Powerpoint
- 1. Generators, Motors and How We Get Electricity
- 2. Topics ï§ What is electricity? ï§ Energy Conversion ï§ The Faraday Effect ï§ Motor vs. Generator ï§ AC/DC ï§ Energy Trends - the case for Green
- 3. What is Electricity? Electricity is energy transported by the motion of electrons **We do not make electricity, we CONVERT other energy sources into electrical energy** Conversion is the name of the game
- 4. Energy Conversion Options for Electricity Non-Thermal Paths âĒ Source to Electrical Source Converter Sun Photovoltaic (photon to electron) Chemical Fuel Cell âĒ Source to Potential/Kinetic to Mechanical to Electrical Source Converter Kinetic to Mechanical Mech to Electrical Dam Penstocks Turbine (water) Generator Tides Machine Turbine (air or water) Generator Wind N/A Turbine (air) Generator
- 5. Energy Conversion Options for Electricity Thermal Paths âĒ Heat to Mechanical to Electrical Source Heat to Mechanical Mech to Electrical Geothermal Turbine (vapor) Generator OTEC Turbine (vapor) Generator âĒ Stored Energy to Heat to Mechanical to Electrical Source Reactor Heat to Mechanical Mech to Electrical Fuel Combustor Turbine (gas or vapor) Generator U, Pu Reactor Turbine (gas or vapor) Generator Sun Collector* Turbine (gas or vapor) Generator H, H2, H3Reactor Turbine (gas or vapor) Generator * More a modifier or concentrator than a reactor
- 6. Faraday Effect âĒ Faraday Effect âĒ Basic Concepts âĒ Voltage â V â Potential to Move Charge (volts) âĒ Current â I â Charge Movement (amperes or amps) âĒ Resistance â R â V = IxR (R in =ohms) âĒ Power â P = IxV = I2xR (watts)
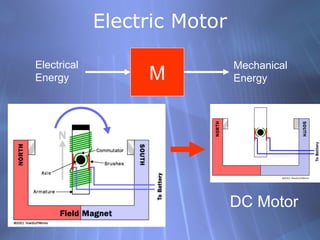
- 7. Electric Motor Electrical Energy M Mechanical Energy DC Motor
- 8. Model Electric Motor Beakman Motor What do you need? 1. Electric Energy 2. Coil 3. Magnetic Field
- 9. Electric Generator Mechanical Energy G Electrical Energy Stationary magnets - rotating magnets - electromagnets
- 10. AC/DC (not the band) ï§ Alternating Current ï§ Large-scale generators produce AC ï§ Follows sine wave with n cycles per second ï§ 1, 2, 3-phase? ï§ US:120 V,60 Hz ï§ Europe: 240 V,50Hz ï§ Transforming ability ï§ Direct Current ï§ Batteries, Photovoltaics, fuel cells, small DC generators ï§ Charge in ONE direction ï§ Negative, Positive terminals ï§ Easy conversion AC to DC, not DC to AC
- 11. Generator Phases 1 Phase â 2 Phase â 3 PhaseâĶSmooth Power Force Driving Motor (Red) 0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03 0.035 250 200 150 100 50 0 50 100 150 220 V(t) V 1(t) V 2(t) V 3(t) - 110 0 t 0.033 0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03 0.035 150 100 50 0 50 100 150 110 V(t) V 1(t) V 2(t) V 3(t) - 110 0 t 0.033 0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03 0.035 200 150 100 50 0 50 100 150 155.563 V(t) V 1(t) V 2(t) V 3(t) - 110 0 t 0.033 Single Phase Two Phase Three Phase Polyphase Systems ï 3 phases for smoother torque delivery
- 12. Where do we get our Electricity? âĒ Fossil â Coal, Natural Gas, Oil â 550 Gigawatts (GW) âĒ Nuclear â 200 GW âĒ Hydro â 75 GW âĒ Geothermal â 2.3 GW âĒ Other Renewable â Wind, Solar, OTEC â 13.6 GW
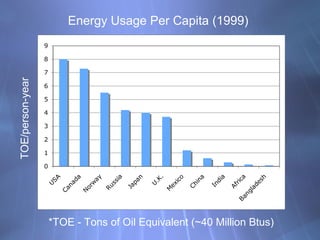
- 13. 9 8 7 TOE/person-year *TOE - Tons of Oil Equivalent (~40 Million Btus) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Energy Usage Per Capita (1999) USA Canada Norway Russia Japan U.K. Mexico China India Africa Bangladesh
- 14. Oil Resources Have OilâĶ Use OilâĶ Saudi Arabia 26% Iraq 11% Kuwait 10% Iran 9% UAE 8% Venezuela 6% Russia 5% Libya 3% Mexico 3% China 3% Nigeria 2% U.S. 2% U.S. 26% Japan 7% China 6% Germany 4% Canada 4% Russia 3% Brazil 3% S. Korea 3% France 3% India 3% Mexico 3% Italy 2% The U.S. uses more than the next 5 highest consuming nations combined.
- 15. U.S. Renewable Energy Resource Assessment Solar Wind Geothermal o Temperature <90C Temperature >o 90C Geopressured resources 10 10 12 12 14 14 16 16 18 20 18 20 22 26 24 22 24 26 14 16 14 16 14 12 10 10 12 <10 10-12 12-14 14-16 16-18 18-20 20-22 22-24 24-26 26-28 >28 6.0-6.5 m/s 13.4-14.6 mph 6.5-70 m/s 14.6-15.7 mph >7.0 m/s 15.7+ mph Megajoules/m 2 Biomass Agricultural resources & residues Wood resources & residues Agricultural & wood residues Low inventory
- 16. Barriers to Change US energy infrastructure is large and deeply entrenched âĒ 400,000+ miles of gas and oil pipelines âĒ 160,000+ of high voltage transmission lines âĒ 176,000 gasoline stations âĒ 1000âs of oil and gas wells drilled annually in the US and Canada
- 17. Barriers to Change ïą oil and gas are readily available as a world commodity at low cost -- equivalent to $ 4 to 5 / million Btu ïą US coal is even more abundant and cheaper â approximately $1/million Btu ïą US electricity prices remain low relative to other commodities The average American family spends only 3 to 4% of their income on energy!!