Plant tissues slides
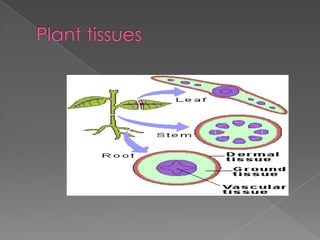
- 4. ÔÇû Dermal tissue ÔÇû Ground tissues ÔÇû Vascular tissue
- 6. ÔÇû Consists of the epidermis and the periderm ÔÇû Epidermis is a single layer of closely packed cells ÔÇû It also covers and protects the plant
- 7.  Epidermis of the plant’s leaves secretes a coating called cuticle  Cuticle helps the plant retain water  Guard cells in the epidermis regulate gas exchange between the plants and the environment
- 9. ÔÇû It synthesize organic compounds ÔÇû Supports and provide storage for the plant ÔÇû It is made up of Parenchyma, Collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells
- 10. ÔÇû Parenchyma cells synthesize and store organic products in the plants ÔÇû Parenchyma cells in leaves control photosynthesis ÔÇû Collenchyma cells have a support function in plants
- 11. ÔÇû They do not restrain growth due to their lack of secondary cells and absence of a hardening agent in their primary walls ÔÇû Sclerenchyma cells also have support function in plants but they have a hardening agent and are much more rigid
- 13. ÔÇû It is made up of xylem and phloem ÔÇû The xylem and phloem allows water and other nutrients to be transported throughout the plant ÔÇû Xylem is made up of two cells called tracheids and vessel elements
- 14. ÔÇû Tracheids and vessel elements form tube shaped structures that provide pathways for water and minerals to travel from the roots to the leaves ÔÇû Tracheids are found in all vascular plants ÔÇû Vessels are found only in angiosperms
- 15. ÔÇû Tracheids are non-living ÔÇû Phloem consists of cells called sieve tubes and companion cells ÔÇû The cells assist in the transportation of nutrients and sugar produced during photosynthesis from leaves to the other parts of the plant
- 16. ÔÇû Sieve-tubes and companion cells of phloem are living ÔÇû Companion cells contain nucleus and actively transport sugar into and out of the sieve tubes