1 of 13
Download to read offline




Ad
Recommended
Łukasz Pancewicz: Proces konsultacji społecznych przy tworzeniu studium uwaru...
Łukasz Pancewicz: Proces konsultacji społecznych przy tworzeniu studium uwaru...Wstawiacz
╠²
Zagadnienie konsultacji społecznych Gminny Program Rewitalizacji Miasta Słupska 2017-2025 +
Gminny Program Rewitalizacji Miasta Słupska 2017-2025 +RadioGdansk
╠²
Przedstawienie wynik├│w prac nad Gminnym Programem Rewitalizacji oraz prezentacja projektowanych dzia┼éa┼ä rewitalizacyjnych o charakterze spo┼éecznymi i inwestycyjnym, s┼éu┼╝─ģcym poprawie jako┼øci ┼╝ycia mieszka┼äc├│w z wykorzystaniem potencja┼éu obszaru.Smart_kom - prezentacja projektu
Smart_kom - prezentacja projektuKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Smart_KOM - prezentacja Agnieszki W┼éodarczyk, koordynatora projektu podczas konferencji ŌĆ×SMART_KOM. Krak├│w w sieci inteligentnych miastŌĆØ, 7.11.2014 r., Krak├│wKrak├│w Living Lab
Krak├│w Living LabKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Krak├│w Living Lab - prezentacja Wojciecha Przybylskiego, dyrektora dzia┼éu rozwoju parku technologicznego podczas konferencji ŌĆ×SMART_KOM. Krak├│w w sieci inteligentnych miastŌĆØ, 7.11.2014 r., Krak├│wSmart Cities supporting Start-ups and their citizen
Smart Cities supporting Start-ups and their citizenKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document discusses the role of the Aalto Design Factory and related initiatives in Espoo, Finland, in fostering a startup culture and supporting entrepreneurs. It highlights the collaborative environment provided by co-working spaces like Startup Sauna and the importance of location, facilities, and community in enabling startups to thrive. Key insights include the need for cost-effective resources and city engagement to promote entrepreneurship and local innovation.Smart city
Smart cityKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Smart city - prezentacja El┼╝biety Koterby, zastepcy Prezydenta ds. Rozwoju Miasta Krakowa podczas konferencji ŌĆ×SMART_KOM. Krak├│w w sieci inteligentnych miastŌĆØ, 7.11.2014, Krak├│wRegion with smart citizen and smart business ecosystem
Region with smart citizen and smart business ecosystemKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document discusses Barcelona's strategy for becoming a smart city and region through ICT-based solutions and community involvement. It outlines key priorities such as smart governance, economic improvement, and environmental management, while emphasizing the importance of collaboration between public and private sectors. The vision extends beyond urban issues to encompass broader regional challenges, driving a new data-driven economy in Catalonia.City of Helsinki urban facts and Helsinki region infoshare
City of Helsinki urban facts and Helsinki region infoshareKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document outlines Helsinki's urban development strategies and population growth projections from 2014 to 2050. It emphasizes the city's commitment to creating a liveable, inclusive, and innovative environment through open data, citizen engagement, and sustainable urban planning. Various urban areas are targeted for growth and job creation, while partnerships with universities and businesses are encouraged to enhance the city's competitiveness and quality of life.Smart Environment -
understanding and meaning
Smart Environment -
understanding and meaningKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
This document summarizes a workshop on understanding smart environments and cities. The workshop objectives were to understand what defines a smart city through an evidence-based learning process. A smart city is defined as one that performs well in key fields of development like economy, environment, mobility, people, living, and governance. For the environment domain, the workshop discussed the most relevant components like green space, pollution levels, ecological awareness, and sustainable resource management. The goal was to identify Krakow's strengths and weaknesses in these areas to help develop a smart city strategy and roadmap.Forum╠²Virium╠²Helsinki
Forum╠²Virium╠²HelsinkiKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document discusses public-private-people partnerships for new digital service innovations through smart city living labs. It provides examples of challenge cities that are retrofitting existing legacy systems including Freiburg, New York, Toronto, Helsinki, and Amsterdam. The document promotes cities as enablers of digital innovations and is signed off by Jarmo Eskelinen from Forum Virium Helsinki.Green areas in city
Green areas in cityKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
This document discusses green areas in Krakow, Poland. It provides statistics on the percentage of land covered by parks, forests, and protected areas in Krakow and other major Polish cities. Krakow currently has 16.5% of its land as green areas, above the average of 13.1% for cities over 500,000 people. However, the document also outlines threats to Krakow's green spaces from private and public development projects that could reduce vegetation and open spaces through new construction, infrastructure projects, and removal of trees. Maintaining and expanding green areas is presented as important for Krakow to develop as a smart, sustainable city.Environmental conditions
Environmental conditionsKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Przemysław Szwałko gave a presentation on January 9th, 2014 about the environmental conditions of Krakow, Poland. He discussed Krakow's orography, including key elevation points. He also covered the hydrographic network, including the Vistula River and its tributaries. Additionally, he examined semi-natural habitats, protected areas, industrial degradation, air pollution, waste treatment, geothermal sources, forests and afforestation, and urban green spaces in Krakow. Szwałko emphasized that understanding Krakow's environmental conditions is the base for sustainable planning and development in the city.More Related Content
More from Krakowski Park Technologiczny (19)
Smart_kom - prezentacja projektu
Smart_kom - prezentacja projektuKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Smart_KOM - prezentacja Agnieszki W┼éodarczyk, koordynatora projektu podczas konferencji ŌĆ×SMART_KOM. Krak├│w w sieci inteligentnych miastŌĆØ, 7.11.2014 r., Krak├│wKrak├│w Living Lab
Krak├│w Living LabKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Krak├│w Living Lab - prezentacja Wojciecha Przybylskiego, dyrektora dzia┼éu rozwoju parku technologicznego podczas konferencji ŌĆ×SMART_KOM. Krak├│w w sieci inteligentnych miastŌĆØ, 7.11.2014 r., Krak├│wSmart Cities supporting Start-ups and their citizen
Smart Cities supporting Start-ups and their citizenKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document discusses the role of the Aalto Design Factory and related initiatives in Espoo, Finland, in fostering a startup culture and supporting entrepreneurs. It highlights the collaborative environment provided by co-working spaces like Startup Sauna and the importance of location, facilities, and community in enabling startups to thrive. Key insights include the need for cost-effective resources and city engagement to promote entrepreneurship and local innovation.Smart city
Smart cityKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Smart city - prezentacja El┼╝biety Koterby, zastepcy Prezydenta ds. Rozwoju Miasta Krakowa podczas konferencji ŌĆ×SMART_KOM. Krak├│w w sieci inteligentnych miastŌĆØ, 7.11.2014, Krak├│wRegion with smart citizen and smart business ecosystem
Region with smart citizen and smart business ecosystemKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document discusses Barcelona's strategy for becoming a smart city and region through ICT-based solutions and community involvement. It outlines key priorities such as smart governance, economic improvement, and environmental management, while emphasizing the importance of collaboration between public and private sectors. The vision extends beyond urban issues to encompass broader regional challenges, driving a new data-driven economy in Catalonia.City of Helsinki urban facts and Helsinki region infoshare
City of Helsinki urban facts and Helsinki region infoshareKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document outlines Helsinki's urban development strategies and population growth projections from 2014 to 2050. It emphasizes the city's commitment to creating a liveable, inclusive, and innovative environment through open data, citizen engagement, and sustainable urban planning. Various urban areas are targeted for growth and job creation, while partnerships with universities and businesses are encouraged to enhance the city's competitiveness and quality of life.Smart Environment -
understanding and meaning
Smart Environment -
understanding and meaningKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
This document summarizes a workshop on understanding smart environments and cities. The workshop objectives were to understand what defines a smart city through an evidence-based learning process. A smart city is defined as one that performs well in key fields of development like economy, environment, mobility, people, living, and governance. For the environment domain, the workshop discussed the most relevant components like green space, pollution levels, ecological awareness, and sustainable resource management. The goal was to identify Krakow's strengths and weaknesses in these areas to help develop a smart city strategy and roadmap.Forum╠²Virium╠²Helsinki
Forum╠²Virium╠²HelsinkiKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
The document discusses public-private-people partnerships for new digital service innovations through smart city living labs. It provides examples of challenge cities that are retrofitting existing legacy systems including Freiburg, New York, Toronto, Helsinki, and Amsterdam. The document promotes cities as enablers of digital innovations and is signed off by Jarmo Eskelinen from Forum Virium Helsinki.Green areas in city
Green areas in cityKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
This document discusses green areas in Krakow, Poland. It provides statistics on the percentage of land covered by parks, forests, and protected areas in Krakow and other major Polish cities. Krakow currently has 16.5% of its land as green areas, above the average of 13.1% for cities over 500,000 people. However, the document also outlines threats to Krakow's green spaces from private and public development projects that could reduce vegetation and open spaces through new construction, infrastructure projects, and removal of trees. Maintaining and expanding green areas is presented as important for Krakow to develop as a smart, sustainable city.Environmental conditions
Environmental conditionsKrakowski Park Technologiczny
╠²
Przemysław Szwałko gave a presentation on January 9th, 2014 about the environmental conditions of Krakow, Poland. He discussed Krakow's orography, including key elevation points. He also covered the hydrographic network, including the Vistula River and its tributaries. Additionally, he examined semi-natural habitats, protected areas, industrial degradation, air pollution, waste treatment, geothermal sources, forests and afforestation, and urban green spaces in Krakow. Szwałko emphasized that understanding Krakow's environmental conditions is the base for sustainable planning and development in the city.Planowanie przestrzenne w Krakowie
- 1. PLANOWANIE PRZESTRZENNE W KRAKOWIE Jan Adam Barański Wydział Rozwoju Miasta Urzędu Miasta Krakowa
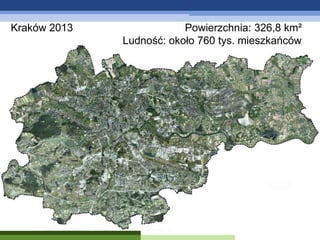
- 2. Krak├│w 2013 Powierzchnia: 326,8 km┬▓ Ludno┼ø─ć: oko┼éo 760 tys. mieszka┼äc├│w
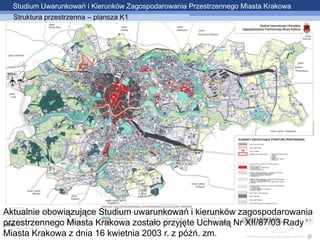
- 3. Studium Uwarunkowa┼ä i Kierunk├│w Zagospodarowania Przestrzennego Miasta Krakowa Struktura przestrzenna ŌĆō plansza K1 Aktualnie obowi─ģzuj─ģce Studium uwarunkowa┼ä i kierunk├│w zagospodarowania przestrzennego Miasta Krakowa zosta┼éo przyj─Öte Uchwa┼é─ģ Nr XII/87/03 Rady Miasta Krakowa z dnia 16 kwietnia 2003 r. z p├│┼║┼ä. zm.
- 4. Obowi─ģzuj─ģce i sporz─ģdzane plany miejscowe ŌĆō stan na 11 kwietnia 2013 r. 130 plan├│w uchwalonych ŌĆō 48,2 % powierzchni miasta
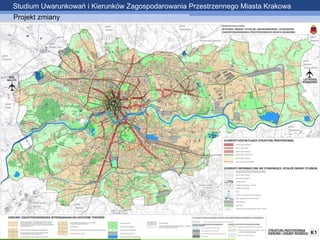
- 5. Studium Uwarunkowań i Kierunków Zagospodarowania Przestrzennego Miasta Krakowa Projekt zmiany
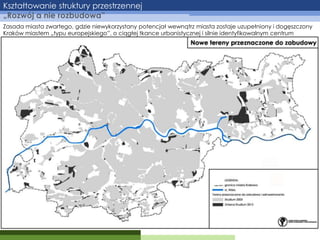
- 6. Kszta┼étowanie struktury przestrzennej ŌĆ×Rozw├│j a nie rozbudowaŌĆØ Zasada miasta zwartego, gdzie niewykorzystany potencja┼é wewn─ģtrz miasta zostaje uzupe┼éniony i dog─Öszczony Krak├│w miastem ŌĆ×typu europejskiegoŌĆØ, o ci─ģg┼éej tkance urbanistycznej i silnie identyfikowalnym centrum
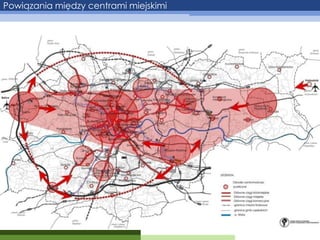
- 7. Powi─ģzania mi─Ödzy centrami miejskimi
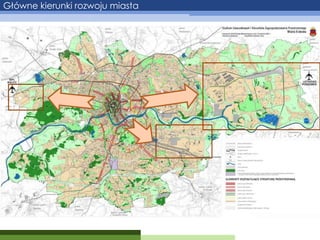
- 8. Główne kierunki rozwoju miasta
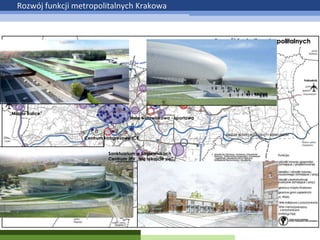
- 9. Rozw├│j funkcji metropolitalnych Krakowa ŌĆ×Miasto BaliceŌĆØ Hala widowiskowo - sportowa Centrum kongresowe ICE Sanktuarium w ┼üagiewnikach Centrum JPII ŌĆ×Nie l─Ökajcie si─ÖŌĆØ OBSZAR NOWEJ HUTY OBJ─śTY KONKURSEM
- 10. Centrum gospodarki, nowoczesnych technologii i nauki www.agh.edu.pl www.ka.edu.pl Akademia Krakowska im. Andrzeja Frycza Modrzewskiego Budynek In┼╝ynierii Materia┼éowej i Ceramiki AGH www.mcm.ar.krakow.pl Ma┼éopolskie Centrum Monitoringu ┼╗ywno┼øci UR skyscrapercity.com Wydzia┼é Informatyki AGH
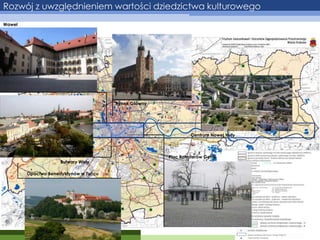
- 11. Rozw├│j z uwzgl─Ödnieniem warto┼øci dziedzictwa kulturowego Wawel Rynek G┼é├│wny Centrum Nowej Huty Bulwary Wis┼éy Opactwo Benedyktyn├│w w Ty┼äcu Plac Bohater├│w Getta
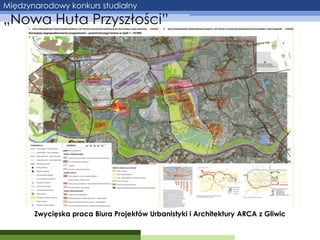
- 12. Mi─Ödzynarodowy konkurs studialny ŌĆ×Nowa Huta Przysz┼éo┼øciŌĆØ Zwyci─Öska praca Biura Projekt├│w Urbanistyki i Architektury ARCA z Gliwic
- 13. DZI─śKUJ─ś ZA UWAG─ś Jan Adam Bara┼äski Wydzia┼é Rozwoju Miasta Urz─Ödu Miasta Krakowa
