Plant Nutrition
- 1. Plant nutrition Dr Jahangeer Ahmad Baba
- 10. Plant nutrition : plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth, plant metabolism and their external supply. Criteria for Essentiality: (Arnon and Stout 1939) ➢ The element must be absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of the element the plants do not complete their life cycle or set the seeds. ➢ The requirement of the element must be specific and not replaceable by another element. In other words, deficiency of any one element cannot be met by supplying some other element. ➢ The element must be directly involved in the metabolism of the plant.
- 12. Complete solution containing all minerals (control) Solution lacking potassium (experimental) – Macronutrients, such as carbon and nitrogen • Are needed in large amounts, mostly to build organic molecules – Micronutrients, including iron and zinc • Are needed in small amounts, act mainly as cofactors of enzymes
- 13. Name Chemical Relative Function in plant symbol % in plant to N Primary macronutrients Nitrogen N 100 Proteins, amino acids Phosphorus P 6 Nucleic acids, ATP Potassium K 25 Catalyst, ion transport Secondary macronutrients Calcium Ca 12.5 Cell wall component Magnesium Mg 8 Part of chlorophyll Sulfur S 3 Amino acids Iron Fe 0.2 Chlorophyll synthesis Micronutrients Copper Cu 0.01 Component of enzymes Manganese Mn 0.1 Activates enzymes Zinc Zn 0.03 Activates enzymes Boron B 0.2 Cell wall component Molybdenum Mo 0.0001 Involved in N fixation Chlorine Cl 0.3 Photosynthesis reactions
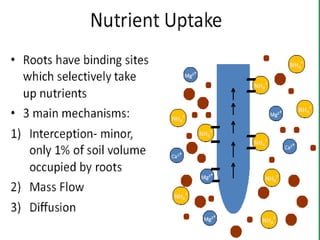
- 14. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings • Plant root hairs – Are closely associated with the soil Soil particle surrounded by film of water Root hair Water Air space
- 16. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings • Cations, positively charged ions – Adhere to soil particles • In cation exchange, root hairs release H+ ions – Which displace cations from the soil particles, allowing the root hairs to absorb them Clay particle Root hair H+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+
- 17. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings • Anions, negatively charged ions – Are readily available to plants because they are not bound to soil particles – Tend to drain out of the soil rapidly
- 18. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Transpiration pulls water up xylem vessels • Transpiration can move xylem sap – Which consists of water and dissolved organic nutrients, to the top of the tallest tree Figure 32.3 Root hair Flowofwater Soil particle Water Water uptake from soil Adhesion Cell wall Cohesion, by hydrogen bonding Xylem cells Cohesion and adhesion in the xylem Xylem sap Mesophyll cells Air space within leaf Stoma Outside air Transpiration Water molecule
- 24. Soil pH Greatest nutrient availability in 5.5-6.5 range