plasma proteins
- 1. PLASMA PROTEINS Chemical pathology Presented by Amna Sahar
- 2. Contents ïą Definition of plasma proteins ïą Functions ïą Compositions ïą Follow-up plasma protein test ïą Methods for detection of different plasma proteins ïą Protein electrophoresis ïą References
- 3. Plasma Proteins The proteins present in the plasma of human blood are a mixture of simple proteins, glycoproteins, lipoproteins and other conjugated proteins are called âPlasma Proteinsâ. These may be separated by salt precipitation, immunological technique and electrophoresis âĒ Plasma is obtained from anti-coagulated blood âĒ Plasma proteins forms 7% of the solids in plasma âĒ Total protein content of normal plasma is 6-8g/100ml âĒ Almost all plasma proteins are synthesized by liver except immunoglobulin
- 4. Functions ïą Protein nutrition ïą Osmotic pressure and water balance ïą Buffering action ïą Transport of lipids ïą Transport of other substances ïą Blood coagulation
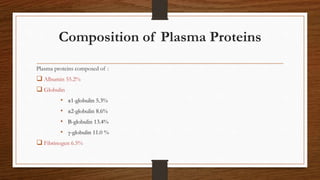
- 5. Composition of Plasma Proteins Plasma proteins composed of : ïą Albumin 55.2% ïą Globulin âĒ Îą1-globulin 5.3% âĒ Îą2-globulin 8.6% âĒ Î-globulin 13.4% âĒ Îģ-globulin 11.0 % ïą Fibrinogen 6.5%
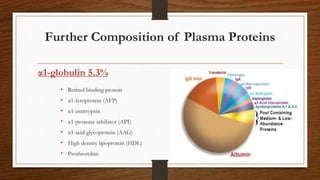
- 6. Further Composition of Plasma Proteins âĒ Retinol binding protein âĒ Îą1-fetoprotein (AFP) âĒ Îą1-antitrypsin âĒ Îą1-protease inhibitor (API) âĒ Îą1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) âĒ High density lipoprotein (HDL) âĒ Prothrombin Îą1-globulin 5.3%
- 7. Further Composition of Plasma Proteins âĒ Ceruloplasmin (ferro-oxidase) âĒ Corticosteroid binding globulin âĒ Hepatoglobin âĒ Thyroxin binding globulin (TBG) âĒ Îą2-macroglobulin (AMG) Îą2-globulin 5.3%
- 8. Further Composition of Plasma Proteins âĒ Transferrin âĒ Hemopexin âĒ Low density lipoprotein LDL âĒ Îē2 macroglobulin âĒ C4 complement âĒ C3 compliment âĒ C1q complement âĒ C-reactive protein Îē-globulin 13.4%
- 9. Further Composition of Plasma Proteins âĒ Ig G âĒ Ig M âĒ Ig E âĒ Ig A âĒ Ig D Îģ-globulin 11.0%
- 10. Follow Up Plasma Protein Test âĒ C-reactive protein tests to evaluate for inflammation âĒ Immunoglobulin tests to measure antibodies âĒ liver enzyme tests âĒ Protein electrophoresis to look for underlying bone marrow disorders
- 11. Methods for detection of Plasma Protein âĒ Precipitation method âĒ BCG method âĒ electrophoresis âĒ Ultra centrifugation âĒ Precipitation method âĒ Radioimmunoassay âĒ Enzyme-labelled Immunoassay âĒ Serum protein electrophoresis Albumin For Îą1-fetoprotein (AFP) Îą1-Globulin
- 12. Methods for detection of Plasma Protein âĒ Precipitation method âĒ Serum protein electrophoresis âĒ Immunodiffusion âĒ Immunonephelometric assay âĒ Immunofixation âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ Immunoturbidity âĒ Nephelometry âĒ Immunofixation For Îą1-anti trypsin For Îą1-acid glycoprotein
- 13. Methods for detection of Plasma Protein âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ Immunonephelometric âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ Immunonephelometric For Hepatoglobin Îą2-Globulin For ceruloplasmin âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ Immunonephelometric âĒ ELISA âĒ Latex agglutination immunoassay For Îą2-microglobin
- 14. Methods for detection of Plasma Protein âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ Immunonephelometric âĒ TIBC âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ ELISA âĒ Nephelometry âĒ CRP assay For Transferrin Îē-Globulin For Hemopexin âĒ Immunoassay âĒ Serum protein electrophoresis âĒ Precipitation âĒ Nephelometric immunoassay âĒ Turbidimetry For Îē2-microglobin For LDL For ComplementCRP
- 15. Methods for detection of Plasma Protein âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ Nephelometry âĒ Turbidimetry âĒ Electro chemiluminescent immunoassay âĒ Radioimmunoassay âĒ Screening âĒ Serum protein electrophoresis Îģ-Globulin
- 16. Methods for detection of Plasma Protein âĒ Radial immunodiffusion âĒ Nephelometry âĒ Turbidimetry âĒ Radioimmunoassay âĒ Plasma protein electrophoresis âĒ Clotting time CT Fibrinogen
- 17. Principles of Methods for detection of Plasma Protein Radial immunodiffusion ïž An antigen sample is placed in a well and allowed to diffuse into agar containing a suitable dilution of an antiserum. ïž As the antigen diffuses into the agar, the region of equivalence is established and a ring of precipitation, a precipitin ring, forms around the well. ïž The area of the precipitin ring is proportional to the concentration of antigen. . Nephelometry The principle is to measure forwarded scattered light when a laser beam passes through a sample and the light is deflected by the particles. Radioimmunoassay ïž The principle of RIA involves competitive binding of radiolabeled antigen and unlabeled antigen to a high-affinity antibody. ïž The labeled antigen is mixed with antibody at a concentration that saturates the antigen-binding sites of the antibody. ïž Then test samples of unlabeled antigen of unknown concentration are added in progressively larger amounts ïž The more unlabeled antigen is present, the less radioactivity there is in the complex. ïž The concentration of the unknown (unlabeled) antigen or hapten is determined by comparison with the effect of standards.
- 18. Plasma Protein Electrophoresis Electrophoresis is a separations technique that is based on the mobility of ions in an electric field. Ions have different migration rates depending on their total charge, size, and shape, and can therefore be separated. The technique is used particularly for macromolecules, such as proteins. âĒ Gel electrophoresis involves the use of gel as supporting media for separation of DNA, RNA or proteins under the influence of electric charge. It is usually performed for analytical purposes but may be used as a preparative technique to partially purify molecules prior to use for other methods such as mass spectrometry, PCR, cloning, DNA sequencing and immuno-blotting. âĒ This is the most commonly used electrophoresis in biotechnology laboratories
- 19. Plasma Protein Electrophoresis It may be of two types; 1. Agarose gel electrophoresis Mostly for the separation of DNA fragments having more than 50 base pairs 2. PAGE (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) For separation of proteins It may be Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate SDS-PAGE and NATIVE
- 20. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is mostly used to separate proteins accordingly by size. This is one of the most powerful techniques to separate proteins on the basis of their molecular weight. Principle This technique uses anionic detergent Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) which dissociates proteins into their individual polypeptide subunits and gives a uniform negative charge along each denatured polypeptide. Power Supply: A power supply of 100-200 volts is needed. This is ideal for running and transferring protein resolving gels. Buffer: Two types of buffers are used in SDS-PAGE. The lower reservoir (which has the running gel) has amine buffers. It is adjusted by using HCl. The upper reservoir (which has stacking gel) also has amine buffers but its pH is slightly above that of running gel buffer and is adjusted with glycine instead of HCl.Stain Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 (CBB) is the most popular protein stain (blue bands). 2- SDS-PAGE Reader Densitometric scanning machine
- 21. Procedure
- 23. References âĒ Books âĒ Bishop âĒ Tietz âĒ Pictures âĒ https://www.biochemden.com/plasma-proteins/