PLANNING Ch 4.pptx
- 1. PLANNING Chapter-4 Class-12 Commerce Subject- Business studies By Educator ĻC Lovely Chouksey
- 2. Meaning of Planning Planning is the process of setting objectives, formulating various courses of action in order achieve them, and selecting the best possible alternative from the various courses of action available in order to ensure completion of organisational goals. Ą°Planning is the thinking process, the organised foresight, the vision based on fact and experience that is required for intelligent action.Ąą ĄŠ Afford and Beatt Ą°Planning is deciding in advance what is to be done. When a manager plans, he projects a course of action for further attempting to achieve a consistent coordinate structure of operations aimed at the desired results.Ąą ĄŠ Theo Haimann Planning aims at bridging the gap between where we are and where we want to go.
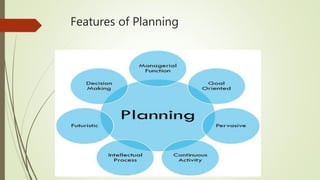
- 4. Features of Planning 1.Planning focuses on achieving objectives. Objectives are set in planning and all the means, resources and courses of action to achieve these objectives are formulated in planning. 2.Planning is the primary function of management. Planning is the base of (and guide to) all the remaining functions of management. 3.Planning is pervasive. It is present everywhere, in all departments and at all levels. 4.Planning is continuous. One plan is followed by another plan after its completion. 5.Planning is futuristic. Planning is a forward looking, forecast involving futuristic function of management. 6.Planning involves decision making. Decision making involves chalking out several options, evaluating and chosing the best out of them. 7.Planning is a mental exercise (Intellectual Process). Planning is a thinking function which involves foresightedness, imagination and good judgement. Planning involves the ability to imagine the future and making the best choice possible.
- 6. Importance of Planning ? Planning provides direction. Once the goals of all employees and departments are set they are properly guided in the required direction. ? Planning reduces the risk of uncertainty. A good plan cannot eliminate uncertainties of future. However it can reduce unnecessary risks. ? Planning reduces overlapping and wasteful activities. Every person and department is assigned an objective and direction which rules out possible confusion. ? Planning involves innovative ideas. Planning is all about thinking in a unique and improved way so it involves innovation. ? Planning helps in decision making. Decision making involves choosing the best among the identified options. ? Planning sets standards for controlling. Controlling only tries to meet the objectives set at the stage of planning.
- 7. Limitations of Planning ? Planning leads to rigidity. Once a plan is formed by the top management and is conveyed to the whole team, it is very difficult to alter it. ? Planning may not work in a dynamic environment. Planning cannot accurately forecast the future changes that occur in various dimensions of business environment. Even a very good plan may fail in the dynamic environment. ? Planning reduces creativity. Once a plan made by the top management is communicated to the middle and lower levels of management, it is difficult to change it for them. The creativity of the lower and middle level employees is thus hampered. ? Planning is a time-consuming process. Planning in itself is a time-consuming process which sometimes reduces the time of its implementation, especially in case of annual plans. ? Planning does not guarantee success. Though the plans formed may be very good on paper yet when it comes to their outcomes they may fail due to everchanging business situations. There is no guarantee that previously tried and tested plans will lead to success in each and every situation.
- 9. Planning Process ? Setting objectives. When the organisational objectives are set they are followed by the setting of departmental objectives. Finally individual objectives are set. ? Developing premises. Premises are developed on the basis of forecasts and previous plans. It is also important to have consensus of all the managers before opting for a plan. ? Identifying alternative courses of action. At this stage it is advisable to identify as many courses of action as possible. ? Evaluating alternative courses. The pros and cons, positives and negatives of all these alternatives should be properly considered. ? Selecting an alternative. The best course of action should be chosen. A single option or a combination of the best options should be finalised. ? Implementing the plan. The chosen plan should be put into action. ? Follow up action. The effectiveness of the plans after their implementation, should be checked through proper follow up.
- 10. CASE STUDIES Q.1. Indian Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Ltd.ĄŊ is engaged in the manufacturing and distribution of medicines. The company has set-up an objective of increasing its sales turnover by 20%. To achieve this objective the company has decided to diversify into baby health care products. Since the company has already set its objectives and developed the premises based on the same, it wants your help for the remaining steps to be taken in this process. Explain briefly these steps. Answer ? Following are the remaining steps in the planning process. ? Identifying alternatives. In this step various alternative courses of action are identified. The identified course of action can either be routine or innovative in nature. An innovative course of action involves sharing of ideas by more and more people. In important projects more and more alternatives should be generated and discussed. ? Evaluating alternative courses. In this step the positive as well as negative aspects associated with each and every alternative course of action is evaluated and analysed. In other words, the pros and cons of each alternative is studied. ? Selecting an alternative. In this step the best plan is adopted and implemented. That plan is selected which has minimum negative aspects. The ideal plan should be the one which is most feasible and profitable. ? Implementing the plan. In this step plans are put into action. All other managerial functions come into picture in this step. It involves doing what is required for the purpose of implementation of plan. ? Follow-up action. This step involves monitoring of the plans. This step ensures that plans are being implemented and activities are performed as per schedule.
- 11. Q.2 ĄŪSerious BusinessĄŊ is a balloon manufacturing firm. With the arrival of foreign firms it is feeling the pressure of improving its business strategy. Because of the firmĄŊs advance planning it could not suddenly bring changes in its plans as the whole organisation had started implementing the plan. But this year the organisation wants to ensure success. However, the firm knows that the environment is changeable and continues to vary in a fast manner. The organisation wants to in advance for a better future. It has decided to allocate a portion of its budget specifically for planning as it knows there are going to be expenses like ExpertĄŊs fee, survey charges, etc. Which limitations of planning have been identified in the above case? Answer: The limitations of planning highlighted in the above case are: Planning leads to rigidity. Because of the firmĄŊs advance planning it could not suddenly bring changes in its plans as the whole organisation had started implementing the decided plan. Planning may not work in a dynamic environment. However, the firm knows that the external environment is changeable and continues to vary in a fast manner. Planning involves huge costs. It has decided to allocate a portion of its budget specifically for proper planning as it knows that there are going to be expenses like ExpertĄŊs fee, survey charges,
- 12. Q.3 Sukumar is an energetic middle level manager. He tries to make best plans. For this he involves foresight and intelligent imagination. Within three years many of his projects have been very successful. His high success rate is due to his good plans. He always makes alternative plans and selects the best out of them after considering relevant aspects. However, he knows it is not necessary that his all plans will be successful. He knows that sometimes his concern for making very good plans eats a lot of time and energy. His friend Jyoti suggests him to take suggestions from others when he makes his plans and also consider plans made by others. Even after so much painstaking Sukumar knows that his plans can yet fail in the uncertain business environment. He has recently decided to plan carefully in future. Which features of Planning have been highlighted in the above case? Which limitations of Planning have been highlighted in the above case? Answer: The features of Planning which have been highlighted in the above case are: Planning is a mental exercise. For this he involves foresight and intelligent imagination. Planning involves decision making. He always makes alternative plans and selects the best out of them after considering relevant aspects. The limitations of Planning which have been highlighted are: Planning is a time consuming process. He knows that sometimes his concern for making very good plans eats a lot time and energy. Planning does not guarantee success. Even after so much painstaking Sukumar knows that his plans can yet fail in the uncertain business environment.