Programming in C Session 1
- 1. C
- 2. 1. Introduction to C 2. Structure of a C program 3. Control Structure 4. Arrays
- 3.  C is a programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie at AT & T’s Bell Laboratories of USA in 1972.  Reserves a set of 32 keywords & 40 operators.  Case sensitive Language (all keywords in lower case).  Structured Programming language(divided into small modules).  High level language (Machine independent, sophisticated programming language that uses familiar English (or any human language).  Also known as Middle level language because it is binding the gap b/w a Machine language & high level language.
- 4. Character Set 32-Keywords  Alphabets Character (in Small & Capital Letters )  Digits(0-9)  Special Symbols (e.g. +, -, *, /, , >, <, @, ; , ?, _, &, %, #, : , =, {, }, [ , ], etc ) return do enum static goto continue for short signed auto register Int break switch struct unsigned if while extern volatile double else case sizeof typedef long float union default void char const
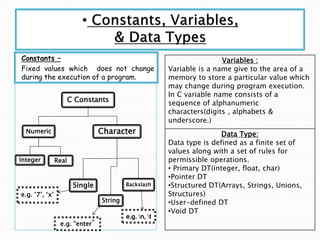
- 5. Constants – Fixed values which does not change during the execution of a program. C Constants Numeric Integer Real Character Single String Backslash Variables : Variable is a name give to the area of a memory to store a particular value which may change during program execution. In C variable name consists of a sequence of alphanumeric characters(digits , alphabets & underscore.) Data Type: Data type is defined as a finite set of values along with a set of rules for permissible operations. • Primary DT(integer, float, char) •Pointer DT •Structured DT(Arrays, Strings, Unions, Structures) •User-defined DT •Void DT e.g. ‘7’, ‘x’ e.g. ”enter” e.g. n, t
- 6. Operators Expressions An Operator is a function which is applied to produce a result. •Arithmetic Operators - (e.g. +, -, *, /, % ) • Relational Operators –(e.g. <, >, <=,>=,==, !=) •Logical Operators – (e.g. ! , &&, II) •Assignment Operators- (e.g. a=3; x=y=z=13; x*=75) •Special Operators – (e.g. ++, --, &, etc) Expression is a combination of one or more operands with operators to compute a value. Example- x+y=c operator Operand or Variable
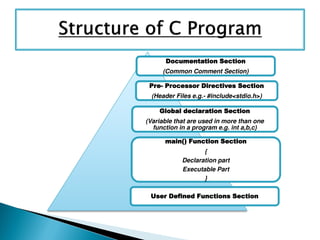
- 7. Documentation Section (Common Comment Section) Pre- Processor Directives Section (Header Files e.g.- #include<stdio.h>) Global declaration Section (Variable that are used in more than one function in a program e.g. int a,b,c) main() Function Section { Declaration part Executable Part } User Defined Functions Section
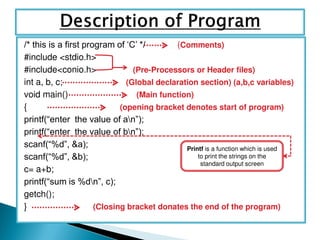
- 8. /* this is a first program of ‘C’ */ (Comments) #include <stdio.h> #include<conio.h> (Pre-Processors or Header files) int a, b, c; (Global declaration section) (a,b,c variables) void main() (Main function) { (opening bracket denotes start of program) printf(“enter the value of an”); printf(“enter the value of bn”); scanf(“%d”, &a); scanf(“%d”, &b); c= a+b; printf(“sum is %dn”, c); getch(); } (Closing bracket donates the end of the program) Printf is a function which is used to print the strings on the standard output screen
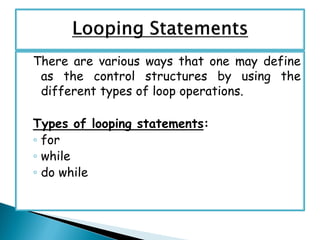
- 10. Control structure is a primary concept in most high- level programming languages. In its simplest sense, it is a block of code. More specifically, a control structure is a container for a series of function calls, instructions and statements. In changing the order of statement’s execution there may be three situations:  Branching  Looping  Jumping
- 11. Branching statements are also know as decision making statement. In these statements one group of statement depending on the result of decisions. The result may be in the form of two type Expressions in True or False. Types of Branching statements: ‚ó¶ if statement ‚ó¶ if else statement ‚ó¶ else if statement ‚ó¶ nested if statement ‚ó¶ Switch statement
- 12. 1. if statement : This is a simple decision making statement which is used to express the condition in only 1 condition & 1 statement or in simple words if the result is True then execute else no result is showed. Syntax: if(expression) <Statement- Set>
- 13. 2. if else statement : It is a two way branching statement. This statement is depends upon the value of expression is True or False. If the 1st condition is true then 1st statement execute else 2nd will execute. Syntax: if(expression) { statement 1 } else { statement 2 }
- 14. 3. else if statement : It is a multiple if-else statement. It works with multiple conditions & statements. The output will be depends upon the true condition. Syntax: if(expression 1) { statement 1 } else if(expression 2) { statement 2 } else if(expression n) { statement n } else { statement p }
- 15. 4. nested if statement : When if statement appears with in another if statement it is called nested if statement. Similarly if else can also be nested. Syntax: if(expression 1) if(expression 2) { statement 1 } else {
- 16. statement 2 } else if(expression 3) { statement 3 } else { statement 4 }
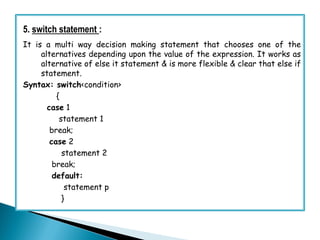
- 17. 5. switch statement : It is a multi way decision making statement that chooses one of the alternatives depending upon the value of the expression. It works as alternative of else it statement & is more flexible & clear that else if statement. Syntax: switch<condition> { case 1 statement 1 break; case 2 statement 2 break; default: statement p }
- 18. There are various ways that one may define as the control structures by using the different types of loop operations. Types of looping statements: ‚ó¶ for ‚ó¶ while ‚ó¶ do while
- 19. 1. for loop : It is commonly used for repetitive processing. For loop is suited for the problems where we already know how many times the body of loop will be executed. Syntax: for(expression 1; expression 2; expression 3) <Statement- Set> Starting Condition that to be satisfied Alternate the value(++, __)
- 20. 2. while loop : While loop is suited for the problems where we are not certain that how many times the body of loop will be execute. In this statement condition is evaluated first & if the condition is true then the body of the loop will execute. Syntax: while(expression) <Statement- Set>
- 21. 2. do while loop : Do while loop is suited for the problems where we are not certain that how many times the body of loop will be executed. More over condition is tested at the end of the loop. Syntax: do { <Statement- Set> } while(expression)
- 22. These are those statements that can go to a particular positions to show the particular result. Types of jumping statements: ‚ó¶ break ‚ó¶ continue ‚ó¶ goto
- 23. 1. break : The break statement is used to terminate loop or to exit from switch case structure. The break statement can be used with a for loop, while loop, do while loop & switch statement to transfer the control out of the block. Syntax: break;
- 24. 2. continue : A continue statement can be used with while, do while, for, & switch statement. Continue statement transfer the control to the beginning of the loop after by passing the statement which one not yet executed. Syntax: continue;
- 25. 3. goto : Statement is used to other of the normal sequence of program execution by transfer control to one point to the program with the goto statement. Syntax: goto Label;
- 26. Array is a collection of homogenous (same kind of )data elements which are stored in a sequential manner in memory location under a single name. This single name is known as array. In simple words 1 variable use one data type & store multiple data elements in it. These multiple or individual elements are known as subscripted variables. Variable size is always declare with square brackets. Array is always initialized from 0. Example – int roll[8]; Types of an Array :  Single dimensional  Two dimensional
- 27. Single Dimensional Array: Single Dimensional Array is also known as Linear or a list array. There is only one subscript is used in this array. It is written either in row or in column form. It can be used with for loop, while loop & do while loop. It may be expressed as: Storage class Data-type Array-name[size]; storage class defines the scope (visibility) and life time of variables and functions in a program. It may be static, auto, extern or register
- 28. Example : int roll[8]; In our example, int specifies the data type of array, roll specifies the name of the array and the value in bracket [8] is specifies that how many elements (values in any array is called elements) it can store. This number is called dimension of array. So, with respect to our example we have declared an array of integer type and named it “roll” which can store roll numbers of 8 students.
- 29. Two Dimensional Array: Two Dimensional Array is known as non-Linear array. Two subscripts are used in this array. These two subscripts are used as row & column form. That’s why it is also known as Row column array or Square array. It may be expressed as: Storage class Data-type Array-name[size1][size2];




![Character Set 32-Keywords
 Alphabets Character
(in Small & Capital
Letters )
 Digits(0-9)
 Special Symbols (e.g.
+, -, *, /, , >, <, @, ; ,
?, _, &, %, #, : , =, {, },
[ , ], etc )
return do enum static goto
continue for short signed auto
register Int break switch struct
unsigned if while extern volatile
double else case sizeof
typedef long float union
default void char const](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-cs-140812001721-phpapp01/85/Programming-in-C-Session-1-4-320.jpg)















![Array is a collection of homogenous (same kind of )data elements
which are stored in a sequential manner in memory location
under a single name. This single name is known as array. In
simple words 1 variable use one data type & store multiple data
elements in it. These multiple or individual elements are known
as subscripted variables. Variable size is always declare with
square brackets. Array is always initialized from 0.
Example – int roll[8];
Types of an Array :
ÔÅΩ Single dimensional
ÔÅΩ Two dimensional](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-cs-140812001721-phpapp01/85/Programming-in-C-Session-1-26-320.jpg)
![Single Dimensional Array:
Single Dimensional Array is also known as Linear or a list array.
There is only one subscript is used in this array. It is written
either in row or in column form. It can be used with for loop,
while loop & do while loop.
It may be expressed as:
Storage class Data-type Array-name[size];
storage class defines the
scope (visibility) and life time
of variables and functions in
a program. It may be static,
auto, extern or register](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-cs-140812001721-phpapp01/85/Programming-in-C-Session-1-27-320.jpg)
![Example :
int roll[8];
In our example, int specifies the data type of array, roll specifies
the name of the array and the value in bracket [8] is specifies that
how many elements (values in any array is called elements) it can
store. This number is called dimension of array.
So, with respect to our example we have declared an array of
integer type and named it “roll” which can store roll numbers of 8
students.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-cs-140812001721-phpapp01/85/Programming-in-C-Session-1-28-320.jpg)
![Two Dimensional Array:
Two Dimensional Array is known as non-Linear array. Two
subscripts are used in this array. These two subscripts are used
as row & column form. That’s why it is also known as Row column
array or Square array.
It may be expressed as:
Storage class Data-type Array-name[size1][size2];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-cs-140812001721-phpapp01/85/Programming-in-C-Session-1-29-320.jpg)
