characteristics of pidgin & creole
- 9. ÔÄ™ A product of multi-lingual ÔÄ™ Unstable grammar ÔÄ™ Socially limited ÔÄ™ Not a mean of group identification ÔÄ™ Short lived ÔÄ™ S-V-O syntax ÔÄ™ No affixation ÔÄ™ Limited vocabulary characteristics of pidgin:
- 10. ÔÄ™ Product of expanded pidgin ÔÄ™ Nativization ÔÄ™ Consistency ÔÄ™ Stable grammar ÔÄ™ Expanded vocabulary ÔÄ™ Systematic ÔÄ™ Complex sentence structure ÔÄ™ Long lived (attained as mother tongue) Characteristics of creole:
- 11. Development of pidgin & creole
- 12. Social situation Linguistic correlate Marginal contact Restricted pidgin Nativization Extended pidgin Mother tongue development Creole Movement towards standard language Decreolization
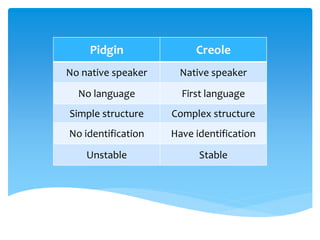
- 14. Pidgin Creole No native speaker Native speaker No language First language Simple structure Complex structure No identification Have identification Unstable Stable
- 15. ÔÄ™ Marginal languages. ÔÄ™ Born unconsciously from inter-linguist social communication. ÔÄ™ Related to each other. ÔÄ™ Have specific characteristics. ÔÄ™ Have geographical and social affection. ÔÄ™ Are systematic & can be investigated or learnt. Conclusion