Plant dna extraction method
- 4. ŌĆó DNA? ŌĆó Structure of DNA ŌĆó Method of DNA isolation ŌĆó Maxwell┬« 16 Plant DNA Kit Method ŌĆó Spin column Method ŌĆó CTAB Method ŌĆó Reagent Used In CTAB Method ŌĆó Procedure for CTAB method ŌĆó Why DNA Extraction? ŌĆó Storage of isolated DNA ŌĆó Use of the DNA
- 5. DNA? Something to say about DNA Cell Nucleus is the empire DNA
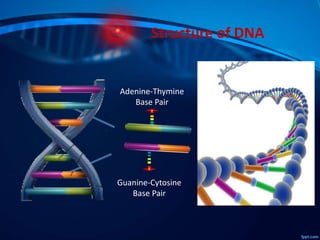
- 6. Structure of DNA Adenine-Thymine Base Pair Guanine-Cytosine Base Pair
- 7. 1. Maxwell® 16 Plant DNA Kit Method 2. Spin column Method 3. CTAB Method Method of DNA isolation
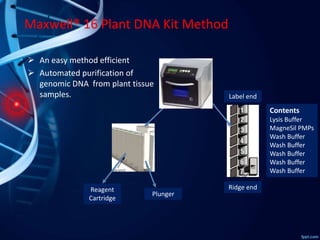
- 8. Ridge end Label end Contents Lysis Buffer MagneSil PMPs Wash Buffer Wash Buffer Wash Buffer Wash Buffer Wash Buffer Plunger Reagent Cartridge Maxwell┬« 16 Plant DNA Kit Method ’āś An easy method efficient ’āś Automated purification of genomic DNA from plant tissue samples.
- 9. Spin column Method ’üČIt is a solid phase extraction method ’üČQuickly purify nucleic acids. ’üČNucleic acid will bind to the solid phase of silica under certain conditions.
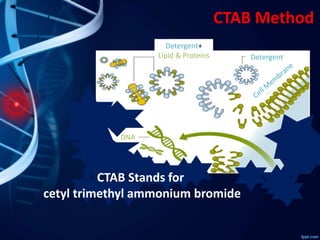
- 10. CTAB Method Detergent+ Lipid & Proteins Detergent DNA CTAB Stands for cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
- 11. oCTAB oChloroform oIsoamyl alchohol oIsopropyl alcohol oRNAse oQiagen oAmbion o Proteinase K oNaCl oMercaptoethanol oAmmonium acetate
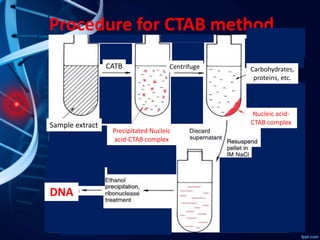
- 12. Procedure for CTAB method Sample extract CATB Centrifuge Carbohydrates, proteins, etc. Nucleic acid- CTAB complex DNA Precipitated Nucleic acid-CTAB complex
- 13. Why DNA Extraction? ŌĆó Genetic Testing Body Identification ŌĆó Analysis of Forensic Evidence
- 14. There are four temperature based strategies for long term DNA conservation. These are storage at: ’üČ -20┬░ C ’üČ -80┬░ C ’üČ -196┬░ C ’üČ Dried, at room temperature ’üČStore DNA in dry state, reduces molecular mobility and inhibits the depurination, depyrimidination, deamination and hydrolytic ’üČThe DNA immobilized on FDA cards is amenable to PCR after 17 years storage. ’üČDNA in aqueous phase is stored under slightly basic conditions. ’üČAt -196┬░ C, DNA is maintained in a vitreous state General consideration for DNA storage:
- 15. ’üČUnderstanding Individuality of Plants ’üČUsing genetic information of DNA for plant modification ’üČ Use in forensic analysis ’üČUse to solve historical puzzle