PPAP Awareness training.pptx
- 1. 2019 1 APQP introduction APQP timing chart and phases APQP application APQP sum up & key take aways PPAP introduction When is PPAP required? PPAP submission level PPAP status application of PPAP PPAP sum up & key take aways Training Outline
- 2. What is APQP? 2019 2 Advanced Product Quality Planning Cycle ’é¦ Advanced Product Quality Planning method to assure that a product satisfies the customer (both internal and external) ’é¦ The goal of APQP is to: ’é¦ Plan before acting ’é¦ Anticipate and prevent issues ’é¦ Validate before moving forward ’é¦ Facilitate communication ’é¦ Each Advanced Product Quality Plan is unique and is a living document ’é¦ Particular emphasis should be placed on identifying critical path activities and ensuring those are fully resourced
- 3. APQP at 2019 3 ŌĆó PDP: Product Development Process ŌĆó Same approach: Plan, Do, Check, Act ŌĆó Phases: Portfolio, Project proposal, FeasibilityŌĆ” till Project Closure ŌĆó Milestones: scope approval, tech solution approvalŌĆ” ŌĆó Roles and Responsibilities: deliverables per project function
- 4. APQP Background 2019 ŌĆó Automotive and Non Automotive industries challenges: ŌĆó Innovation, product complexity ŌĆó Reduce NPD times (Time to Market!) ŌĆó Complicated Supply chain (Global presence) ŌĆó Increasing customer and quality requirements (Zero Defect!) ŌĆó Solution: ŌĆó Ford, GM, Chrysler APQP Task Force jointly developed in the late 80ŌĆÖs to standardize their respective supplier quality systems. ŌĆó Continuous Improvement: ŌĆó Many industries outside the Automotive industry have embraced the AIAG APQP process to achieve similar benefits
- 5. APQP ŌĆō timing chart and phases - AIAG 2019 5 ŌĆó The Advanced Product Quality Planning process consists of four phases and five major activities and has some 20+ supporting tools (e.g. DFMEA, PFMEA, CTQ, Special Characteristics, Control Plan, SPC) along with ongoing feedback assessment and corrective action.
- 6. ’é¦ Voice of the Customer ’é¦ Market Research (ie IHS Markit) ’é¦ Historical Warranty and Quality Information ’é¦ Team Experience ’é¦ Business Plan/Marketing Strategy ’é¦ Product/Process Benchmark Data ’é¦ Product/Process Assumptions ’é¦ Product Reliability Studies ’é¦ Customer Inputs INPUTS: ’é¦ Design Goals ’é¦ Reliability & Quality goals ’é¦ CONC targets ’é¦ Preliminary Bill of Materials ’é¦ Preliminary Process Flow Chart ’é¦ Preliminary list of Special Product and Process Characteristics ’é¦ Product Assurance Plan ’é¦ Management Support OUTPUTS: Assure that customer needs and expectations are clearly understood and assessed * The inputs and outputs applicable to the process may vary according to the product process and customer needs and expectations. Phase 1: Plan and Define Program 2019 6
- 7. ’é¦ Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA) ’é¦ Design For Manufacturability and Assembly ’é¦ Design Verification ’é¦ Design Reviews ’é¦ Prototype Build ŌĆō Control plan ’é¦ Engineering Drawings (Including Math Data) ’é¦ Engineering Specifications ’é¦ Material Specifications ’é¦ Drawing and Specification Changes ’é¦ Design Goals ’é¦ Reliability & Quality goals ’é¦ Preliminary Bill of Materials ’é¦ Preliminary Process Flow Chart ’é¦ Preliminary list of Special Product and Process Characteristics ’é¦ Product Assurance Plan Cont. next slide Phase 2: Product Design and Development 2019 7 INPUTS: OUTPUTS: Develop design into a near final form. Prototype and feasibility studies ŌĆō volumes, schedule, manufacturing.
- 8. ’é¦ New Equipment, Tooling and Facilities Requirements ’é¦ Special Product and Process Characteristics ’é¦ Gages/Testing Equipment Requirements ’é¦ Team Feasibility Commitment ’é¦ Management Support ’é¦ Design Goals ’é¦ Reliability & Quality goals ’é¦ Preliminary Bill of Materials ’é¦ Preliminary Process Flow Chart ’é¦ Preliminary list of Special Product and Process Characteristics ’é¦ Product Assurance Plan 2019 8 Phase 2: Product Design and Development INPUTS: OUTPUTS: Develop design into a near final form. Prototype and feasibility studies ŌĆō volumes, schedule, manufacturing.
- 9. ŌĆó Packaging Standards ŌĆó Product/Process Quality System Review ŌĆó Process Flow Chart ŌĆó Floor Plan Layout ŌĆó Characteristics Matrix ŌĆó Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) ŌĆó Pre-Launch Control Plan ŌĆó Process Instructions ŌĆó Measurement Systems Analysis Plan ŌĆó Preliminary Process Capability Study Plan ŌĆó Packaging Specifications ŌĆó Management Support ŌĆó Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA) ŌĆó Design For Manufacturability and Assembly ŌĆó Design Verification ŌĆó Design Reviews ŌĆó Prototype Build ŌĆō Control Plan ŌĆó Engineering Drawings (Including Math Data) ŌĆó Engineering Specifications ŌĆó Material Specifications ŌĆó Drawing and Specification Changes ŌĆó New Equipment, Tooling and Facilities Requirements ŌĆó Special Product and Process Characteristics ŌĆó Gages/Testing Equipment Requirements ŌĆó Team Feasibility Commitment ŌĆó Management Support 2019 9 Phase 3: Process Design and Development INPUTS: OUTPUTS: Develop a manufacturing system and its related control plans to achieve quality products.
- 10. ’é¦ Measurement Systems Evaluation ’é¦ Significant Production Run ’é¦ Preliminary Process Capability Study ’é¦ Production Part Approval ’é¦ Production Validation Testing ’é¦ Packaging Evaluation ’é¦ Production Control Plan ’é¦ Quality Planning Sign-Off - formal ’é¦ Management Support ’é¦ Packaging Standards ’é¦ Product/Process Quality System Review ’é¦ Process Flow Chart ’é¦ Floor Plan Layout ’é¦ Characteristics Matrix ’é¦ Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) ’é¦ Pre-Launch Control Plan ’é¦ Process Instructions ’é¦ Measurement Systems Analysis Plan ’é¦ Preliminary Process Capability Study Plan ’é¦ Packaging Specifications ’é¦ Management Support 2019 10 Phase 4. Product and Process Validation INPUTS: OUTPUTS: Validate manufacturing process through production trial run. Validate that the control plan and process flow chart are effective and that the product meets customer expectation.
- 11. ’é¦ Production Trial Run ’é¦ Measurement Systems Evaluation ’é¦ Preliminary Process Capability Study ’é¦ Production Part Approval ’é¦ Production Validation Testing ’é¦ Packaging Evaluation ’é¦ Production Control Plan ’é¦ Quality Planning Sign-Off and Management Support ’é¦ Reduced Variation ’é¦ Improved Customer Satisfaction ’é¦ Improved Delivery and Service ’é¦ Effective use of best practice, lessons learned ’é¦ Maximum ROI ’é¦ Minimum Waste 2019 11 Feedback, Assessment, Corrective actions INPUTS: OUTPUTS: Evaluate outputs, effectiveness of the product quality planning efforts.
- 12. Application to Different Mfg. Environments 2019 12 ŌĆó High Volume ŌĆó APQP plans and activities are organized by part number and are very specific to the part ŌĆó Low Volume ŌĆó APQP plans may be specific to part families with activities focused on the parent part ŌĆó More limited validation would be done on child parts ŌĆó Family part differences should be understood and higher risk differences incorporated into APQP plans
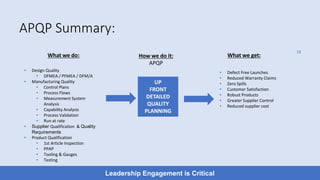
- 13. ŌĆó Design Quality ŌĆó DFMEA / PFMEA / DFM/A ŌĆó Manufacturing Quality ŌĆó Control Plans ŌĆó Process Flows ŌĆó Measurement System Analysis ŌĆó Capability Analysis ŌĆó Process Validation ŌĆó Run at rate ŌĆó Supplier Qualification & Quality Requirements ŌĆó Product Qualification ŌĆó 1st Article Inspection ŌĆó PPAP ŌĆó Tooling & Gauges ŌĆó Testing What we do: ŌĆó Defect Free Launches ŌĆó Reduced Warranty Claims ŌĆó Zero Spills ŌĆó Customer Satisfaction ŌĆó Robust Products ŌĆó Greater Supplier Control ŌĆó Reduced supplier cost How we do it: APQP What we get: Leadership Engagement is Critical UP FRONT DETAILED QUALITY PLANNING 13 APQP Summary:
- 14. CONC APQP Benefits: 2019 14 ŌĆó Manufacturing process functions that are clearly planned, validated, documented and communicated that result in: ŌĆó Robust and reliable designs ŌĆó Reduced process variation ŌĆó Enhanced confidence in supplierŌĆÖs capabilities ŌĆó Better controlled process changes ŌĆó Defect free launches ŌĆó Improved Customer satisfaction ŌĆó Improved Delivery and Service ŌĆó Maximum ROI ŌĆó Minimum Waste ŌĆó Minimum Cost of Non-conformance Development Production Prevention through APQP Current state Time $$ Total Cost of Quality Redesign Re-qualifications Escape Investigations
- 15. Key Take Aways: 2019 ŌĆó APQP is cross-functional planning and execution to produce product that fully meets the customerŌĆÖs expectations the first time ŌĆó AIAG APQP phases are Planning, Product Design, Process Design, Validation, Production ŌĆó Phase approach ensures activities are completed in the appropriate order ŌĆó Can be applied to different manufacturing environments ŌĆō High Volume, Low Volume ŌĆó ItŌĆÖs cross-functional ŌĆō Marketing/Design/Manufacturing/SCM/Quality
- 16. Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) 2019 16
- 17. What is PPAP? 2019 17 ŌĆó Production Part Approval Process ŌĆó Standard used to formally reduce risks prior to product or service release, in a team oriented manner using well established tools and techniques ŌĆó Initially developed by AIAG (Auto Industry Action Group) in 1993 with input from the Big 3 - Ford, Chrysler, and GM ŌĆó AIAGŌĆÖs 4th edition effective June 1, 2006 is the most recent version ŌĆó PPAP has now spread to many different industries beyond automotive
- 18. PPAP at 2019 18 ŌĆó Aligned to AIAG PPAP Manual rev 4 ŌĆó Requirements set up during Technical Reviews (DPAR Process*) ŌĆó Continuous validation approach ŌĆó Embedded to our APQP (output of phase 4 ŌĆō Production Part Approval) *DPAR: Design, Process & Assembly Review ŌĆō you can refer to DPAR Training Material for further information
- 19. Production Run 2019 19 ŌĆó PPAP data must be submitted from a production run using: ŌĆó Production equipment and tooling ŌĆó Production employees ŌĆó Production rate ŌĆó Production process All data shall reflect the actual production process that will be used at start-up!
- 20. Purpose of PPAP 2019 20 ŌĆó Provide evidence that all customer engineering design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the organization ŌĆó To demonstrate that the manufacturing process has the potential to produce product that consistently meets all requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate
- 21. When is PPAP Required? 2019 21 ŌĆó New part ŌĆó Engineering change(s) ŌĆó Durable Tooling: transfer, replacement, refurbishment, or additional ŌĆó Tooling inactive > one year ŌĆó Correction of discrepancy ŌĆó Change to optional construction or material ŌĆó Sub-supplier or material source change ŌĆó Change in part processing ŌĆó Parts produced at a new or additional location PPAP is required with any significant change to product or process!
- 22. Benefits of PPAP Submissions 2019 22 ŌĆó Helps to maintain design integrity ŌĆó Identifies issues early for resolution ŌĆó Reduces warranty charges and prevents cost of poor quality ŌĆó Assists with managing supplier changes ŌĆó Prevents use of unapproved and nonconforming parts ŌĆó Identifies suppliers that need more development ŌĆó Improves the overall quality of the product & customer satisfaction
- 23. PPAP Submission Levels 2019 23 Level 1 Production Warrant and Appearance Approval Report (if applicable) submitted Level 2 Production Warrant, product samples, and dimensional results submitted Level 3 Production Warrant, product samples, and complete supporting data submitted Level 4 Production Warrant and other requirements as defined by Level 5 Production Warrant, product samples and complete supporting data (a review will be conducted at the supplier's manufacturing location)
- 24. PPAP Submission Requirements 2019 24 Requirement Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 1.Design Record R S S * R 2.Engineering Change Documents, if any R S S * R 3.Customer Engineering approval, if required R R S * R 4.Design FMEA R R S * R 5.Process Flow Diagrams R R S * R 6.Process FMEA R R S * R 7.Control Plan R R S * R 8.Measurement System Analysis studies R R S * R 9.Dimensional Results R S S * R 10.Material, Performance Test Results R S S * R 11.Initial Process Studies R R S * R 12.Qualified Laboratory Documentation R S S * R 13.Appearance Approval Report (AAR), if applicable S S S * R 14.Sample Product R S S * R 15.Master Sample R R R * R 16.Checking Aids R R R * R 17.Records of Compliance With Customer Specific Requirements R R S * R 18.Part Submission Warrant S S S S R 19.Bulk Material Checklist S S S S R S = The organization shall submit to the customer and retain a copy of records or documentation items at appropriate locations R = The organization shall retain at appropriate locations and make available to the customer upon request * = The organization shall retain at the appropriate location and submit to the customer upon request Note: For each level, full PPAP is required. The PPAP level simply indicates which elements you submit, and which you retain at your site.
- 25. PPAP Element 17: Requirements 2019 25 ŌĆó Depending on the specific business, may require: ŌĆó Measurement Agreement ŌĆó Gage Drawing ŌĆó Safe Launch Control Plan ŌĆó Annual layout ŌĆó Special Processes qualification ŌĆó Packaging Specification Data Sheet ŌĆó Submit Bar Code Label Packaging Approval ŌĆó Capacity R@R Worksheet ŌĆó MSDS ŌĆó ŌĆ”
- 26. PPAP Status 2019 26 ŌĆó Approved ŌĆó The part meets all requirements ŌĆó Supplier is authorized to ship production quantities of the part ŌĆó Interim Approval ŌĆó Permits shipment of part on a limited time or piece quantity basis ŌĆó Rejected ŌĆó The part does not meet requirements, based on the production lot from which it was taken and/or accompanying documentation Production quantities shall not be shipped before Approval + Order!
- 27. PPAP Sum up & Take Aways 2019 27 ŌĆó PPAP is a result of a good APQP! ŌĆó DPAR* is an important activity to determine PPAP expectations! ŌĆó Commitment on part and process feasibility ŌĆó We plan a good Control Plan: Measurement Agreement on key characteristics ŌĆó determines PPAP level based on component risk ŌĆó Submission requirements are increased for higher risk components ŌĆó Requirements are defined and agreed during DPAR phase ŌĆó provides a standard PPAP workbook with all necessary tools ŌĆó Supplier can use their own templates and tools if they meet the AIAG requirements ŌĆó LetŌĆÖs be Smart! ŌĆó Going through PPAP process as a routine ŌĆó Identifying opportunities: Master PFMEA, Master CPŌĆ” *: refer to DPAR Training ŌĆō DPAR = Design Process & Assembly Review
- 28. Thanks 2019 28