Population ecology
- 2. population ecology ï Population ecology is the study of population in relation to environment, including environmental influence on density and distribution, age structure and population size.
- 3. important terms ï Population is the a group of individuals of the same species, living in the same area, at he same time. ï Density is the total number of individual per unit area. ï Dispersion is the pattern amongst individuals within boundaries of the population
- 4. POPULATION SIZE IS PRIMARILY INFLUENCED BY:
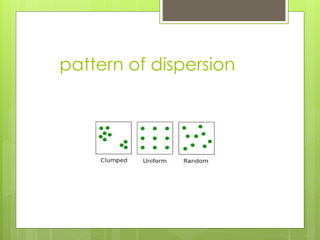
- 6. 2. PATTERNS OF DISPERSION Environmental and social factors influence spacing of individuals in a population: 1. In a clumped dispersion, individuals aggregate in patches. A clumped dispersion may be influenced by resource availability and behaviour. 2. A uniform dispersion is one in which individuals are evenly distributed. It may be influenced by social interactions such as territoriality 3. In a random dispersion, the position of each individual is independent of other individuals. It occurs in the absence of strong attractions or repulsions.
- 7. Social organization ï ï ï ï An organism that is highly interactive with other members of its species is said to be a social animal. All mammals (and birds) are social to the extent that mothers and offspring bond. A few species, notably insects (ants, bees wasps and termites) show an extreme form of sociality, involving highly organized societies, with individual organisms specialized for distinct roles. This form of social behaviour is referred to as eusociality.