Ppt exc
- 1. 5-1 CHAPTER 5 The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions, and Interest Rates ’ü« Financial markets ’ü« Types of financial institutions ’ü« Determinants of interest rates ’ü« Yield curves
- 2. 5-2 Define These Markets ’ü« Markets in general ’ü« Physical assets ’ü« Financial assets ’ü« Money vs. Capital ’ü« Primary vs. Secondary ’ü« Spot vs. Future
- 3. 5-3 Three Primary Ways Capital Is Transferred Between Savers and Borrowers ’ü« Direct transfer ’ü« Investment banking house ’ü« Financial intermediary
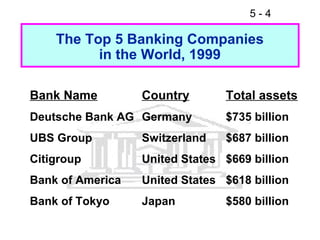
- 4. 5-4 The Top 5 Banking Companies in the World, 1999 Bank Name Country Total assets Deutsche Bank AG Germany $735 billion UBS Group Switzerland $687 billion Citigroup United States $669 billion Bank of America United States $618 billion Bank of Tokyo Japan $580 billion
- 5. 5-5 Physical Location Stock Exchanges vs. Electronic Dealer-Based Markets ’ü« Auction market vs. Dealer market (Exchanges vs. OTC) ’ü« NYSE vs. Nasdaq system ’ü« Differences are narrowing
- 6. 5-6 ’ü« What do we call the price, or cost, of debt capital? The interest rate ’ü« What do we call the price, or cost, of equity capital? Required Dividend Capital return = yield + gain
- 7. 5-7 What four factors affect the cost of money? ’ü« Production opportunities ’ü« Time preferences for consumption ’ü« Risk ’ü« Expected inflation
- 8. 5-8 ŌĆ£RealŌĆØ Versus ŌĆ£NominalŌĆØ Rates k* = Real risk-free rate. T-bond rate if no inflation; 1% to 4%. k = Any nominal rate. kRF = Rate on Treasury securities.
- 9. 5-9 k = k* + IP + DRP + LP + MRP. Here: k = required rate of return on a debt security. k* = real risk-free rate. IP = inflation premium. DRP = default risk premium. LP = liquidity premium. MRP = maturity risk premium.
- 10. 5 - 10 Premiums Added to k* for Different Types of Debt ’ü« S-T Treasury: only IP for S-T inflation ’ü« L-T Treasury: IP for L-T inflation, MRP ’ü« S-T corporate: S-T IP, DRP, LP ’ü« L-T corporate: IP, DRP, MRP, LP
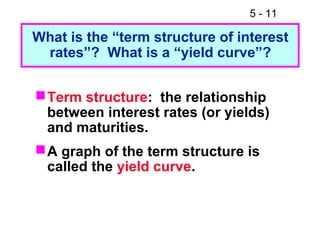
- 11. 5 - 11 What is the ŌĆ£term structure of interest ratesŌĆØ? What is a ŌĆ£yield curveŌĆØ? ’ü« Term structure: the relationship between interest rates (or yields) and maturities. ’ü« A graph of the term structure is called the yield curve.
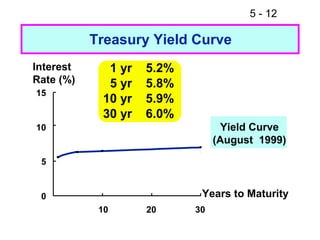
- 12. 5 - 12 Treasury Yield Curve Interest 1 yr 5.2% Rate (%) 5 yr 5.8% 15 10 yr 5.9% 30 yr 6.0% 10 Yield Curve (August 1999) 5 0 Years to Maturity 10 20 30
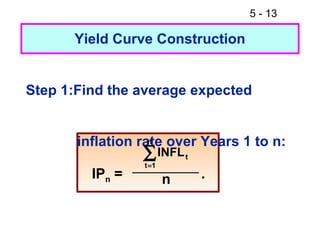
- 13. 5 - 13 Yield Curve Construction Step 1:Find the average expected inflation rate over Years 1 to n: n Ōłæ INFL t =1 t IPn = n .
- 14. 5 - 14 Suppose, that inflation is expected to be 5% next year, 6% the following year, and 8% thereafter. IP1 = 5%/1.0 = 5.00%. IP10 = [5 + 6 + 8(8)]/10 = 7.50%. IP20 = [5 + 6 + 8(18)]/20 = 7.75%. Must earn these IPs to break even vs. inflation; these IPs would permit you to earn k* (before taxes).
- 15. 5 - 15 Step 2: Find MRP Based on This Equation: MRPt = 0.1%(t ŌĆō 1). MRP1 = 0.1% x 0 = 0.0%. MRP10 = 0.1% x 9 = 0.9%. MRP20 = 0.1% x 19 = 1.9%.
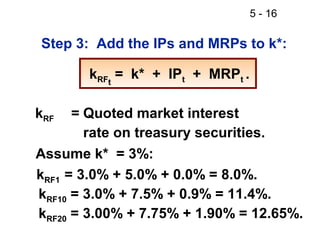
- 16. 5 - 16 Step 3: Add the IPs and MRPs to k*: kRFt = k* + IPt + MRPt . kRF = Quoted market interest rate on treasury securities. Assume k* = 3%: kRF1 = 3.0% + 5.0% + 0.0% = 8.0%. kRF10 = 3.0% + 7.5% + 0.9% = 11.4%. kRF20 = 3.00% + 7.75% + 1.90% = 12.65%.
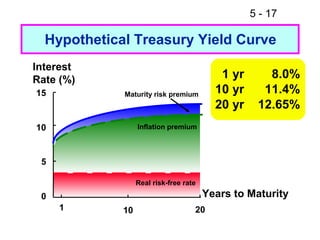
- 17. 5 - 17 Hypothetical Treasury Yield Curve Interest Rate (%) 1 yr 8.0% 15 Maturity risk premium 10 yr 11.4% 20 yr 12.65% 10 Inflation premium 5 Real risk-free rate 0 Years to Maturity 1 10 20
- 18. 5 - 18 What factors can explain the shape of this yield curve? ’ü« This constructed yield curve is upward sloping. ’ü« This is due to increasing expected inflation and an increasing maturity risk premium.
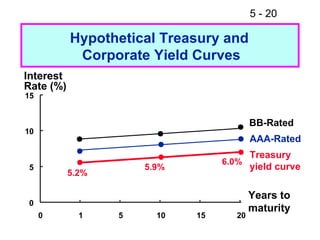
- 19. 5 - 19 What kind of relationship exists between the Treasury yield curve and the yield curves for corporate issues? ’ü« Corporate yield curves are higher than that of the Treasury bond. However, corporate yield curves are not neces- sarily parallel to the Treasury curve. ’ü« The spread between a corporate yield curve and the Treasury curve widens as the corporate bond rating decreases.
- 20. 5 - 20 Hypothetical Treasury and Corporate Yield Curves Interest Rate (%) 15 BB-Rated 10 AAA-Rated Treasury 6.0% 5 5.9% yield curve 5.2% Years to 0 maturity 0 1 5 10 15 20
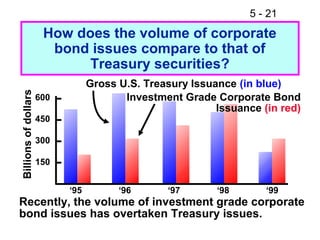
- 21. 5 - 21 How does the volume of corporate bond issues compare to that of Treasury securities? Gross U.S. Treasury Issuance (in blue) Billions of dollars 600 Investment Grade Corporate Bond Issuance (in red) 450 300 150 ŌĆś95 ŌĆś96 ŌĆś97 ŌĆś98 ŌĆś99 Recently, the volume of investment grade corporate bond issues has overtaken Treasury issues.
- 22. 5 - 22 The Pure Expectations Hypothesis (PEH) ’ü« Shape of the yield curve depends on the investorsŌĆÖ expectations about future interest rates. ’ü« If interest rates are expected to increase, L-T rates will be higher than S-T rates and vice versa. Thus, the yield curve can slope up or down.
- 23. 5 - 23 ’ü« PEH assumes that MRP = 0. ’ü« Long-term rates are an average of current and future short-term rates. ’ü« If PEH is correct, you can use the yield curve to ŌĆ£back outŌĆØ expected future interest rates.
- 24. 5 - 24 Observed Treasury Rates Maturity Yield 1 year 6.0% 2 years 6.2% 3 years 6.4% 4 years 6.5% 5 years 6.5% If PEH holds, what does the market expect will be the interest rate on one-year securities, one year from now? Three-year securities, two years from now?
- 25. 5 - 25 x% 6.0% 0 1 2 3 4 5 6.2% (6.0% + x%) 6.2% = 2 12.4% = 6.0 + x% 6.4% = x%. PEH tells us that one-year securities will yield 6.4%, one year from now (x%).
- 26. 5 - 26 6.2% x% 0 1 2 3 4 5 6.5% [ 2(6.2%) + 3(x%) ] 6.5% = 5 32.5% = 12.4% + 3(x%) 20.1% = 3(x%) 6.7% = x%. PEH tells us that three-year securities will yield 6.7%, two years from now (x%).
- 27. 5 - 27 Conclusions about PEH ’ü« Some argue that the PEH isnŌĆÖt correct, because securities of different maturities have different risk. ’ü« General view (supported by most evidence) is that lenders prefer S-T securities, and view L-T securities as riskier. ’ü« Thus, investors demand a MRP to get them to hold L-T securities (i.e., MRP > 0).
- 28. 5 - 28 What various types of risks arise when investing overseas? Country risk: Arises from investing or doing business in a particular country. It depends on the countryŌĆÖs economic, political, and social environment. Exchange rate risk: If investment is denominated in a currency other than the dollar, the investmentŌĆÖs value will depend on what happens to exchange rate.
- 29. 5 - 29 Two Factors Lead to Exchange Rate Fluctuations 1. Changes in relative inflation will lead to changes in exchange rates. 2. An increase in country risk will also cause that countryŌĆÖs currency to fall.








![5 - 14
Suppose, that inflation is expected to
be 5% next year, 6% the following year,
and 8% thereafter.
IP1 = 5%/1.0 = 5.00%.
IP10 = [5 + 6 + 8(8)]/10 = 7.50%.
IP20 = [5 + 6 + 8(18)]/20 = 7.75%.
Must earn these IPs to break even vs.
inflation; these IPs would permit you to
earn k* (before taxes).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptexc-130301225253-phpapp01/85/Ppt-exc-14-320.jpg)







![5 - 26
6.2% x%
0 1 2 3 4 5
6.5%
[ 2(6.2%) + 3(x%) ]
6.5% =
5
32.5% = 12.4% + 3(x%)
20.1% = 3(x%)
6.7% = x%.
PEH tells us that three-year securities
will yield 6.7%, two years from now (x%).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptexc-130301225253-phpapp01/85/Ppt-exc-26-320.jpg)


