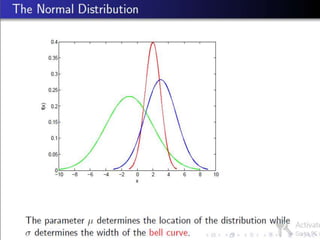
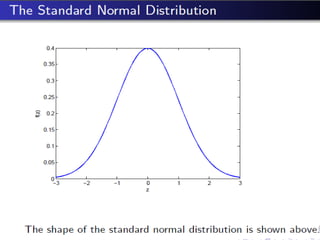
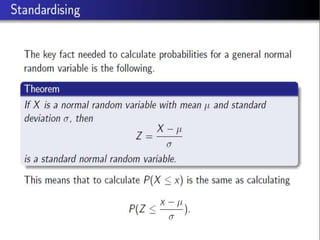
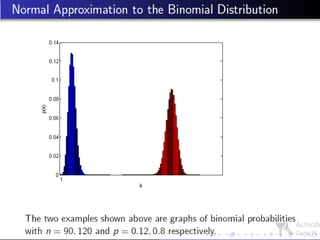
Poisson distribution
- 2. Probability Model: âĒ Binomial DistributionâĶâĶ. âĒ Poison Distribution âĒ Normal Distribution.
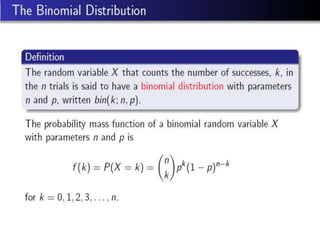
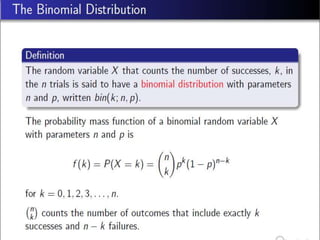
- 4. Defination:
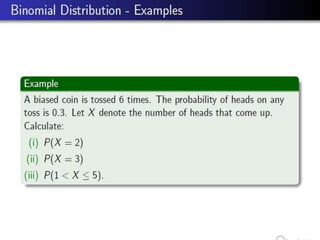
- 5. Examples:
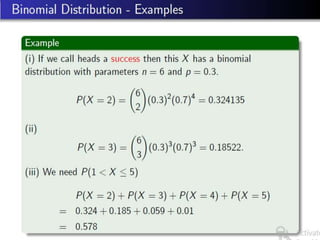
- 6. Examples::
- 7. Examples:::
- 21. Probability Model: âĒ Binomial Distribution. âĒ Poison DistributionâĶâĶ âĒ Normal Distribution.
- 23. Historical Note: âĒ Discovered by Mathematician Simeon Poisson in France in 1781. âĒ The modelling distribution that takes his name was originally derived as an approximation to the binomial distribution.
- 24. Defination: âĒ Is an eg of a probability model which is usually defined by the mean no. of occurrences in a time interval and simply denoted by Îŧ.
- 25. Uses: âĒ Occurrences are independent. âĒ Occurrences are random. âĒ The probability of an occurrence is constant over time.
- 26. Sum of two Poisson distributions: âĒ If two independent random variables both have Poisson distributions with parameters Îŧ and Ξ, then their sum also has a Poisson distribution and its parameter is Îŧ + Ξ .
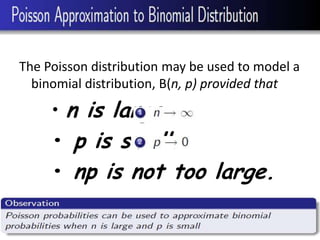
- 27. The Poisson distribution may be used to model a binomial distribution, B(n, p) provided that âĒ n is large. âĒ p is small. âĒ np is not too large.
- 28. F o r m u l a: âĒ The probability that there are r occurrences in a given interval is given by Where, = Mean no. of occurrences in a time interval r =No. of trials.
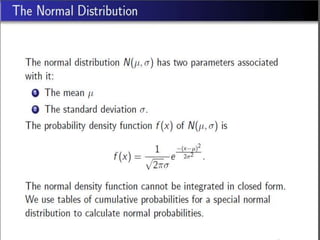
- 29. The Poisson distribution is defined by a parameter, Îŧ.
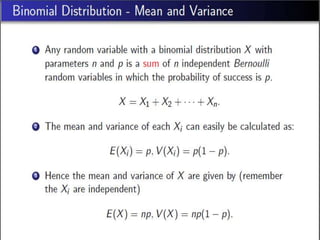
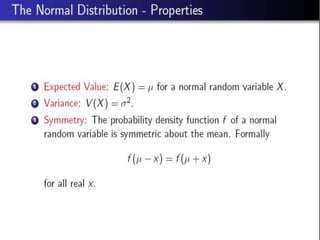
- 30. Mean and Variance of Poisson Distribution âĒ If Ξ is the average number of successes occurring in a given time interval or region in the Poisson distribution, then the mean and the variance of the Poisson distribution are both equal to Ξ. i.e. E(X) = Ξ & V(X) = Ï2 = Ξ
- 31. Examples: 1. Number of telephone calls in a week. 2. Number of people arriving at a checkout in a day. 3. Number of industrial accidents per month in a manufacturing plant.
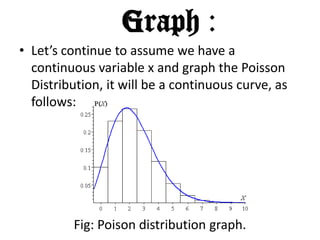
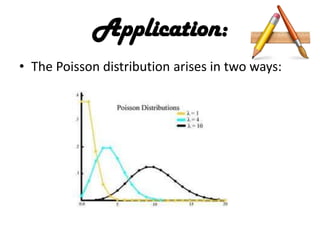
- 32. Graph : âĒ Letâs continue to assume we have a continuous variable x and graph the Poisson Distribution, it will be a continuous curve, as follows: Fig: Poison distribution graph.
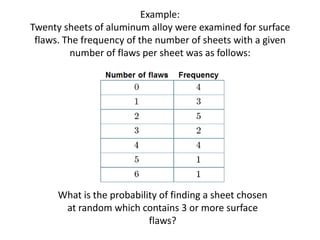
- 33. Example: Twenty sheets of aluminum alloy were examined for surface flaws. The frequency of the number of sheets with a given number of flaws per sheet was as follows: What is the probability of finding a sheet chosen at random which contains 3 or more surface flaws?
- 34. Generally, âĒ X = number of events, distributed independently in time, occurring in a fixed time interval. âĒ X is a Poisson variable with pdf: âĒ where is the average.
- 35. Application: âĒ The Poisson distribution arises in two ways:
- 36. 1. As an approximation to the binomial when p is small and n is large: âĒ Example: In auditing when examining accounts for errors; n, the sample size, is usually large. p, the error rate, is usually small.
- 37. 2. Events distributed independently of one another in time: X = the number of events occurring in a fixed time interval has a Poisson distribution. Example: X = the number of telephone calls in an hour.
- 39. Probability Model: âĒ Binomial Distribution. âĒ Poison Distribution âĒ Normal DistributionâĶâĶ.
- 53. âĒThe End
- 54. Thank YouâĶ.