Platform Based Business Strategies for Connected IoT Value Chains
- 1. Platform Based Business Strategies for Connected IoT Value Chains Tom Katsioulas, Board Chair Global Semiconductor Alliance Trusted IoT Ecosystem Security (TIES) Mindspark+ HAMAC Webinar Market Entry Strategies 15-Oct-2021 From Ecology of Competition to Collaborative Innovation enabled by digital transformation & ecosystem platforms
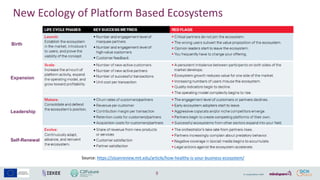
- 2. 2 Old Ecology of Competition ŌĆō Four Stages A business ecosystem is like its biological counterpart, moving from a random collection of species and elements to a more structure community of capital, partners, suppliers, and customers that create cooperative networks. Predators and Prey, HBR 1993 Birth Expansion Leadership Self-Renewal or Death Photography Source: http://www.catherinenelson.com/
- 3. 3 Evolutionary Stages of a Business Ecosystem Source: https://hbr.org/1993/05/predators-and-prey-a-new-ecology-of-competition
- 4. 4 Evolution of Market Strategies & Business Models Scalable Growth & Value 1990 2000 2010 2020 ŌĆó Complete Product ŌĆó Sales Channels ŌĆó Customer Support Vertically Integrated Suppliers of HW + SW Disaggregation of the Electronics Value Chain ŌĆó Product from Parts ŌĆó Web Config Portal ŌĆó Complex Support Enterprise Automation & Open Source Models ŌĆó Internet Commerce ŌĆó SaaS / PaaS / IaaS ŌĆó MSP* Strategies Digital Transformation + Virtual Re-aggregation ŌĆó IoT Value Chain ŌĆó Digital Threads ŌĆó Platform Ecosystems From Products to Connected Complex Systems *Multi-sided Platform
- 5. 5 2011 Company Market Cap $ Billion Exxon Mobil 414.6 Apple 323.9 Microsoft 215.3 Chevron 214.4 Berkshire Hathaway 210.8 General Electric 209.7 IBM 197.8 Google 186.4 Wal-Mart Stores 182.8 Chase 182.7 AT&T 170.5 Procter & Gamble 170.5 Wells Fargo 168.6 Oracle 165.2 Pfizer 162.6 Company Market Cap $ Billion Apple 2252.3 Microsoft 1897.2 Saudi Aramco 1897.2 Amazon 1711.8 Google 1538.9 Facebook 870.5 Tencent 773.8 Tesla 710.1 Alibaba 567.5 Berkshire Hathaway 624.4 Taiwan Semi 558.1 Samsung 510.5 Visa 483.9 Chase 464.8 Johnson & Johnson 427.1 2021 WorldŌĆÖs Most Valuable Companies Scaled With MSPs MSPs Build on Multi- sided Platforms MSPs are technologies, products or services that create value by enabling direct interactions between two or more customer or participant groups Source: https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/strategic-decisions-for-multisided-platforms/
- 6. 6 Platforms Use Dramatically Lower Resources Platforms are "inverted firms" having shifted production from inside to outside *Source: Marshal Van Alstyne https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/platform-strategy-and-the-internet-of-things/ Company Start Year Employees Market Cap ($B) BMW 1916 120,700 66 Uber 2009 30,000 94 Mariott 1927 121,000 52 Airbnb 2008 11,000 106 Walt Disney 1923 223,000 321 Facebook 2004 63,000 986 IBM 1911 350,000 105 SalesForce 1999 56,600 267 New York Times 1851 4,700 7 Twitter 2006 5,500 50
- 7. 7 Why Platform Businesses Scale So Fast? Since COVID-19 Finance & Energy have led losses, Big Tech Platforms have led gains Source: https://www.ft.com/content/844ed28c-8074-4856-bde0-20f3bf4cd8f0
- 8. 8 Typed of Platforms and Scaling Factors Transaction Platforms enable the exchange of information, goods, or services. Examples: Uber, Airbnb, Amazon Market Innovation Platforms enable third parties to add, products & services to core products. Examples: Apple, Google, AWS Source: https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/the-future-of-platforms/ Collaboration Platforms bring diverse experts from firms in connected value chains to co- innovate end-to-end solutions Growing rapidly since COVID-19 The platform serves as an intermediary for direct exchange of transaction subject to network effects The platform serves as a technological foundation upon which other firms develop complementary innovations
- 9. 9 New Ecology of Platform Based Ecosystems Birth Expansion Leadership Self-Renewal Source: https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/how-healthy-is-your-business-ecosystem/
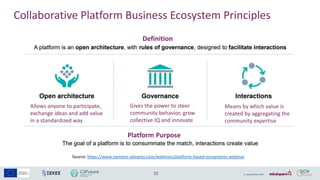
- 10. 10 Collaborative Platform Business Ecosystem Principles Definition Platform Purpose Means by which value is created by aggregating the community expertise Gives the power to steer community behavior, grow collective IQ and innovate Allows anyone to participate, exchange ideas and add value in a standardized way Source: https://www.siemens-advanta.com/webinars/platform-based-ecosystems-webinar
- 11. TIES Example of Platform Based Business Ecosystem ’é¦ Architecture - Open and Participatory ’é¦ Governance - Network Effects Broaden IQ ’é¦ Interactions - ŌĆ£Shift LeftŌĆØ Value Creation ’é¦ Global Brand with 270+ Members ’é¦ Industry Leading Board of Directors ’é¦ Over 70% of $530 Billion Industry Semiconductors EDA, IP, IC, Foundries, OSATs Devices & Systems ODMs, Systems, OEMs, EMS IoT Edge Applications CSPs, IT, PLM, Apps, Operators Trusted Digital Transformation Trusted Digital Thread Trusted Data Analytics Trusted Digital Twins Secure & Trusted Edge Apps & Services Quality and Security Vulnerabilities Source: https://www.gsaglobal.org/iot/ties/ 11
- 12. Smart-Connected Product Supplier Economics Billions of Connected Devices Powered by trillions of chips ŌĆó Better visibility on product field use ŌĆó Remote lifecycle management ŌĆó Reduced support costs and RMAs ŌĆó Lower OPEX, higher differentiation ŌĆó New IoT services business models ŌĆó Security, trust and sharing of data Industrial Automation Manufacturing Energy & Utilities Automotive & Mobility Aerospace & Defense Telco & Media Comms Healthcare, Campus, etc. OT* Edges IoT Edges IT Edges *Source: HPE Edge Data & IoT Services *Operational Technology *Enterprise Infrastructure Smart industries, Cities and Transportation Infrastructure Smart Connected Device Supplier* Managed Edge Device Lifecycle Management Field Use Analytics Fragmented Supply Chain Product-as-a-Service 12 *Source: https://hbr.org/2014/11/how-smart-connected-products-are-transforming-competition
- 13. CSPs, AI, ML Trusted Data, Services and Digital Twins User Apps Digitalization Enables Monetization for All Stakeholders Design-to-Mfg Vendors PLM Enterprise Vendors GSA TIES Digital Workflow Digital Workflow Digital Workflow Digital Workflow PCB Design/Assembly Embedded System IC Design to Silicon Manufacture & Test Digital MES Digital MES Digital MES Zero Touch Onboarding Ecosystem IQ Use Cases Provenance Root-of-Trust Blockchain Digital Thread Config Keys Certs *Source: GSA TIES Intro Presentation Digital and Physical Assets 13
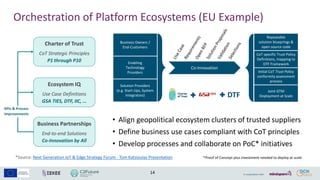
- 14. Business Owners / End-Customers Enabling Technology Providers Solution Providers (e.g. Start-Ups, System Integrators) Co-Innovation Repeatable solution blueprings & open source code CoT specific Trust Policy Definitions, mapping to DTF Framework Initial CoT Trust Policy conformity assessment process Joint GTM Deployment at Scale ŌĆó Align geopolitical ecosystem clusters of trusted suppliers ŌĆó Define business use cases compliant with CoT principles ŌĆó Develop processes and collaborate on PoC* initiatives Charter of Trust CoT Strategic Principles P1 through P10 Ecosystem IQ Use Case Definitions GSA TIES, DTF, IIC, ŌĆ” Business Partnerships End-to-end Solutions Co-Innovation by All KPIs & Process Improvements DTF Orchestration of Platform Ecosystems (EU Example) *Proof of Concept plus investment needed to deploy at scale 14 *Source: Next Generation IoT & Edge Strategy Forum - Tom Katsioulas Presentation